Understanding Ear Infections in Infants: A Complete Guide
This comprehensive guide explains the prevalence, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ear infections in infants. It highlights when to seek medical attention and discusses the role of ear tubes for persistent cases. Useful for parents seeking to understand and manage their child's ear health effectively.
Sponsored

Prevalence of Ear Infections in Young Children
Ear infections are a frequent health concern among young children. By age three, more than 80% of kids have experienced at least one ear infection, making it one of the most common pediatric ailments.
Causes of Ear Infections in Children
When children suffer from upper respiratory infections, fluid can build up behind the eardrum. Typically, this fluid gets infected a few weeks after the initial illness. In infants, the Eustachian tube is shorter, which makes fluid buildup and infections more common.
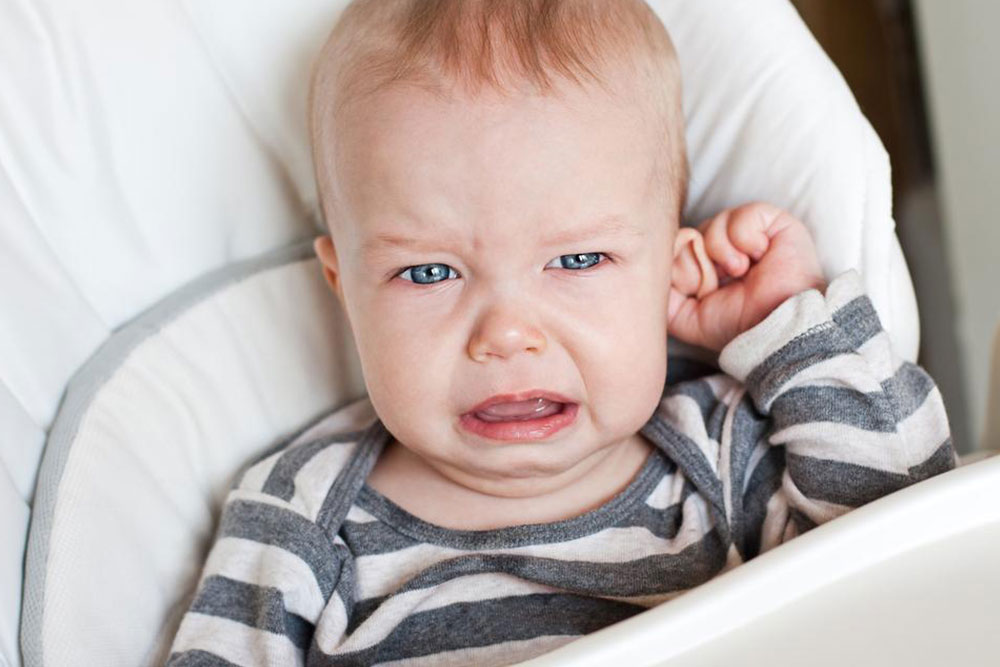
Recognizing Symptoms of Ear Infections
If your child shows any of these signs, consult an ENT specialist:
Increased irritability and crying
Pulling or tugging at the ear
Fever accompanying other symptoms
Difficulty sleeping
Recovery Time for Ear Infections
Most ear infections resolve within 36 to 48 hours. However, bacterial resistance to antibiotics may cause some infections to persist longer.
Viral infections and mild bacterial cases often heal without antibiotics. Fluid behind the eardrum may take from one to three months to drain completely.
Persistent Ear Fluid or Infections Over Three Months
If symptoms continue beyond three months, it's crucial to check for hearing loss. The ENT doctor might suggest inserting ear tubes (tympanostomy tubes), which are placed under anesthesia and typically stay in the ear for about a year before falling out naturally.