Managing Diarrhea with Proper Nutrition and Care
Learn effective ways to manage diarrhea through proper diet and hydration. This article covers dietary tips, foods to avoid, and the role of probiotics, emphasizing timely medical consultation for persistent cases. Proper nutrition supports recovery and prevents complications, especially in vulnerable groups like children and seniors.
Sponsored

Diarrhea is a common health issue characterized by frequent, watery bowel movements. It can vary from mild to severe, requiring medical attention in some cases to prevent dehydration and complications. Typically caused by infections viruses, bacteria, or parasites, it often resolves within a few days. Vulnerable groups like children and the elderly need extra care to prevent dehydration. Knowing suitable foods to consume during episodes of diarrhea is essential, especially while traveling, to support recovery and maintain hydration.
Persistent or chronic diarrhea might indicate underlying conditions such as
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Crohn’s disease
Coeliac disease
Bowel cancer
Most cases result from infections caused by bacteria like Salmonella, Shigella, or E. coli, but they are generally treatable with proper medication and diet adjustments. In acute cases, rehydration is vital to replace lost fluids and electrolytes, often achieved through oral solutions containing salt and glucose, which aid absorption in the intestines.
Diet tips during diarrhea
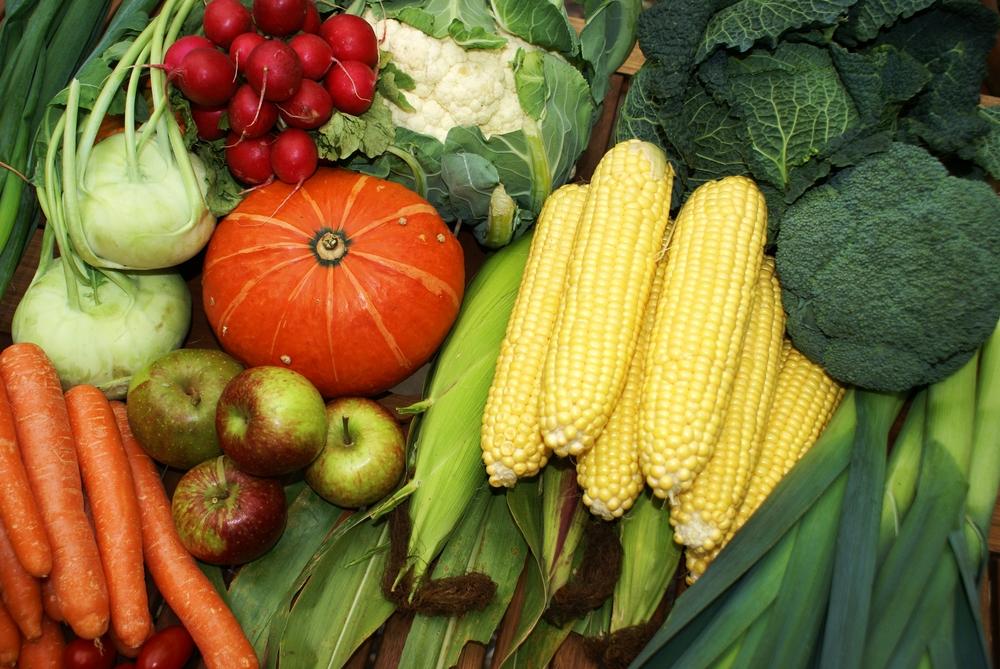
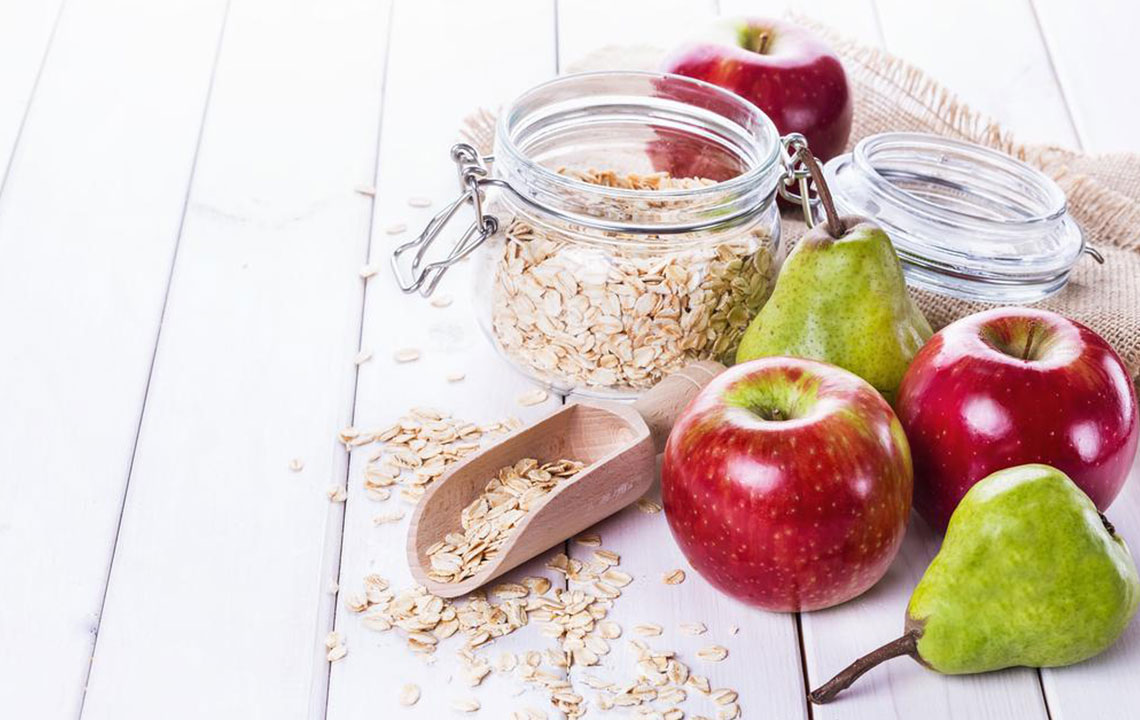
Consume bland, easily digestible foods such as bananas, rice, boiled potatoes, toast, or lean chicken without skin.
Drink clear fluids like water, herbal teas, or electrolyte solutions to stay hydrated.
Include potassium-rich foods like bananas, potatoes, and fruit juices, and sodium-rich items such as broths and salted crackers.
Opt for gentle teas like black tea, which can soothe the stomach.
Eat root vegetables including carrots and sweet potatoes to support digestion.
Try rice pudding made with plant-based milks and minimal sweeteners.
Food items to avoid during diarrhea include high-sugar foods like candies and fruit juices, caffeine, fatty or spicy dishes, dairy products containing lactose, and high-fiber foods that may irritate the gut.
Role of Probiotics
Probiotics can be beneficial in managing certain types of diarrhea, such as traveler’s diarrhea or antibiotic-associated diarrhea. They help restore healthy gut bacteria and can be taken in capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid form. Consulting a healthcare provider before starting probiotics is recommended, especially for infants and older adults, to avoid dehydration risks.
If diarrhea persists beyond three days despite proper hydration and diet, seeking medical advice is crucial. Over-the-counter medicines should be used cautiously and under medical supervision to ensure proper treatment. Overall, selecting the right foods and prompt medical care are key to recovery from diarrhea.