Effective Medical Strategies for Managing Neurofibromatosis
This article provides a comprehensive overview of medical treatment options for neurofibromatosis, including FDA-approved drugs, pain management, surgical procedures, radiation therapy, and hearing implants. Early diagnosis and tailored therapy are key to managing this complex genetic disorder effectively.
Sponsored

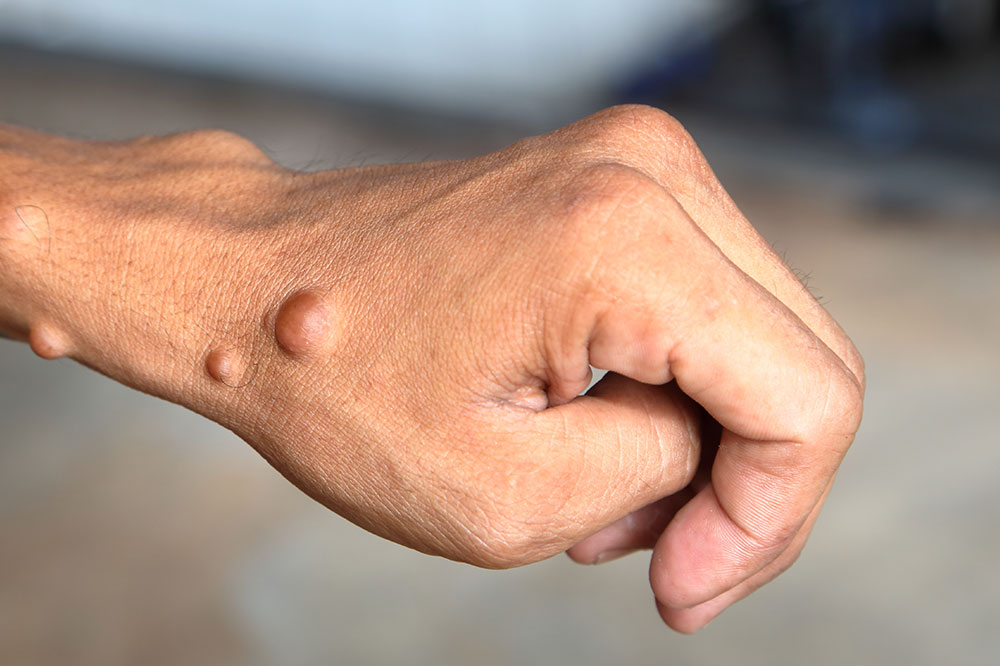
Neurofibromatosis is a hereditary condition affecting the nervous system, characterized by tumor growth along nerve tissues. It primarily exists in two forms: Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), which is more prevalent, and type 2 (NF2), each presenting distinct symptoms. Treatment approaches vary based on the specific type. Here are some of the most recommended interventions.
KOSELUGO® (selumetinib)
Physicians often prescribe KOSELUGO® (selumetinib), the only FDA-approved medication for treating plexiform neurofibromas in children. Ongoing trials aim to evaluate similar drugs for both children and adults.
Pain management medications
For conditions like Schwannomatosis, which results in tumor formation, doctors may suggest specific drugs to alleviate pain.
Medications used to control pain include:
Amitriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant
Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) or pregabalin (Lyrica) for nerve pain
Antiepileptic drugs like topiramate (Topamax, Qudexy XR, Trokendi XR) or carbamazepine (Carbatrol, Tegretol)
Duloxetine (Cymbalta, Drizalma Sprinkle), an SNRI
Surgical removal of tumors
For NF2 patients experiencing brainstem pressure or tumor growth, surgery may be recommended to remove tumors like acoustic neuromas, which can impact hearing and nearby tissues.
Complete removal of schwannomas in Schwannomatosis can dramatically decrease pain levels.
Stereotactic radiosurgery
This non-invasive radiation therapy targets tumors precisely, minimizing damage and potentially preserving hearing functions in NF2 cases.
Implant options for hearing loss
Auditory brainstem implants and cochlear implants significantly improve hearing in patients with NF2-associated hearing impairment.
Cancer treatments
Neurofibromatosis may increase the risk of malignant tumors, which are treatable with conventional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation. Early diagnosis and intervention are vital for better outcomes.