Comprehensive Guide to Effective Gout Management and Treatments
Learn about effective gout treatments, including medications, lifestyle changes, and dietary tips to manage symptoms and prevent long-term joint damage. Early diagnosis and proper management are essential for controlling gout and reducing flare-ups effectively.
Sponsored
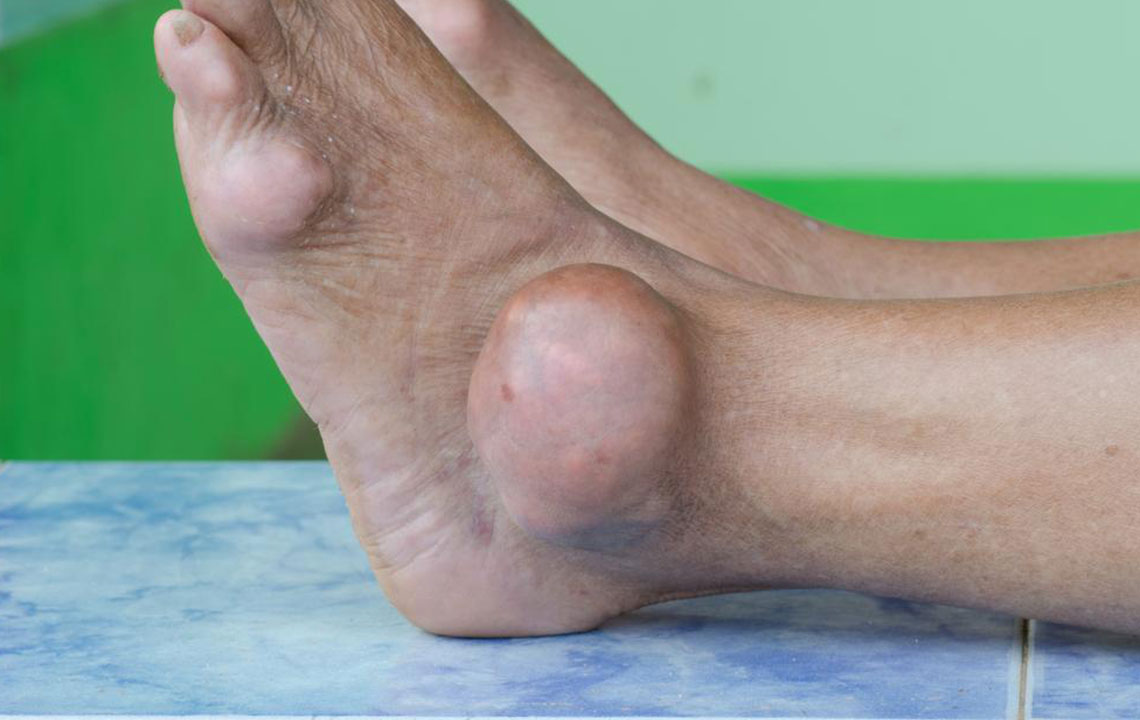
Gout is a form of arthritis characterized by sudden joint inflammation caused by excess uric acid in the bloodstream. It commonly impacts the big toe, fingers, knees, and elbows, resulting in pain, swelling, redness, and stiffness. Without proper treatment, gout attacks can become frequent and potentially lead to joint and tissue damage over time. Early diagnosis and effective management are crucial to prevent long-term complications.
How is gout diagnosed?
Doctors usually diagnose gout through physical examinations and by analyzing joint fluid samples for uric acid crystals. Blood tests are also performed to measure uric acid levels, helping confirm the diagnosis.
Medications for Gout Treatment
Managing gout effectively involves medications aimed at reducing uric acid levels and alleviating symptoms. These can be classified into short-term and long-term treatments.
Short-term treatments
During acute attacks, NSAIDs such as naproxen, indomethacin, and ibuprofen are the primary options to relieve pain and inflammation. Corticosteroids may also be prescribed in pill or injectable form. These medications are used at high doses initially and tapered as symptoms improve, providing prompt relief and preventing future attacks.
Long-term therapies
To control chronic gout and prevent flare-ups, several medications are used. Uricosuric agents help eliminate excess uric acid, while uric acid inhibitors reduce its production. The choice of treatment depends on attack frequency and severity. It's vital to follow your physician’s instructions meticulously when taking these drugs, as improper use can hinder effectiveness and cause complications.
If prescribed, always adhere to the doctor’s guidance and consult before stopping or adjusting medication. Avoid OTC drugs unless approved by your healthcare provider, and report any adverse effects promptly. In cases of joint or tissue damage, surgical options may be considered under medical advice.
Besides medication, lifestyle modifications and home remedies play a vital role in managing gout. Limiting purine-rich foods like red meats, shellfish, and sugary products can help lower uric acid levels. Incorporate a diet rich in vegetables, low-fat dairy, plant oils, citrus fruits, coffee, and whole grains. Reducing alcohol intake and increasing water consumption support hydration and kidney function. During gout attacks, rest and avoid joint strain to ease discomfort. When symptoms subside, gentle exercises like walking or stretching can improve joint flexibility.