Understanding COPD: Symptoms, Causes, and Disease Stages
This article provides an overview of COPD, explaining its symptoms, risk factors, and disease stages. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis, regular monitoring, and personalized treatment options, including advanced therapies like stem cell treatment, to improve quality of life and lung health.
Sponsored

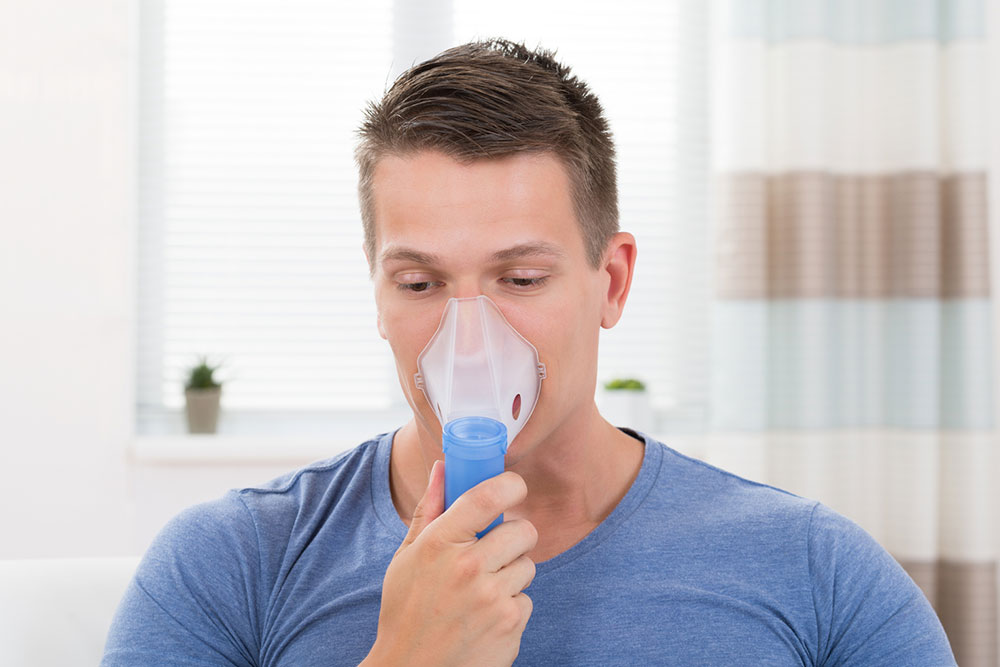
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) encompasses lung conditions such as chronic bronchitis, emphysema, stubborn asthma, and bronchiectasis. It is marked by increasing breathlessness that develops gradually over time. Early symptoms are often mild or unnoticed but become more apparent as the disease advances. Prompt medical attention and spirometry testing are essential upon noticing symptoms.
Common COPD Symptoms:
Elevated shortness of breath
Wheezing sounds during breathing
Coughing spells with or without mucus
Chest tightness
Risk Factors and Causes:
Prolonged exposure to pollutants, especially cigarette smoke
Environmental irritants such as chemicals, fumes, and dust
Genetic predisposition
Smoking, environmental toxins, and genetic factors all contribute to disease development.
Early diagnosis is vital to prevent lung deterioration or fatality. Healthcare providers utilize tools like the GOLD classification system and BODE index to evaluate disease severity and guide treatment plans. Regular check-ups and lung function tests, including spirometry and imaging, assist in identifying disease stages.
COPD Disease Stages:
Stage 1 - Mild: Often symptomless, some may experience a cough but continue daily activities.
Stage 2 - Moderate: Mucus production and cough increase; breathing difficulties lead to medical consultation. Bronchodilators and pulmonary rehab may be recommended.
Stage 3 - Severe: Lung function declines substantially, causing fatigue, exercise difficulty, and lifestyle limitations.
Stage 4 - Very Severe: Critical decline in respiratory capacity; oxygen therapy may be needed. Breathing becomes life-threatening, requiring urgent medical management.
Monitoring symptoms and working closely with your doctor is crucial throughout COPD progression. Diagnostic tests like CT scans and X-rays help assess lung health. Adapting treatment strategies and exploring options such as lifestyle modifications, stem cell therapy, and supplements can enhance quality of life and lung function. Early intervention and customized care are key to managing COPD effectively.