Effective Strategies for Managing Pneumonia
Discover comprehensive methods for diagnosing and treating pneumonia effectively. This guide covers symptoms, diagnostic procedures, medication options, and specialized care for children and the elderly to ensure timely recovery and prevent complications.
Sponsored

Sudden exposure to cold weather and rapid temperature drops can lead to various health issues, including respiratory problems. While some ailments are minor like coughs and colds, others may severely affect the lungs. If not diagnosed early, these can be life-threatening. Pneumonia, an infection causing inflammation of the lung air sacs, is a serious condition that requires prompt treatment to prevent complications.
Symptoms
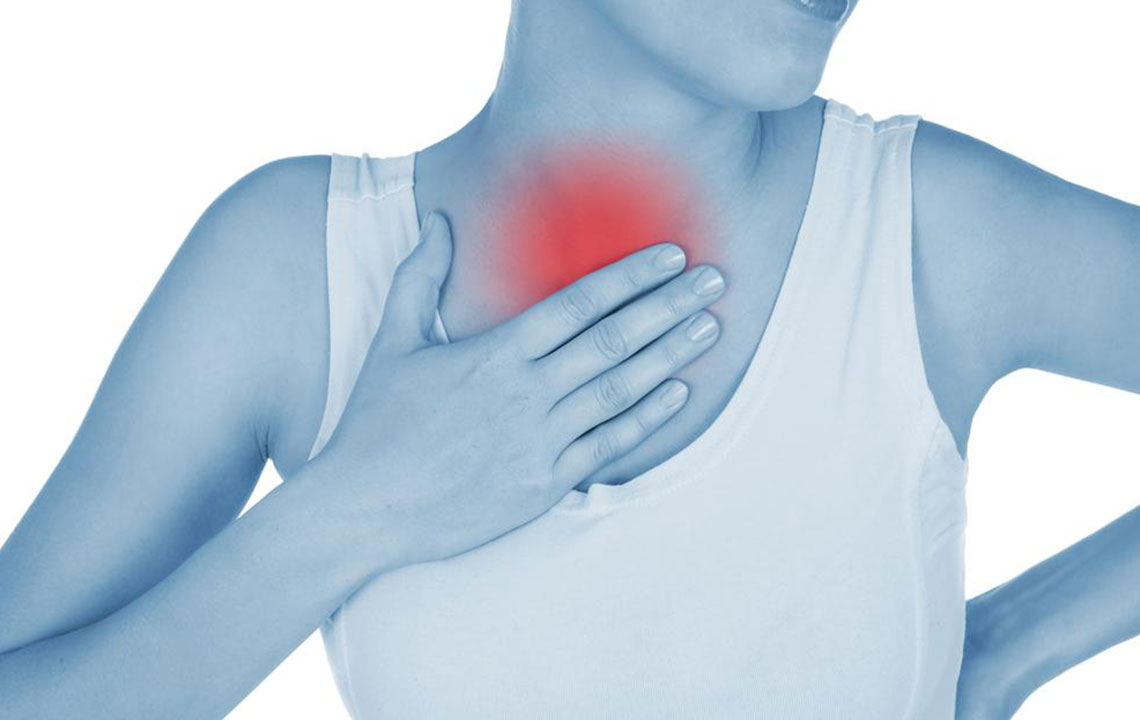
Patients typically experience persistent cough with excessive phlegm, high fever, and chills. Breathing may become difficult and painful, often accompanied by chest discomfort.
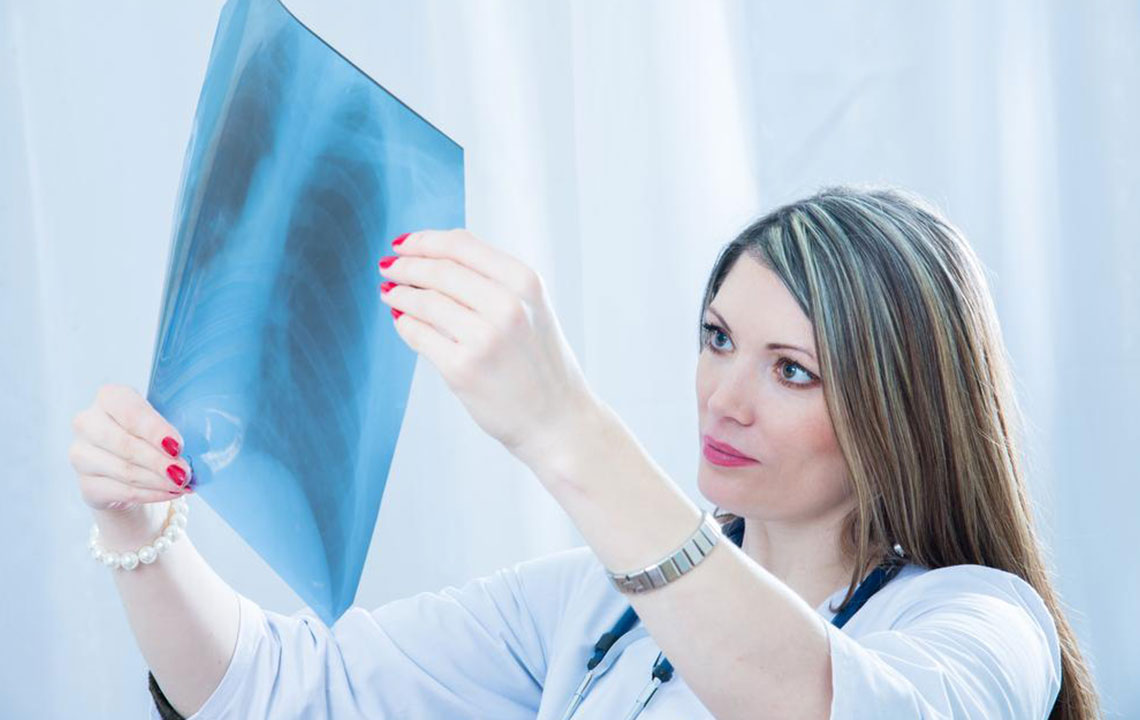
Accurate diagnosis is vital. Doctors start with medical history assessments, especially if previous respiratory issues or chronic conditions like asthma are present. Diagnostic tests include chest X-rays, blood work, sputum analysis, and pulse oximetry. Physical exams may reveal chest cracking sounds when breathing deeply or coughing, aiding diagnosis.
Treatment Options
The primary goal in treating pneumonia is to eradicate the infection and prevent life-threatening complications. The following methods are commonly employed:
Pharmacological Treatment
Antibiotics are the cornerstone of pneumonia treatment, targeting and destroying the causative bacteria or virus. In severe cases, medications may be given intravenously. Cough suppressants and pain relievers like paracetamol help alleviate chest discomfort and reduce fever. Maintaining hydration with fever medications ensures patient comfort.
Hospital Admission
Severe pneumonia cases often necessitate hospitalization for close monitoring, IV medication administration, and oxygen therapy. Elderly patients and those with compromised health are particularly vulnerable and require inpatient care to ensure stability and recovery.
Additional Care
Managing Dehydration
Due to persistent coughing and chills, dehydration risk increases. IV fluids are administered to maintain proper hydration throughout treatment.
Care for Children and Infants
Young children, especially under two years, may need hospitalization for tailored treatment. Care involves careful observation and dosage adjustments to support healthy growth while combating infection.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential for effective pneumonia management, minimizing risks and supporting full recovery.