Recognizing the Early Symptoms of Diabetes
Early detection of diabetes symptoms is vital for effective management. This guide highlights common signs such as increased hunger, thirst, fatigue, and vision issues, emphasizing the importance of timely medical consultation. Adopting a balanced diet rich in vegetables and whole grains, combined with regular exercise, can help prevent the disease. Awareness about early signs empowers individuals to seek prompt healthcare, reducing risks and leading a healthier life with minimal reliance on medications.
Sponsored
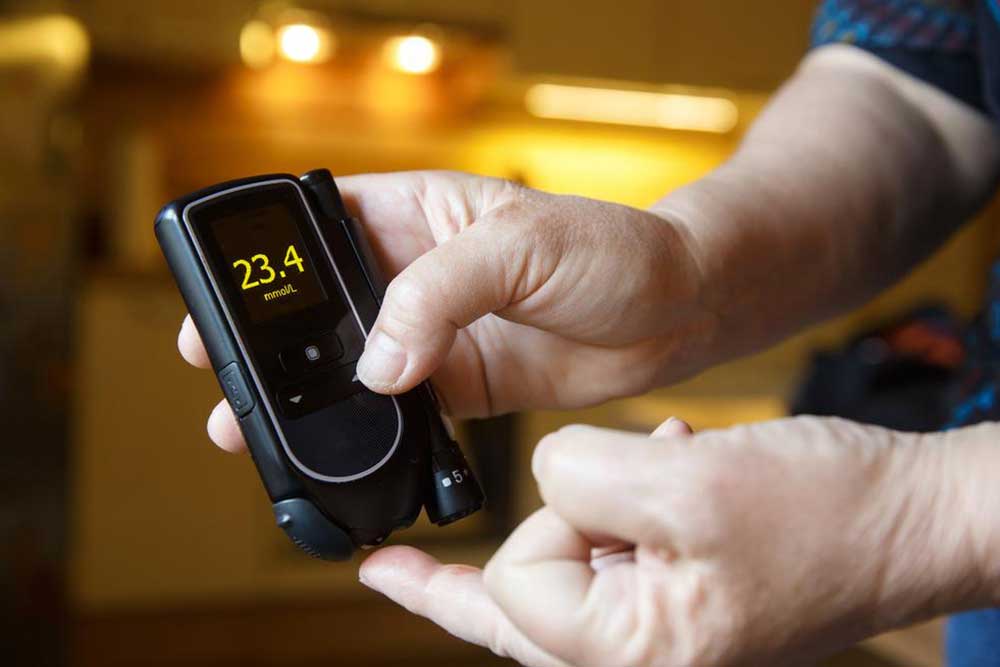

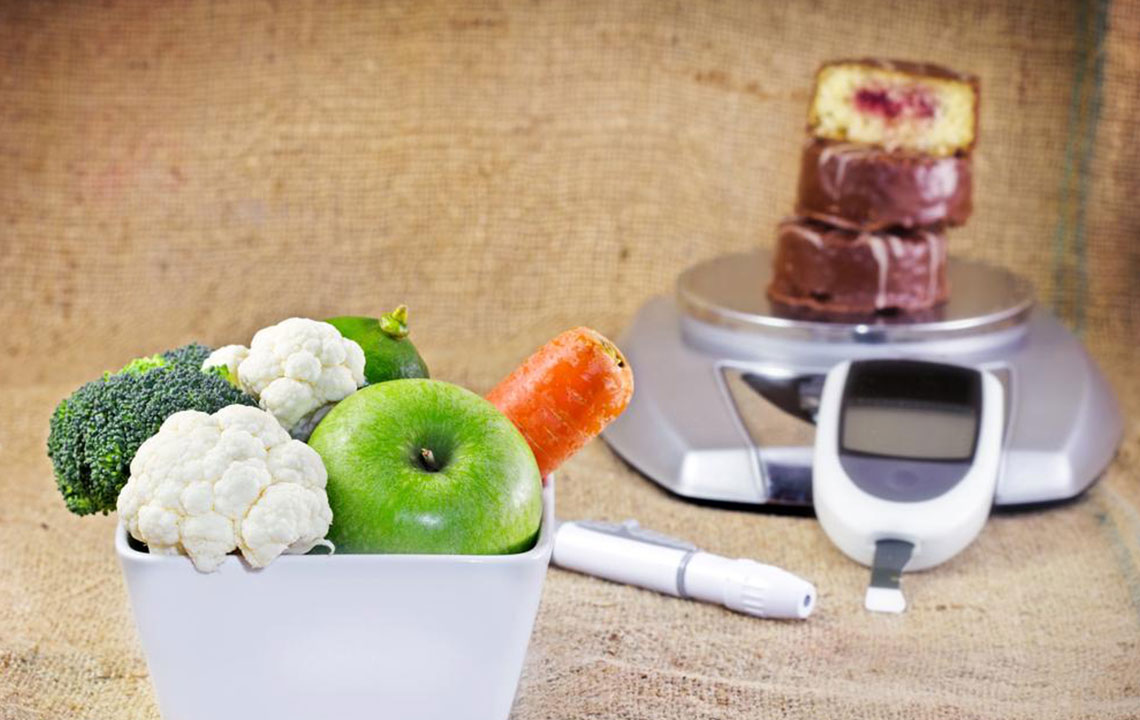
Many individuals indulge in sweets and desserts after meals, often craving sugar and spices to satisfy their tastes. However, consuming excessive carbohydrates and sugars can be detrimental to health. With approximately 9.4% of the population affected by diabetes, the numbers are alarming and expected to grow. Diabetes ranks as the seventh leading cause of death globally. Early detection of symptoms enables better disease management and improves outcomes. Recognizing these signs early is crucial for maintaining health and preventing complications.
Common Early Indicators of Diabetes
Sometimes, diabetes can develop silently with no apparent symptoms. In fact, nearly one-third of type 2 diabetes cases present without warning signs. Don’t be discouraged—consult your healthcare provider to assess your risk and determine if testing is necessary. Some early signs to watch for include:
Persistent increased hunger despite sufficient food intake
Excessive thirst even after drinking fluids
Dry mouth sensation
Recurrent urinary infections or frequent urination
Unexpected weight loss despite normal eating habits
Severe fatigue and weakness
Blurry vision
Headaches
If you notice any of these symptoms, see your doctor promptly and get tested. Proper lifestyle adjustments, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help manage and potentially prevent the progression of diabetes.
Maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in routine physical activity, and following medical advice are key to controlling the disease. Focus on reducing sugar intake and avoiding processed foods like sweet drinks, trans fats, white bread, and packaged snacks. Incorporate whole grains like millet and quinoa, along with an abundance of vegetables, to promote better health. Early detection and proactive measures can significantly reduce dependency on medications and improve quality of life. Your health is in your hands—act early to prevent complications and maintain optimal sugar levels.