Understanding Epilepsy: Key Facts Everyone Should Know
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder with unpredictable seizures caused by abnormal brain activity. Treatments include medications, dietary changes, and surgery, with ongoing research to better understand its causes. Proper management is crucial, especially during pregnancy, to ensure safety and effectiveness. Understanding the differences between epilepsy and seizures is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective care. Advances like the ketogenic diet and implantable stimulators offer hope for those with resistant epilepsy, emphasizing a personalized approach to treatment.
Sponsored

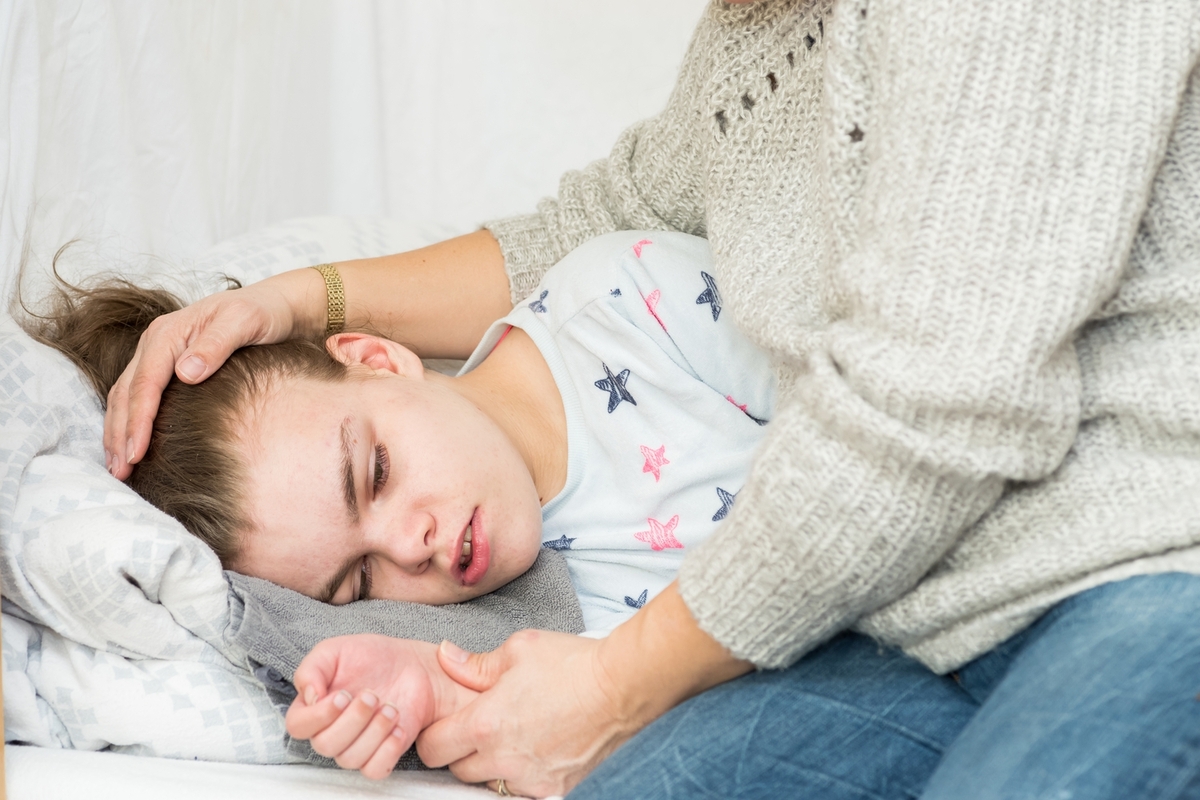
Epilepsy, commonly known as seizure disorder, is a neurological condition characterized by recurring unprovoked seizures in the brain. These episodes result from abnormal electrical activity, resembling a storm within the brain. Often, the root cause remains unknown, prompting ongoing research to identify the genetic factors involved and improve treatment options.
Distinguishing Epilepsy from Seizures
Seizures are a common symptom of epilepsy, but not everyone experiencing seizures has the disorder. Unprovoked seizures without injury, infection, or alcohol withdrawal might indicate epilepsy.
Medication is the primary treatment for epilepsy
Anti-epileptic drugs, also called anticonvulsants, are the most effective way to manage the condition. They reduce brain electrical activity responsible for seizures. Since the exact cause of epilepsy isn't fully understood, accurate diagnosis and treatment optimization are vital for controlling symptoms while minimizing side effects.
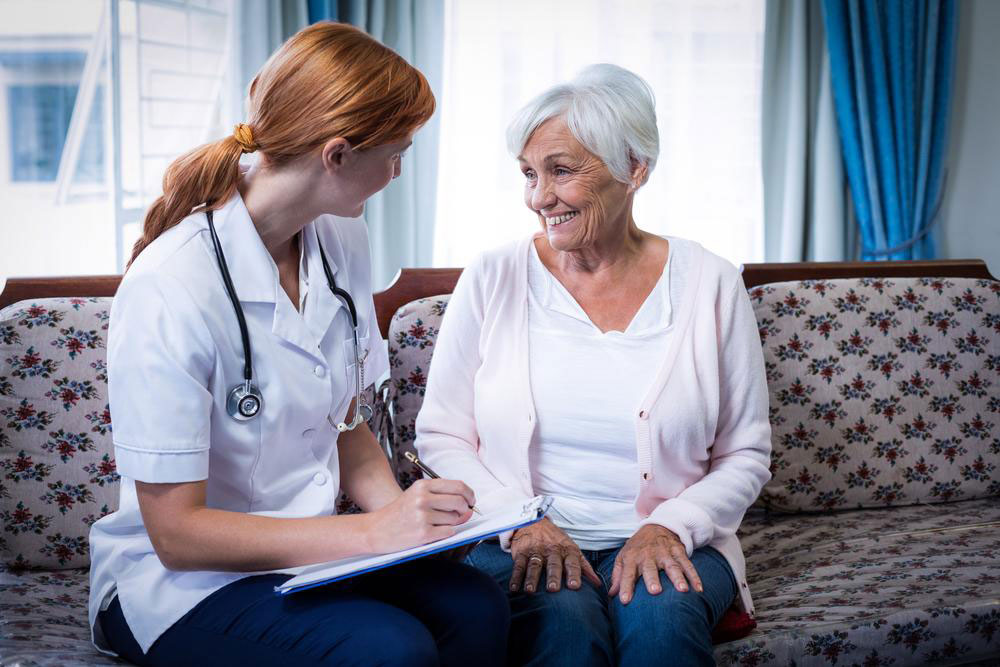
Epilepsy management during pregnancy
While no medication is completely risk-free, careful medical supervision ensures safer management during pregnancy. Consulting healthcare providers helps identify suitable treatment options to control seizures without compromising maternal health.
Alternative approaches beyond medication
Emerging treatments include diets like the ketogenic diet, particularly effective for children unresponsive to medicines. In some cases, minor surgical procedures involving implantable stimulators are used, similar to cardiac pacemakers. Nonetheless, medication often remains necessary even after surgical intervention.
In summary, epilepsy management involves medications, dietary adjustments, and, occasionally, surgery to effectively control seizures and improve quality of life.