Recognizing the Key Signs of Crohn's Disease
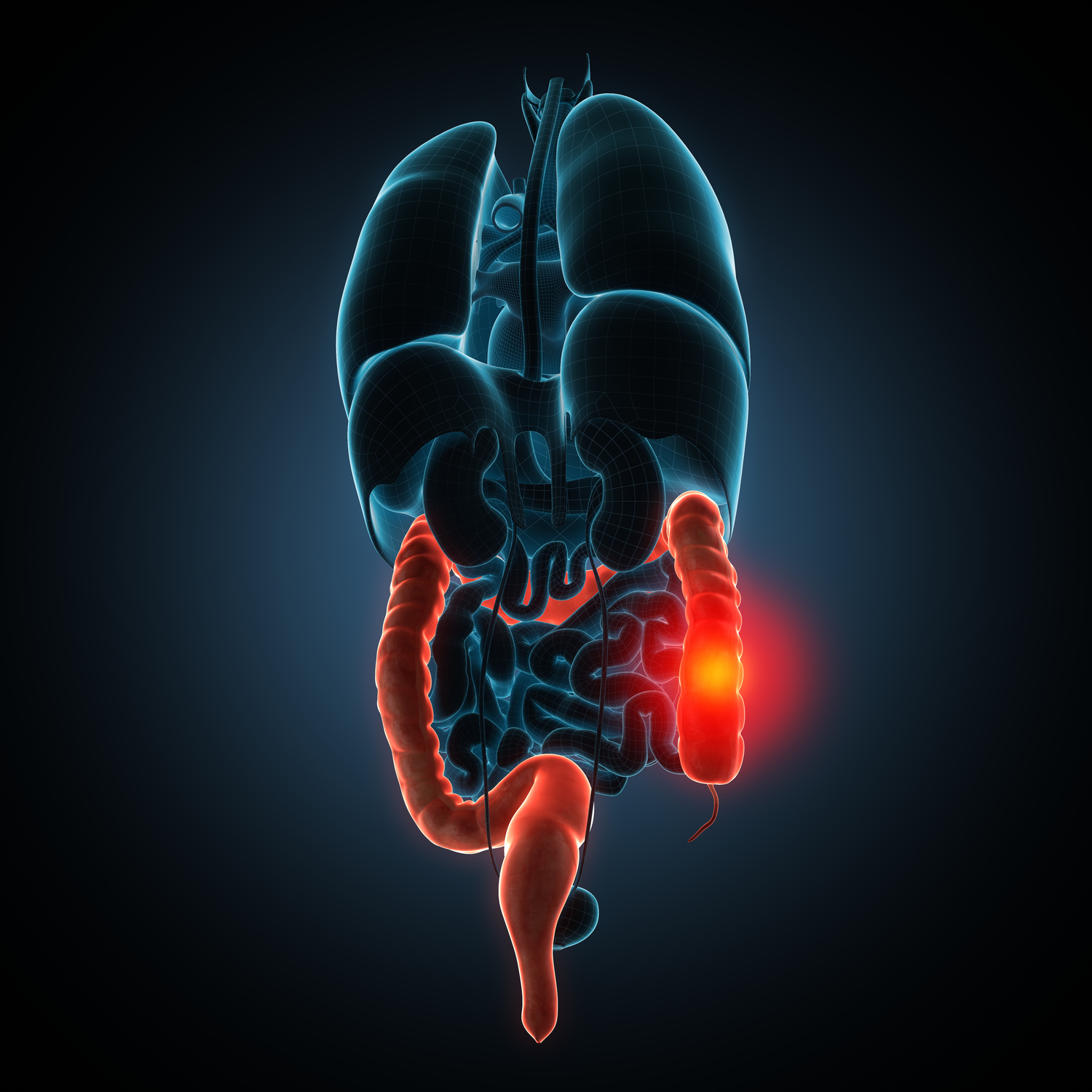
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the digestive tract, causing symptoms like diarrhea, weight loss, and abdominal pain. Diagnosis involves endoscopic procedures, imaging, and lab tests to confirm inflammation and assess complications. Early detection is crucial for effective management and preventing severe health issues.
Sponsored

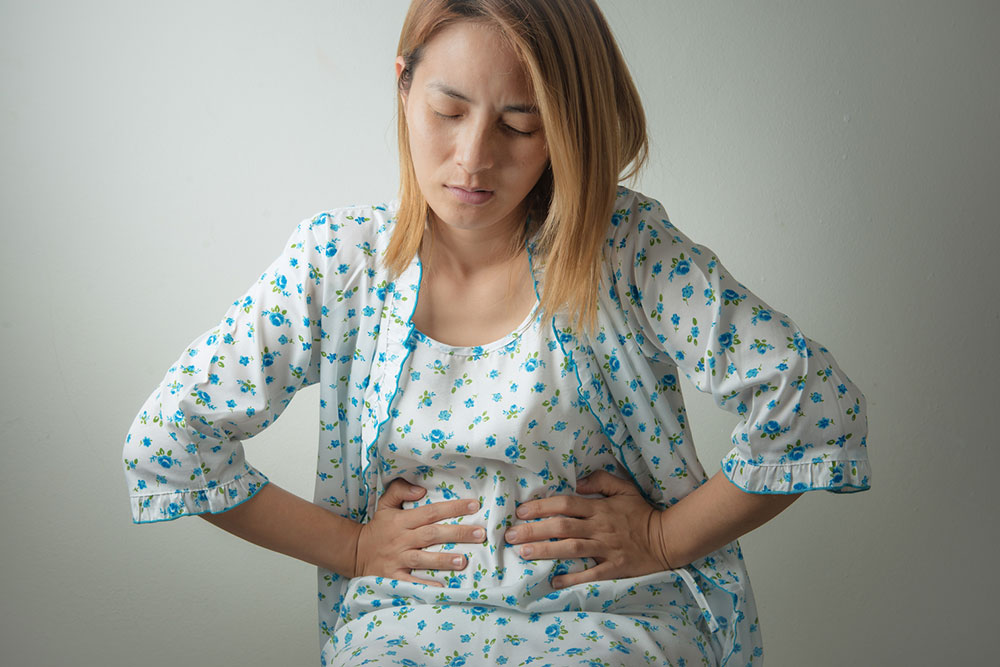
Crohn's disease is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the digestive system, impacting approximately 200,000 individuals annually. It can lead to severe complications if untreated, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and tiredness. Initially believed to be autoimmune, its cause is now linked to immune responses targeting infections caused by bacteria and viruses. Chronic inflammation may also extend to other body parts like eyes, skin, mouth, and joints.
The disease can even lead to kidney stones and affect growth and sexual development in children. While the exact cause remains unknown, immune system irregularities play a significant role.
Common symptoms include:
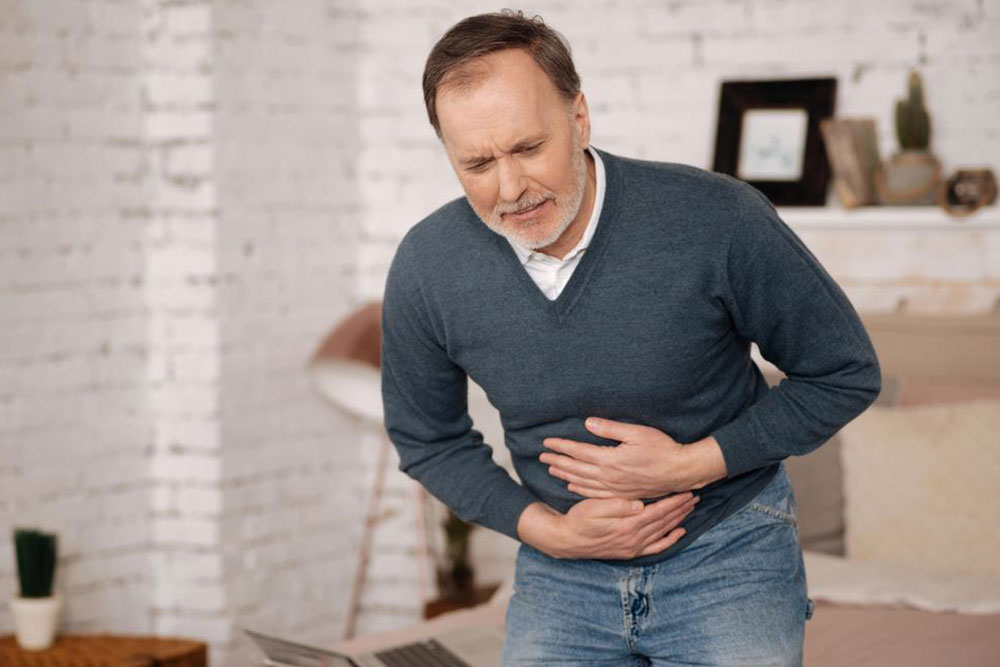
Persistent diarrhea with mucus, pus, or blood
Unintentional weight loss due to decreased appetite
Fever from complications
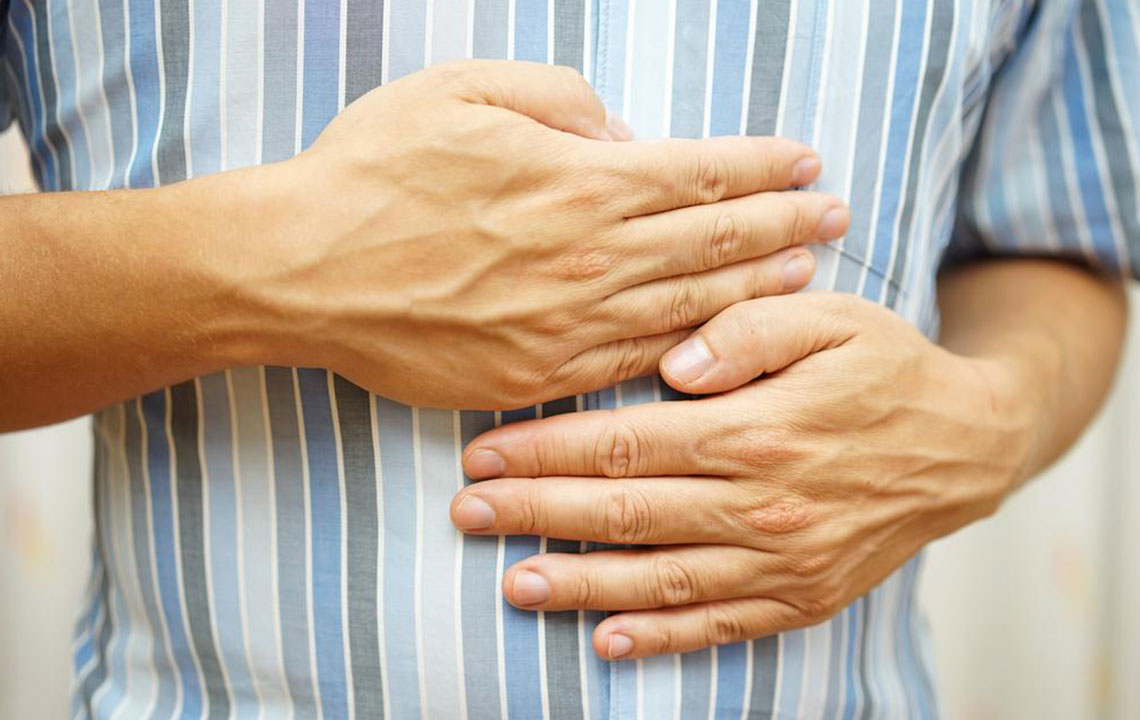
Stomach pain with tenderness
Rectal bleeding
Potential life-threatening issues like bowel perforation, distension, severe pain, and fever
Diagnosis involves:
Medical history review, colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy to examine and collect tissue samples
Additional tests such as upper endoscopy and capsule endoscopy for the small intestine, along with blood, stool, CT scans, or MRIs