Comprehensive Guide to Pain Relief Medications
This comprehensive guide explores various pain relief options, including OTC remedies, topical treatments, and prescription medications like corticosteroids, opioids, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants. It emphasizes the importance of consulting healthcare professionals for persistent pain and highlights advanced therapies like TENS. Understanding these options helps in effective pain management and improving everyday life quality.
Sponsored
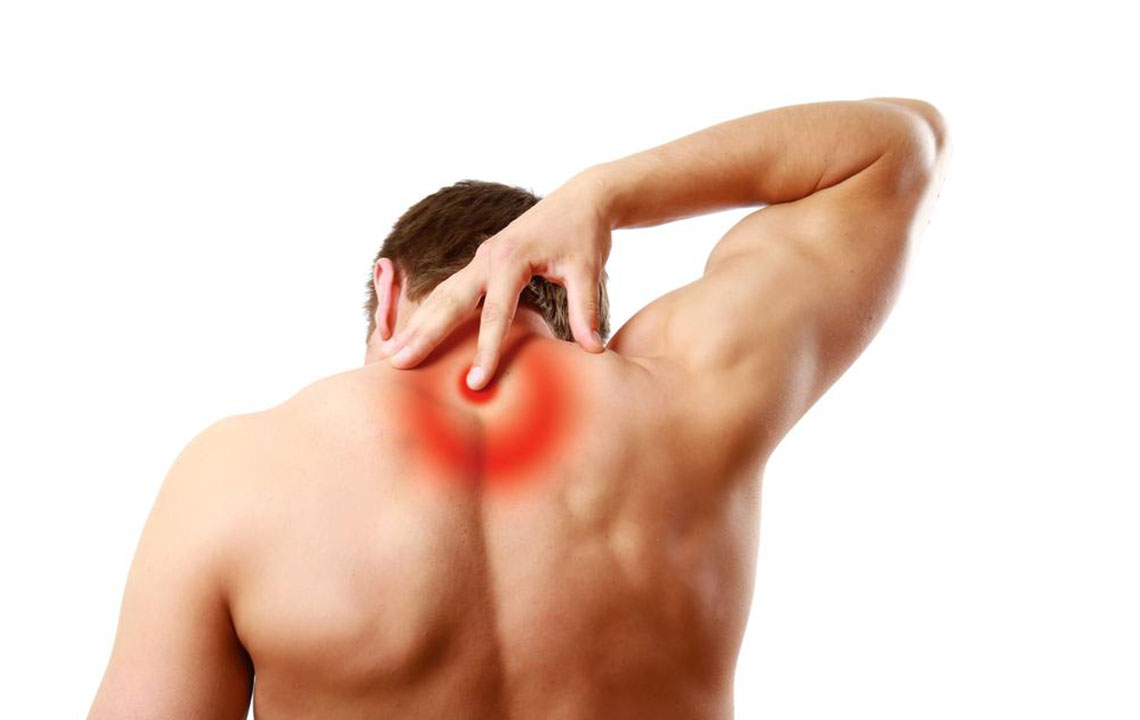
Effective Strategies for Managing Different Types of Pain
Pain is a physical sensation that causes discomfort, distress, and sometimes severe suffering. It can manifest in various forms, such as constant aches, throbbing sensations, or sharp stabbing pains. The severity of pain can impact daily activities and overall well-being, making effective treatment essential.
To manage pain effectively, several medication options are available. Here's a breakdown of common pain relief medicines:
Over-the-Counter Remedies
Includes medications like Acetaminophen (Tylenol) and NSAIDs. These help reduce fever and alleviate muscle aches and pains.
NSAIDs can also reduce tissue inflammation. They work by decreasing prostaglandin, a hormone-like compound that causes pain. Acetaminophen targets the brain's pain signals. Excessive use of NSAIDs may cause stomach issues and increase the risk of strokes and heart attacks.
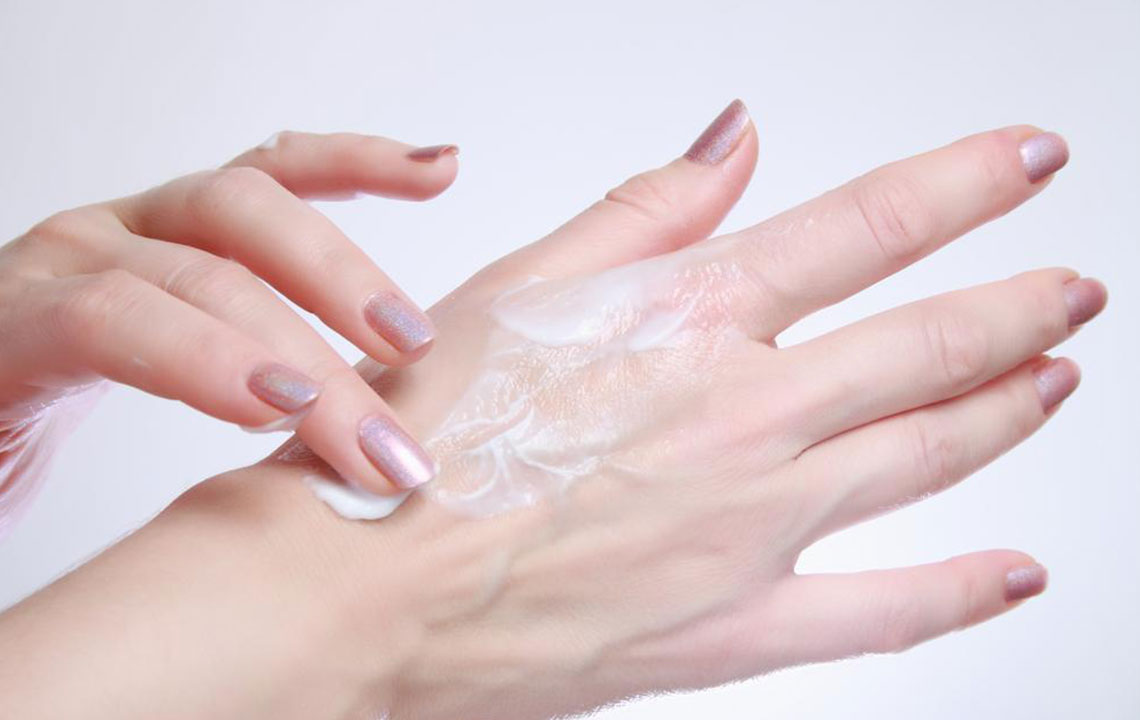
Topical Pain Medications
These include creams, gels, sprays, and lotions applied directly to the affected skin areas to ease muscle soreness or joint pain, ideal for minor discomforts.
These OTC options are suitable for mild pain and can be used without a doctor's prescription. For persistent or severe pain, prescription medications may be necessary.
Prescription Pain Relief Options
The category includes corticosteroids, opioids, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants, each with specific uses and considerations:
Corticosteroids
Used to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with conditions like arthritis and allergies. They are administered orally or via injections but may cause side effects like weight gain or weakened bones if used long-term.
Opioids
Powerful narcotic drugs such as Morphine, Oxycodone, and Fentanyl are prescribed for acute, severe pain, often after surgery. They are effective but carry risks of addiction and side effects like drowsiness and nausea. Short-term use is recommended.
Antidepressants
These medications help reduce chronic pain and emotional stress by balancing brain chemicals. They are often used for migraines and menstrual cramps, with fewer side effects like dry mouth, fatigue, or dizziness.
Anticonvulsants
Originally meant for seizure control, anticonvulsants like Gabapentin and Pregabalin are also effective for nerve pain. Side effects are minimal but may include drowsiness and dizziness.
Additional Pain Management Techniques
Other treatments include lidocaine patches or creams, which temporarily numb affected areas, and advanced procedures like TENS therapy that send electrical signals to reduce pain. Consulting a specialist can help determine the most suitable approach for ongoing pain issues.
If you experience persistent pain, seeking medical advice is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Proper medication and therapy can greatly improve quality of life.