Key Insights for Managing Living with Psoriasis
This article offers essential insights into managing psoriasis, emphasizing triggers, types, diagnosis, and dietary strategies. It highlights that while psoriasis is incurable, proper treatment and lifestyle adjustments can control symptoms effectively. Recognizing triggers like stress, infections, and diet is vital for flare-up prevention. The piece also explains the different psoriasis types, diagnosis methods, and recommendations for dietary improvements to manage the condition better. Understanding these key aspects empowers individuals to live healthier with psoriasis and reduce its impact.
Sponsored

Vital information for those coping with psoriasis
Despite maintaining healthy eating habits and regular exercise, some health conditions can still impact us profoundly. Psoriasis, a chronic skin disorder, affects millions worldwide and presents unique challenges. Individuals living with psoriasis must monitor their condition carefully while combating societal misconceptions. This disease can develop at any age and may worsen without proper care.
It’s important to understand that psoriasis is incurable, but its symptoms can be managed effectively through prescribed topical treatments and medications. Keep reading to learn how to better live with psoriasis and manage its flare-ups.
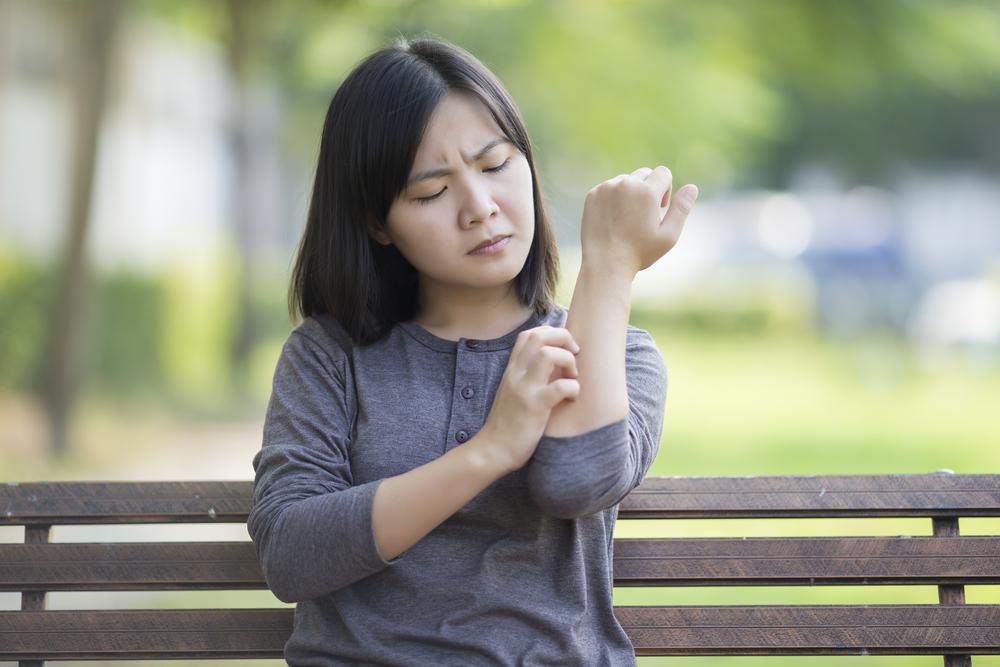
What causes psoriasis to flare?
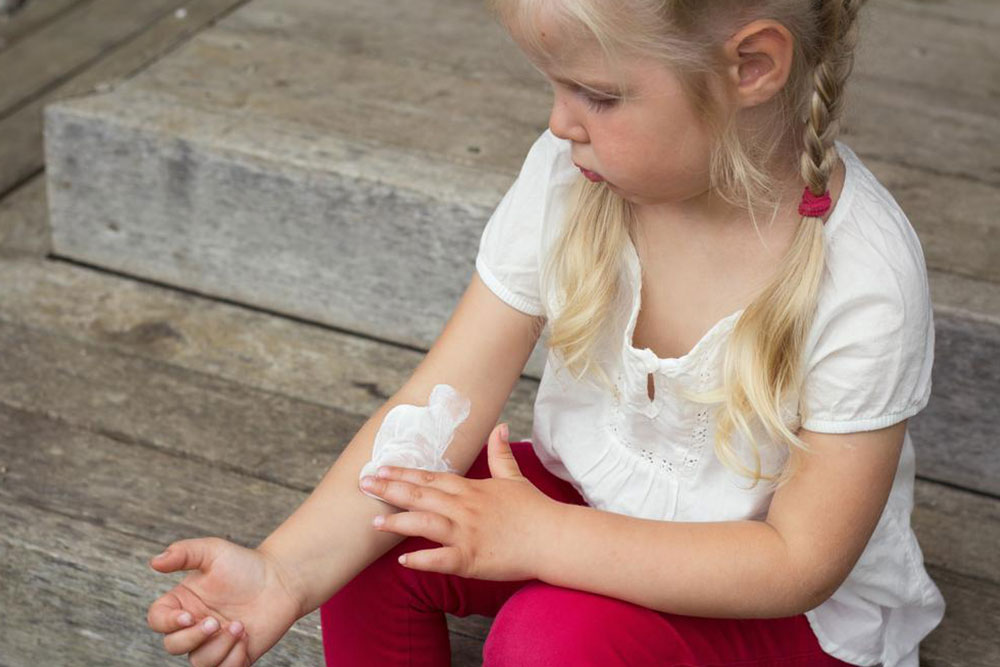
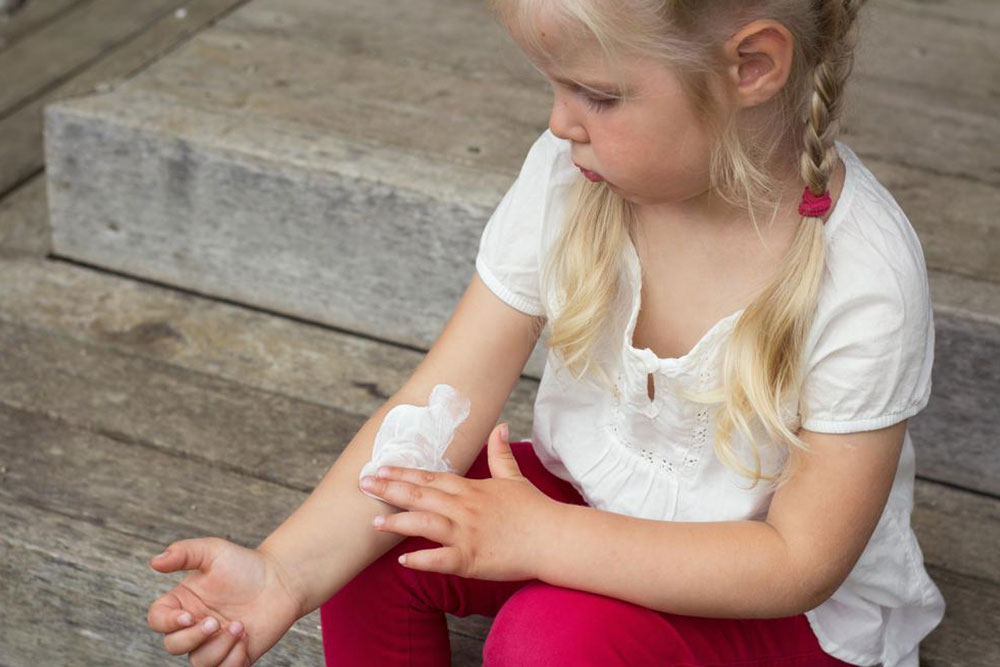
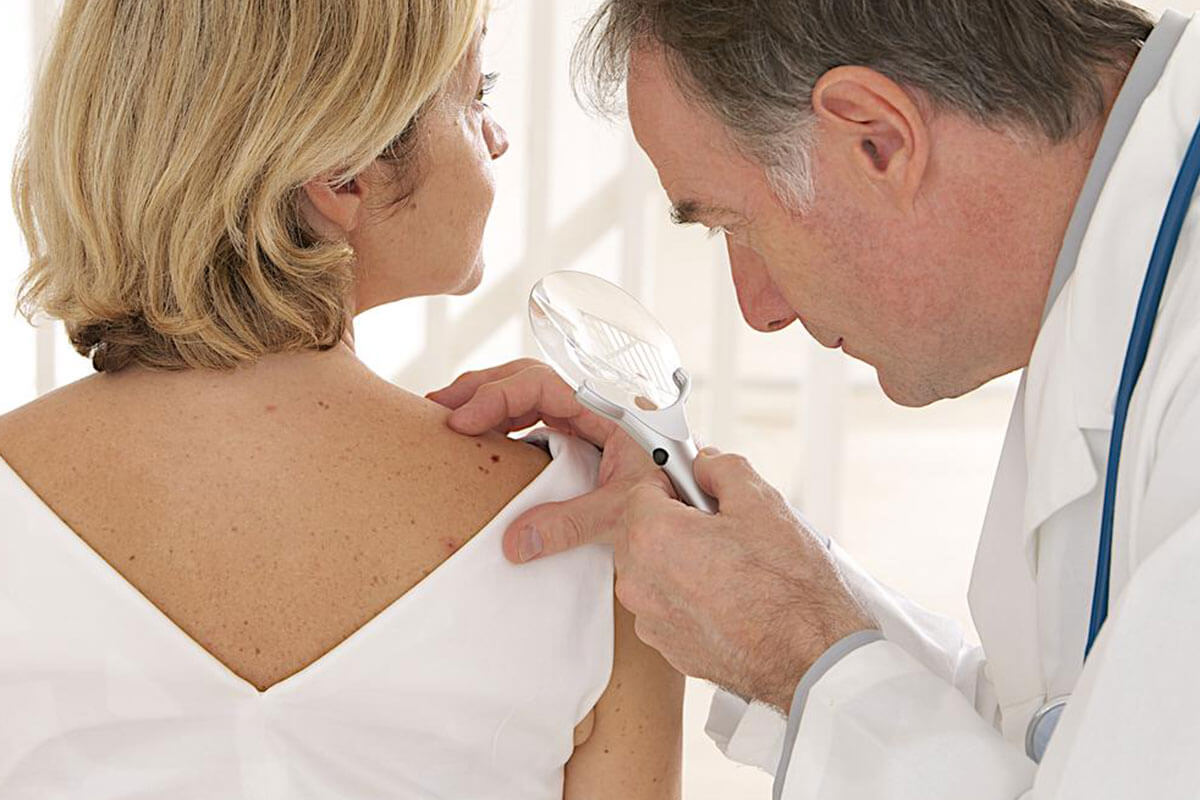
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by rapid skin cell buildup, leading to scales forming on the skin, especially on the hands, feet, neck, face, and scalp.
During flare-ups, inflammation and redness appear around affected areas. The scales are whitish-silver and form thick, red patches.
Triggers such as stress, injuries, alcohol, infections, or certain medications (like lithium or high blood pressure drugs) can provoke psoriasis episodes. Contact with these triggers often results in sudden exacerbations.
Types of psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis: The most prevalent form, affecting about 80% of sufferers, manifests as red, inflamed patches of skin.
Guttate psoriasis: Common in children, featuring small pink spots on the arms, legs, and torso.
Pustular psoriasis: More frequent in adults, producing white, pus-filled blisters over large skin areas causing redness and swelling.
Inverse psoriasis: Affects armpits, groin, under breasts, and skin folds around genital areas, leading to shiny, red, irritated skin.
Erythrodermic psoriasis: A severe, rare form that covers much of the body, giving a sunburned look, with skin shedding in large sheets, potentially life-threatening.
Diagnosing psoriasis
Physical exam: Doctors typically diagnose psoriasis through visual inspection, noting the characteristic scaly, inflamed skin. Disclosure of any family history is helpful as psoriasis has genetic factors.
Skin biopsy: A small skin sample may be taken to rule out other conditions or infections, confirming the diagnosis.
Diet tips for psoriasis management
Limit saturated fats from meats and dairy; incorporate omega-3 rich lean proteins.
Weight loss is crucial for overweight individuals, as it reduces severity and enhances treatment efficacy.
Avoid trigger foods like red meats, refined sugars, processed foods, and dairy.
Alcohol consumption should be minimized or avoided, as it can trigger flare-ups.
Enhance your diet with vitamin-rich foods and consider supplements after consulting your doctor.
Tags- Psoriasis management, skin health, autoimmune skin disease