Effective Strategies and Treatments for Alleviating Lower Back Discomfort
This comprehensive guide offers effective methods to ease lower back pain, including causes, diagnosis, medication options, and specialized exercises. It emphasizes the importance of consulting healthcare professionals for personalized care and highlights practical ways to strengthen back muscles, improve posture, and prevent future discomfort. Incorporating suitable physical activity and understanding symptoms can significantly enhance recovery and quality of life.
Sponsored
Strategies and Treatments to Relieve Lower Back Discomfort
Lower back discomfort affects nearly everyone at some point, presenting with varying degrees of pain. It may be a persistent dull ache or an intense, shooting sensation that hampers daily activities. Acute episodes often result from sports injuries or lifting heavy objects.
If you experience additional symptoms like bowel or bladder control issues, fever, or pain when coughing or urinating along with lower back pain, seek medical advice promptly.
Typical causes of lower back discomfort
Persistent lower back issues should be evaluated by a healthcare professional, especially if accompanied by unexplained weight loss, family history of cancer, or other concerning symptoms. Common causes include muscle strains leading to herniated discs, which cause pain radiating from hips to legs.
Repetitive activities like lifting, pulling, or prolonged sitting in poor posture contribute significantly to lower back pain. Excessive exercise or being overweight can also increase risk. Sedentary lifestyles may necessitate regular back-strengthening routines.
Chronic conditions such as fibromyalgia, spinal stenosis, or inflammatory diseases like spondylitis can also cause ongoing lower back discomfort.
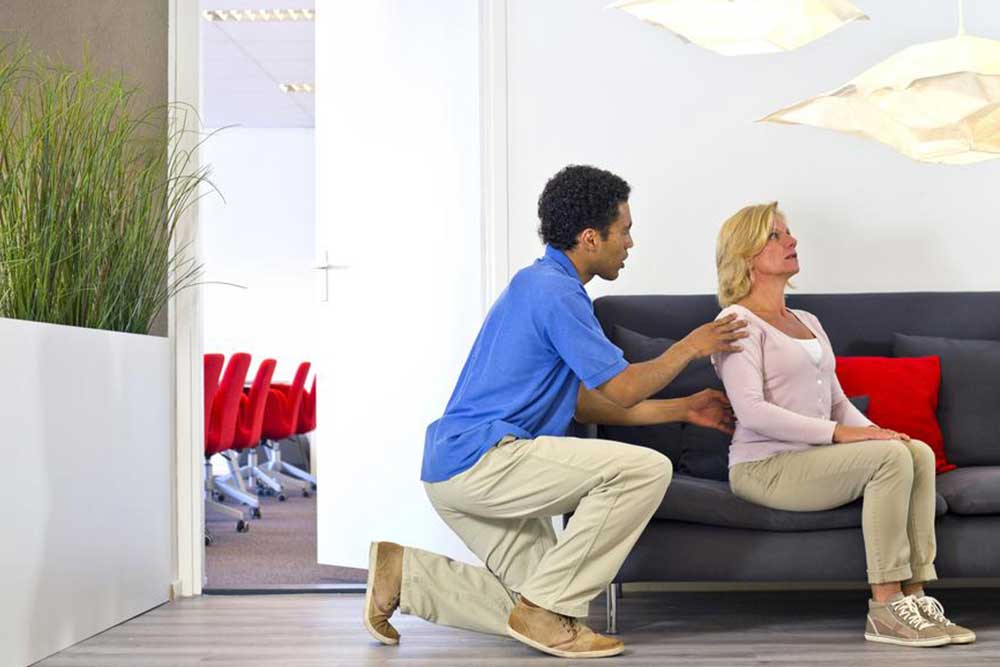
Diagnosing this condition typically involves imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans. Your doctor will assess symptoms, medical history, and physical exams. Mild pain may be managed with over-the-counter drugs like ibuprofen or naproxen, and topical pain relief creams may provide additional relief. Always consult a healthcare professional before initiating medication.
Back-strengthening exercises you can try
Staying inactive worsens back pain; instead, targeted exercises that strengthen back, core, and leg muscles are recommended. Consult your doctor before starting any new routine to avoid injury. Exercises such as toe touches and sit-ups are not advisable as they may strain your back.
Better options include hamstring stretches, partial crunches, and wall sits. The wall sit involves standing about 12 inches from a wall, sliding down into a seated position with your back flat against the wall, holding for around 10 seconds, and repeating 10-12 times.
Additional effective exercises include pelvic tilts, knee-to-chest stretches, bridging, and press-up back extensions. For bridging, lie on your back with knees bent, feet flat, then lift your hips, hold briefly, and lower slowly. Avoid heavy lifting during pain episodes and consider low-impact aerobic activities like swimming, walking, or cycling. Pilates may also aid in relief and strengthening muscles.