Recognizing the Initial Signs of Diabetes
Learn to identify early signs of diabetes, including excessive thirst, hunger, frequent urination, weight loss, and fatigue. Understand the importance of diet and lifestyle changes to manage this common metabolic disorder effectively and ensure timely medical intervention.
Sponsored
Symptoms indicating the onset of diabetes
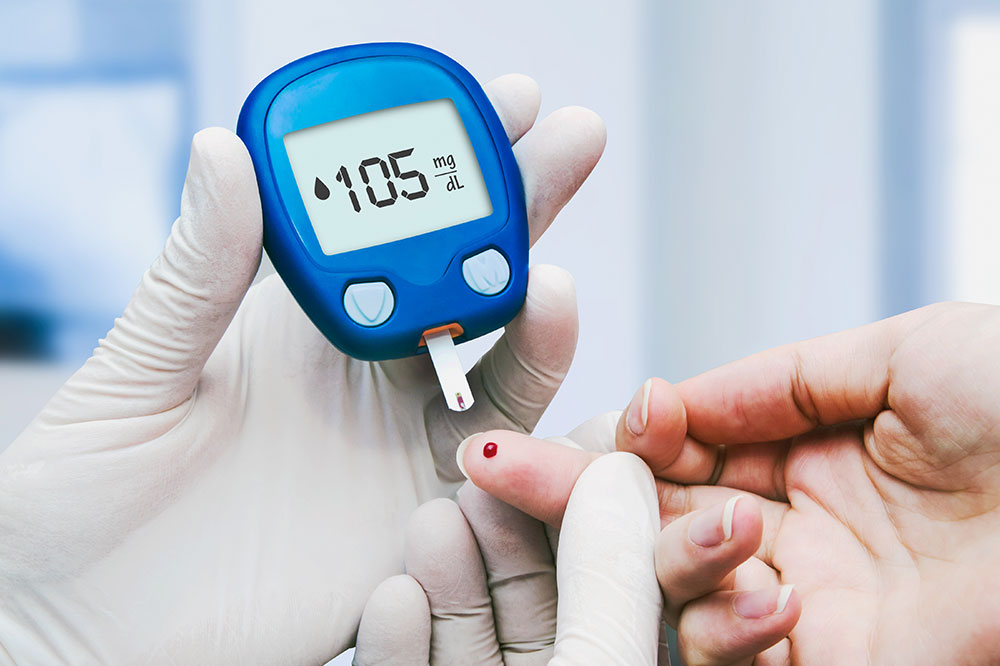
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that may be inherited or triggered by poor lifestyle choices. It is characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to the body's inability to produce enough insulin, the hormone responsible for managing blood sugar. When we consume carbohydrate-rich foods, they convert into glucose which enters the bloodstream to nourish our cells. In diabetes, insufficient insulin production leads to high blood sugar levels, impacting health.
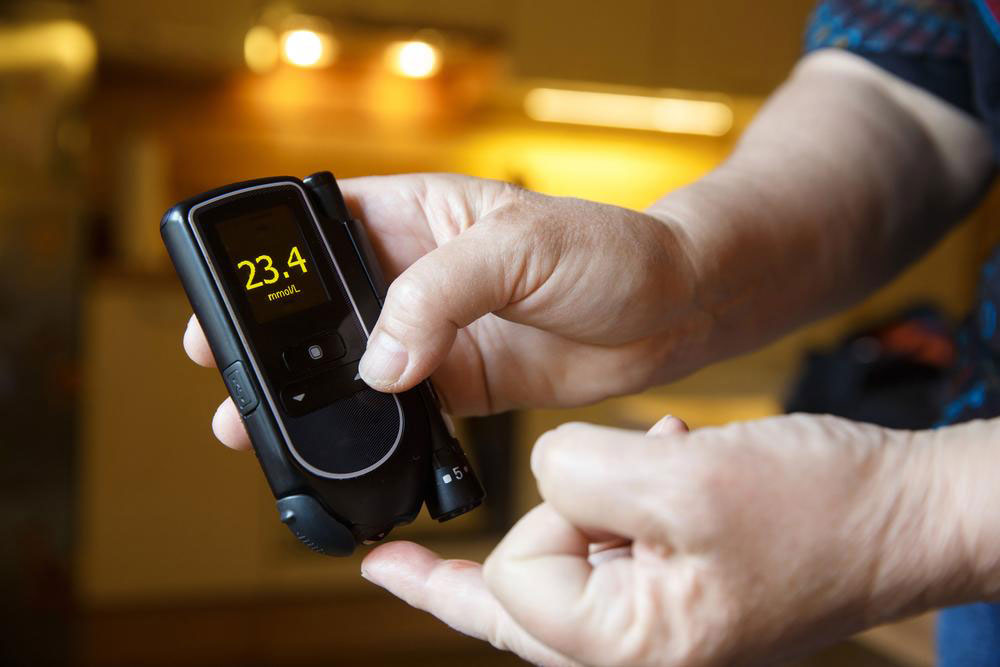
Research shows that pancreatic beta cells produce insulin, controlling blood glucose. Damage or dysfunction in these cells results in sugar build-up in the blood, leading to symptoms. Blood sugar levels above 400 mg per 100 ml often cause sugar in urine and blood. Diabetes is mainly categorized into Type 1 (juvenile onset) and Type 2 (adult-onset), with the latter being more common in those over 40.
Type 1 diabetes involves destruction of pancreatic cells, whereas Type 2 can often be managed through lifestyle changes. Type 2 has two forms: insulin-dependent (IDDM) and non-insulin-dependent (NIDDM). NIDDM patients may control the disease with diet and exercise, while IDDM patients rely on external insulin. Recognizing early symptoms can help in timely management.
Common early signs include:
Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia)
Persistent feeling of dryness in the mouth despite fluid intake is a key sign. It results from high blood sugar causing dehydration.
Constant Hunger (Polyphagia)
Feeling hungry all the time, despite eating, occurs due to the body's inability to process glucose efficiently, leading to increased appetite and energy deficiency.
Frequent Urination (Polyuria)
Needing to urinate frequently, often over 3 liters a day, happens because excess sugar is excreted through urine, pulling fluids from the body.
Unintentional Weight Loss
Sudden, significant weight reduction signals insulin issues, as the body can't properly utilize or store fats and sugars, leading to energy loss.
Fatigue
Persistent tiredness and lack of energy are common, making routine activities difficult. Noticing these signs warrants medical consultation.
Diet Recommendations
Diabetics should emphasize vegetables, fiber-rich foods, and avoid refined grains. Limiting white flour, fried foods, starchy items like potatoes and rice, and processed snacks is crucial. Alcohol and sugary drinks should be minimized. Regular exercise, such as morning walks, can help control but not cure diabetes. Adopting healthy routines is essential for managing the condition effectively.