Understanding the Factors Contributing to Fibromyalgia Risk
This article explores the various factors influencing the risk of fibromyalgia, including genetic, hormonal, and lifestyle elements. It discusses how pain sensitivity, stress, and hormonal changes such as menopause contribute to the disorder. Recognizing these factors can aid in understanding and managing fibromyalgia effectively.
Sponsored

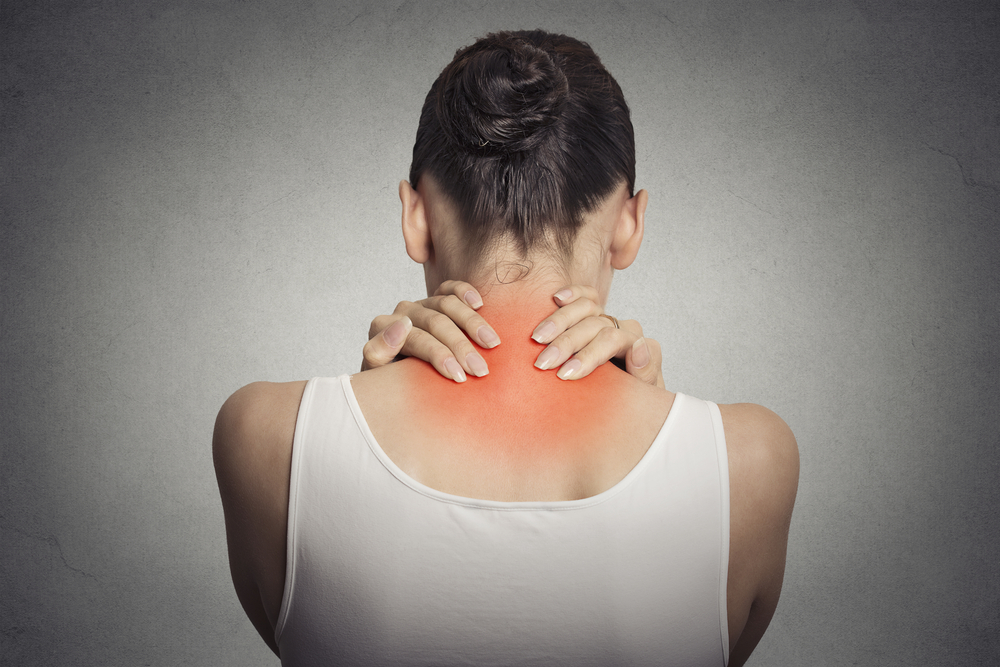
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition impacting muscles and soft tissues across the body. Often mistaken for arthritis, its symptoms make diagnosis challenging. Research indicates women are twice as likely to develop fibromyalgia compared to men, partly due to slower serotonin production. The exact cause remains unknown, but theories suggest heightened sensitivity in pain pathways due to central nervous system changes. Genetic predispositions, lifestyle habits like smoking or obesity, stress, and hormonal fluctuations such as menopause may increase susceptibility. Additionally, stress-related trauma and sleep issues commonly co-occur with fibromyalgia.
Fibromyalgia is linked with neurochemical imbalances affecting mood, sleep, and energy, leading to common comorbidities like depression and fatigue. Genetic variations, especially in serotonin receptors, also play a role, although these are shared with other syndromes like irritable bowel. Lifestyle factors and psychological stress can trigger or worsen symptoms, highlighting the importance of a holistic approach to management.
fibromyalgia
chronic pain
genetics
lifestyle factors
stress and hormonal influences