Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy
Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy (FECD) is a progressive eye disease impacting vision. This guide explores non-surgical options like artificial tears and hypertonic saline, as well as surgical procedures such as endothelial keratoplasty and full corneal transplants. Emerging research on advanced surgical techniques and regenerative therapies promises future improvements. Early detection and personalized treatment are essential for managing FECD effectively, preserving vision and enhancing quality of life.
Sponsored

Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy (FECD) is a progressively worsening eye disorder impacting the cornea, often resulting in visual decline. It mainly affects the endothelial cells responsible for keeping the cornea clear by controlling fluid balance. Over time, cell degeneration causes corneal swelling, cloudiness, and vision loss. This article explores available management approaches for FECD, providing insights into both non-invasive and surgical treatments aimed at preserving eyesight.
Understanding FECD
Typically appearing in people over 50, FECD begins with early endothelial cell deterioration, eventually leading to corneal edema and impaired vision.
Notable symptoms include:
– Blurred or hazy vision, especially in the morning
– Halos and glare around lights
– Eye discomfort or soreness
– Increased light sensitivity
Early detection and timely intervention are vital to slow disease progression and maintain quality of life.
Non-Invasive Management Methods
While no cure exists for FECD, various conservative treatments can ease symptoms and improve visual clarity.
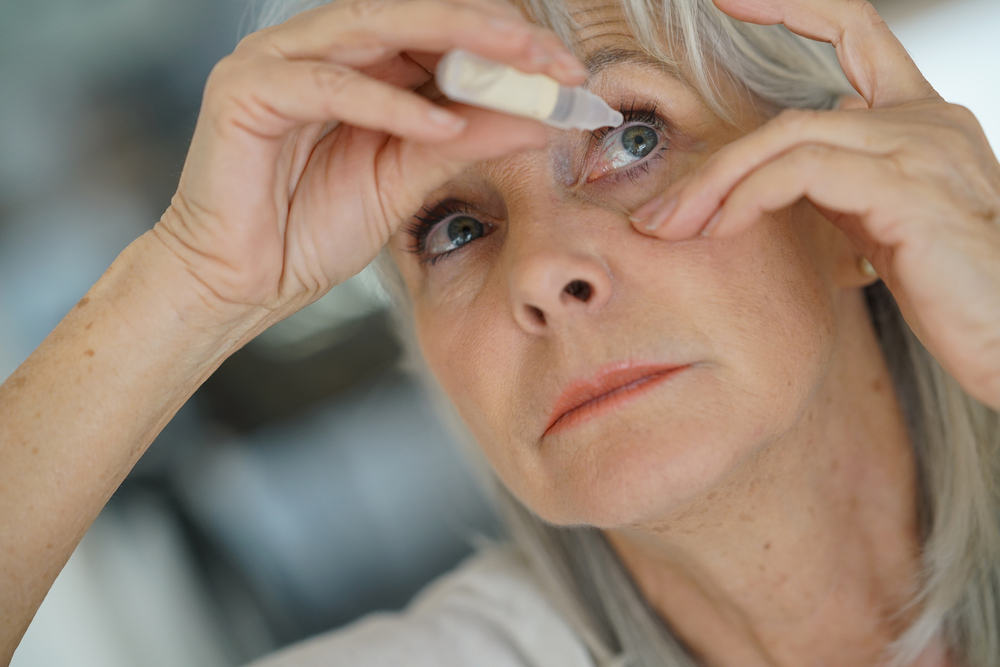
1. Artificial Tears and Lubricants
Over-the-counter artificial tears help keep the cornea moist, reducing dryness-related discomfort. Though they do not address the root cause, they provide temporary relief.
2. Hypertonic Saline Solutions
5% hypertonic saline drops or ointments help draw excess fluid out of the cornea, decreasing swelling and enhancing sharpness of vision. Usually used in the mornings when swelling peaks.
3. Home Dehydration Technique
A simple remedy involves using a warm, cool-setting hairdryer at arm’s length directed towards the eyes for a few minutes daily, aiding in corneal dehydration and visual improvement throughout the day.
Surgical Interventions
As FECD advances, conservative treatments might become insufficient, requiring surgical procedures. Several surgical options exist, from minimally invasive procedures to full-thickness corneal transplants.
1. Endothelial Keratoplasty (EK)
This partial corneal transplant replaces damaged endothelial cells with donor tissue. Types include:
– DSEK: Transplants the Descemet membrane and endothelium.
– DMEK: Transplants only the Descemet membrane and endothelium, allowing faster recovery and sharper vision.
2. Full-Thickness Transplantation
Penetrating Keratoplasty involves replacing the entire cornea. It’s used for severe scarring, but has longer recovery and higher complication risks.
3. Managing Graft Rejection
Monitoring and early treatment of rejection signs like redness, pain, light sensitivity, or vision decline are crucial for graft survival, relying on consistent medication use and follow-up.
Innovative Treatments and Ongoing Research
New developments aim to improve management:
– Advanced surgical tools like femtosecond laser enhance transplant precision.
– Pharmacological research seeks drugs to support endothelial cell health, potentially delaying surgery.
– Gene therapy and regenerative techniques may offer future cures by repairing defective cells at the genetic level.
While FECD presents challenges, evolving treatments and ongoing research offer renewed hope. Early diagnosis, tailored therapies, and continuous scientific advances are key to better outcomes and preserving vision.
Patients should consult eye care specialists promptly to determine the best course of action. Staying informed and proactive can significantly improve disease management and life quality.