Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Managing Vertigo
Learn about vertigo's causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options. From inner ear issues to medication and therapy, this guide provides comprehensive insights to manage and understand vertigo better.
Sponsored

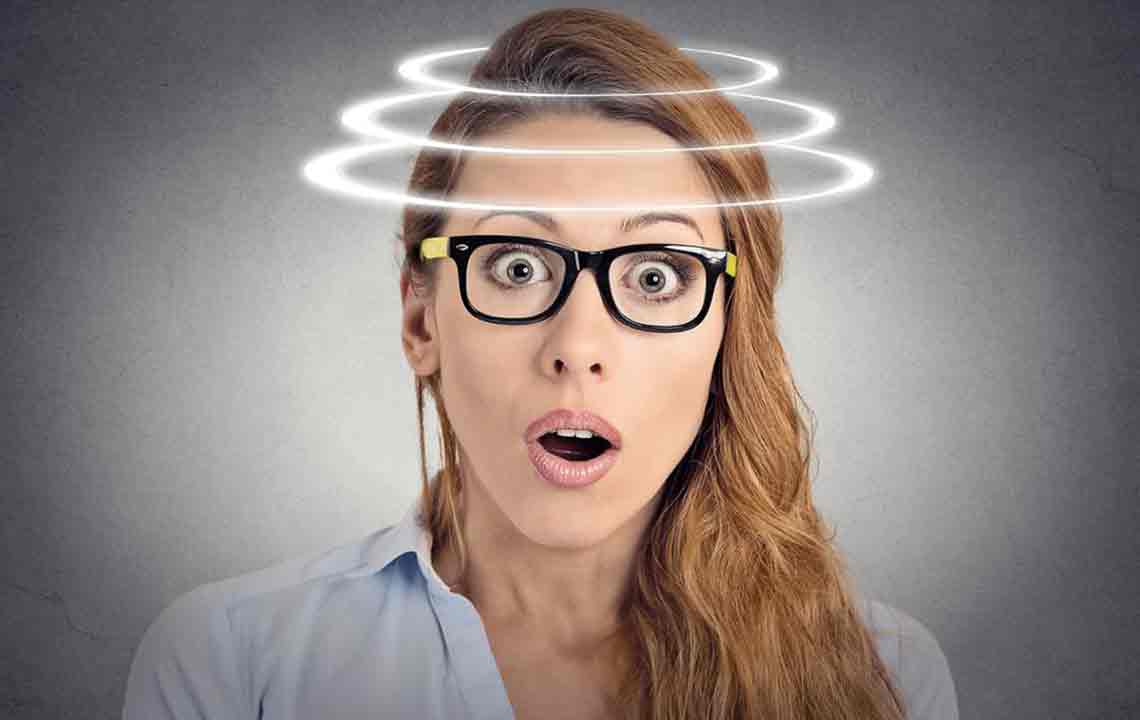
Vertigo is a condition characterized by a sensation of spinning or movement, even when there is no actual motion. It often accompanies symptoms like nausea, vomiting, sweating, or difficulty walking, and tends to worsen with head movements.
What causes vertigo?
Various factors can trigger vertigo, most commonly issues within the inner ear. Here are the primary causes:
BPPV: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo occurs when tiny calcium particles accumulate in the ear's semicircular canals, disrupting balance signals to the brain.
It plays a key role in maintaining body stability.
Vestibular Neuritis or Labyrinthitis: These inner ear infections involve nerve inflammation that affects balance and spatial orientation.
Meniere’s Disease: Caused by fluid buildup in the inner ear, this condition leads to vertigo, ringing ears, and hearing difficulties.
Physiologic Vertigo: Usually occurs after prolonged motion, like on ships or during rapid spinning with eyes closed.
Other triggers include exposure to toxins such as carbon monoxide, alcohol, or certain medications like aspirin, which can impair vestibular function. Additional causes encompass presyncope, disequilibrium, and nonspecific dizziness.
Vertigo Treatment Options
Therapies vary depending on the root cause; many cases resolve without intervention.
Vestibular Rehabilitation: Tailored exercises aim to strengthen the vestibular system, enhancing balance and spatial awareness.
Canalith Repositioning: Specific head and body movements are performed to relocate calcium deposits in BPPV, often triggering temporary vertigo during the procedure.
Medications: Drugs may alleviate symptoms such as nausea or motion sickness, especially when vertigo stems from infection or inflammation. Steroids or antimicrobials can also reduce inner ear swelling or treat infections.
Surgery: In severe cases involving tumors or head/neck injuries, surgical interventions may be necessary to resolve vertigo.