Comprehensive Guide to Dairy and Egg Nutrition
This guide offers a detailed overview of dairy products and eggs, clarifying misconceptions, explaining nutritional benefits, and providing tips for optimal consumption. Learn the differences between dairy and eggs, their health advantages, and how to incorporate them into your diet effectively. Perfect for those seeking balanced nutrition and versatile meal ideas.
Sponsored

All You Need to Know About Dairy and Eggs
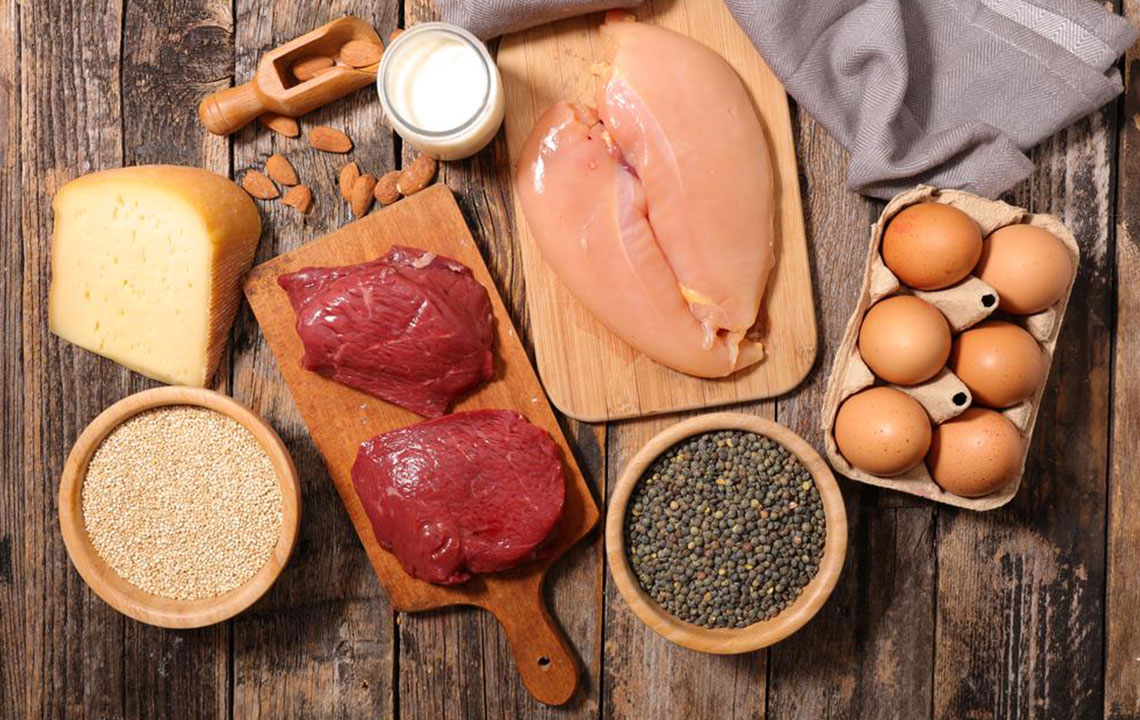
Dairy products and eggs are vital components of a balanced diet, offering essential nutrients that support overall health. Both are rich in protein and can boost the immune system. Dairy items vary in form, from milk to cheese, while eggs are versatile in cooking methods. Despite their similarities, eggs are not classified as dairy since they are laid by birds, not mammals. Dairy is derived from mammal milk, like cows and goats, while eggs come from hens and ducks, which do not produce milk.
Eggs stored in the dairy aisle are there for refrigeration reasons, not because they are dairy products. Dairy is categorized into four classes based on usage: Class I for beverages, Class II for products like yogurt and sour cream, Class III for hard cheese production, and Class IV for butter and dry milk. Nutritionally, both dairy and eggs contribute crucial vitamins and minerals, including calcium, vitamins B12, D, and riboflavin, supporting bone health, immune function, and more.
Eggs are a nutritious source of protein, with a large egg providing 78 calories, healthy fats, essential vitamins, and minerals like selenium and vitamin B12. Dairy products, rich in calcium and vitamin D, support bone integrity and overall health. Both foods are linked to reducing risks of chronic illnesses, improving heart health, and supporting immune function. For vegans or those seeking alternatives, plant-based options can provide similar nutrients.
Including eggs in meals can promote satiety, help manage weight, and boost HDL cholesterol levels, beneficial for heart health. Consuming dairy helps strengthen bones and reduces inflammation, with low-fat options being especially beneficial for chronic disease prevention. Potassium-rich dairy also aids in regulating blood pressure.
To enjoy eggs at their best, choose from chicken, quail, duck, turkey, or ostrich eggs, prepared in various ways—boiled, fried, poached, or scrambled. Opt for cooking methods that minimize calorie intake, such as boiling or poaching. Pair eggs with vegetables to enhance nutrient intake, and use stable cooking oils like sunflower or avocado oil for frying. Prefer organic or pasture-raised eggs for higher nutritional quality and avoid overcooking to preserve nutrients.