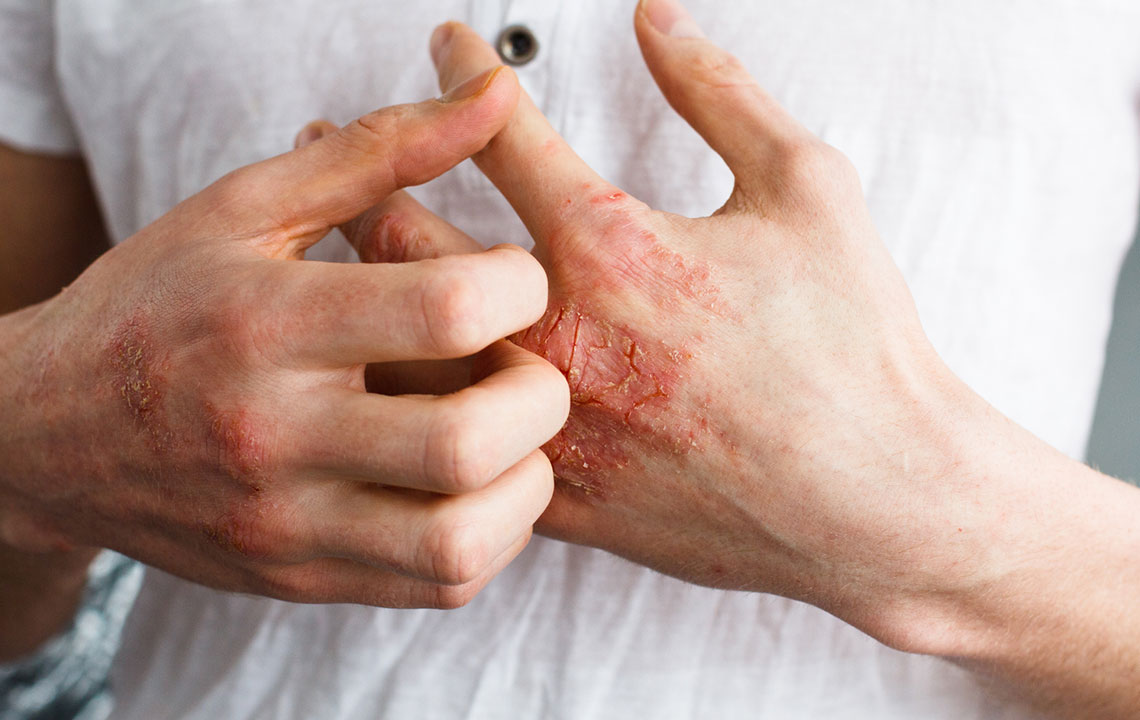
Diet Strategies to Alleviate Eczema Symptoms
Discover effective dietary strategies to control eczema symptoms. Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods like omega-3s, probiotics, and antioxidants while avoiding common triggers such as eggs, dairy, gluten, and nickel-rich foods. Proper nutrition can reduce flare-ups and promote healthier skin.
Sponsored
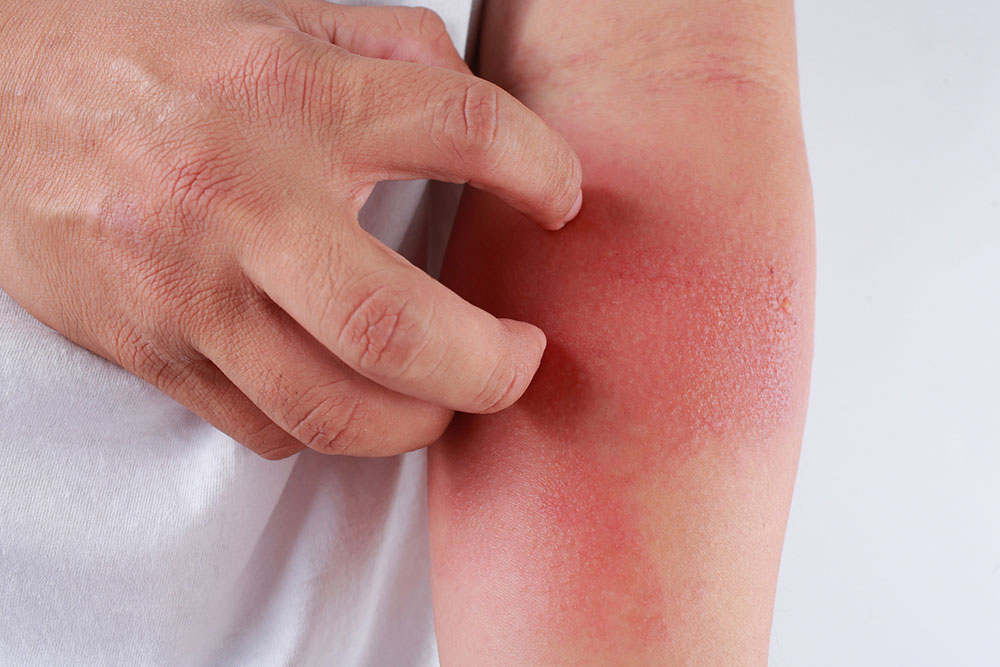
Eczema is a chronic skin disorder that often worsens due to allergic reactions. Certain foods can contribute to these allergies, making dietary management essential. Patients with eczema should focus on foods that support skin health and avoid triggers that cause flare-ups.
Proper Eczema Nutrition Proper diet plays a crucial role in reducing allergy risks and minimizing eczema symptoms. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods can naturally soothe the skin and decrease discomfort.
Recommended Foods The following foods are beneficial for individuals with eczema:
Many of these options contain anti-inflammatory compounds that help reduce swelling, itching, and redness associated with eczema.
Quercetin: An antioxidant responsible for vibrant colors in fruits and vegetables, quercetin helps diminish inflammation and acts as a natural antihistamine, preventing allergic reactions. Found in apples, blueberries, broccoli, spinach, cherries, and kale.
Probiotics: Beneficial bacteria support healthy digestion and enhance immunity, which can reduce allergy severity. Sources include yogurt, unpasteurized sauerkraut, kefir, and tempeh.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Known for their anti-inflammatory properties, omega-3s help soothe eczema symptoms. Rich sources are fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, sardines, and plant-based options such as nuts.
High-Fiber Foods: Consuming fiber-rich foods such as whole grains, legumes, mangoes, nuts, and seeds can support overall skin health and reduce inflammation.
Foods to Steer Clear Of Certain foods may trigger allergy symptoms, worsening eczema. Identifying personal sensitivities through elimination diets can help manage flare-ups.
Eggs: Eggs are common allergens that can rapidly trigger eczema reactions.
Dairy Products: While some can tolerate dairy, others, especially children, may experience worsening symptoms. Alternatives like soy milk can be helpful.
Gluten: Found in wheat, rye, and barley, gluten can cause reactions in sensitive individuals, so avoiding gluten-containing foods may benefit eczema sufferers.
Nickel-Rich Foods: Beans, oats, chocolate, canned foods, and soy contain nickel, which may increase itching and irritation. Including more fruits and vegetables can help reduce nickel absorption.
Managing eczema involves careful dietary choices. Following a tailored diet plan helps prevent allergic triggers and supports skin health.