Key Questions About Mold: What You Need to Know
This article provides essential insights into mold, including health effects, common growth areas, testing methods, and professional removal options. It emphasizes the importance of early detection and professional remediation for extensive infestations to ensure safety and property preservation.
Sponsored
Understanding Mold: Common Questions Answered
Mold is a type of fungus that exists both indoors and outdoors. There are thousands of mold varieties, including common indoor types like Penicillium, Aspergillus, Cladosporium, and Alternaria. The CDC advises against routine mold sampling or trying to identify species without professional help. Mold gradually damages building materials and can impact health, making awareness essential. Recognizing where mold thrives and how to handle it can prevent property damage and health issues.
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about mold:
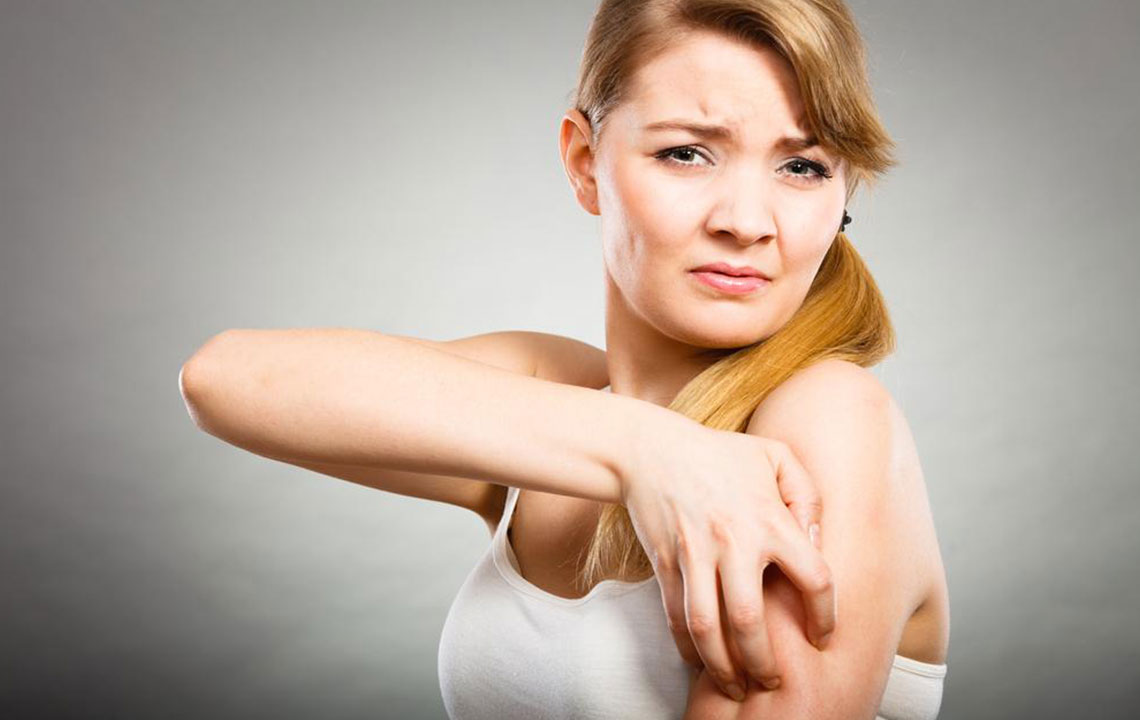
How does mold impact health?
While not everyone is affected, some individuals, especially those sensitive to mold, may experience symptoms like wheezing, nasal congestion, itchy skin, or irritated eyes. Allergic individuals or those with asthma often face stronger reactions. Workers exposed regularly to mold, especially in occupational settings, can develop severe symptoms including fever and breathing difficulties. Those with weakened immune systems, such as cancer patients or transplant recipients, are at higher risk of mold infections. Additionally, prolonged exposure to damp environments can lead to asthma.
What areas are most susceptible to mold growth?
Mold can develop anywhere moisture exists. Common spots include wet floors, leaking roofs, plumbing leaks, or flood-affected areas. Building materials like drywall, carpets, plywood, and padding are vulnerable if damp. Often, mold problems are seasonal and linked to poor ventilation or airtight spaces that trap humidity.
What mold testing methods are available?
The EPA generally does not recommend testing but acknowledges several methods:
Air sampling: Detects airborne mold spores, revealing hidden mold presence.
Surface sampling: Measures mold spores on surfaces or dust deposits, collected via tape or swabs.
Swab testing: Involves collecting samples from affected areas for lab analysis.
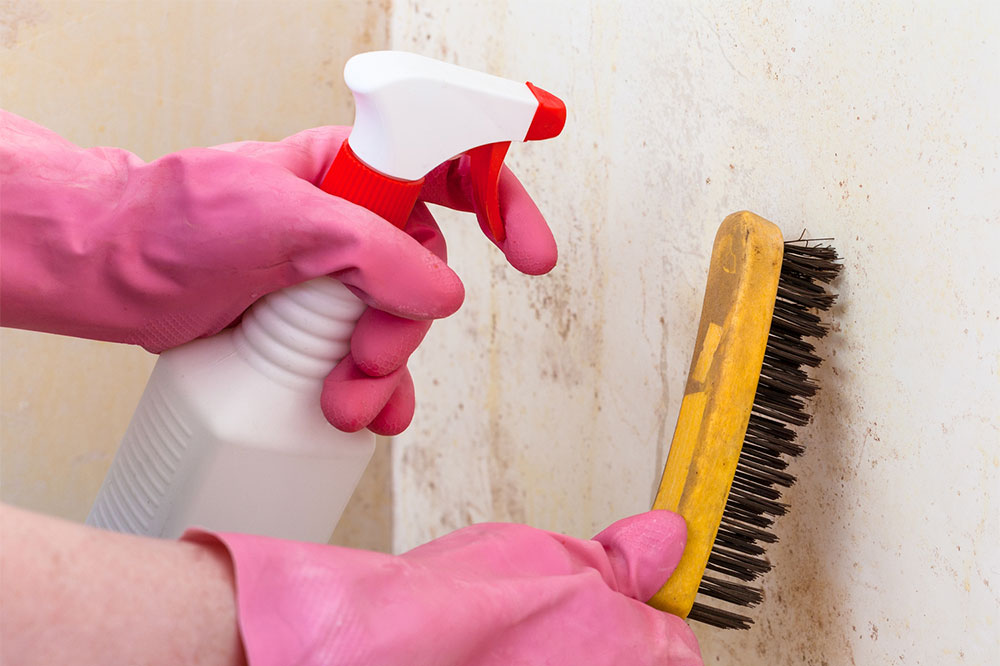
How do professionals remove black mold?
Removing black mold depends on the extent of growth. While some DIY removal is possible, large infestations require professional intervention. Options include:
Mold remediation: Best for extensive mold exceeding 10 square feet or involving water damage.
Contractor services: Hire experienced mold removal specialists for thorough cleaning.
Building cleanup experts: Essential when mold results from sewage or contaminated water, ensuring safe removal and remediation.






