Risks Associated with Excessive Smartphone Usage
Excessive smartphone use can lead to various health issues, including musculoskeletal pain, eye strain, digital motion sickness, and increased risk of accidents. Limiting screen time and adopting ergonomic habits are essential to mitigate these risks while enjoying the convenience of modern mobile technology.
Sponsored

Risks Linked to Excessive Use of Mobile Devices
Smartphones are now essential tools for modern life, helping us with navigation, communication, shopping, and entertainment. Nonetheless, excessive use can pose significant health risks.
Many activities require a smartphone, making it nearly impossible to avoid overuse. Just a few years ago, such services were accessible without smartphones, but now they're integral to daily routines.
Despite their usefulness, smartphones can cause health issues if used for prolonged periods. Scientific research highlights several concerns associated with chronic usage.
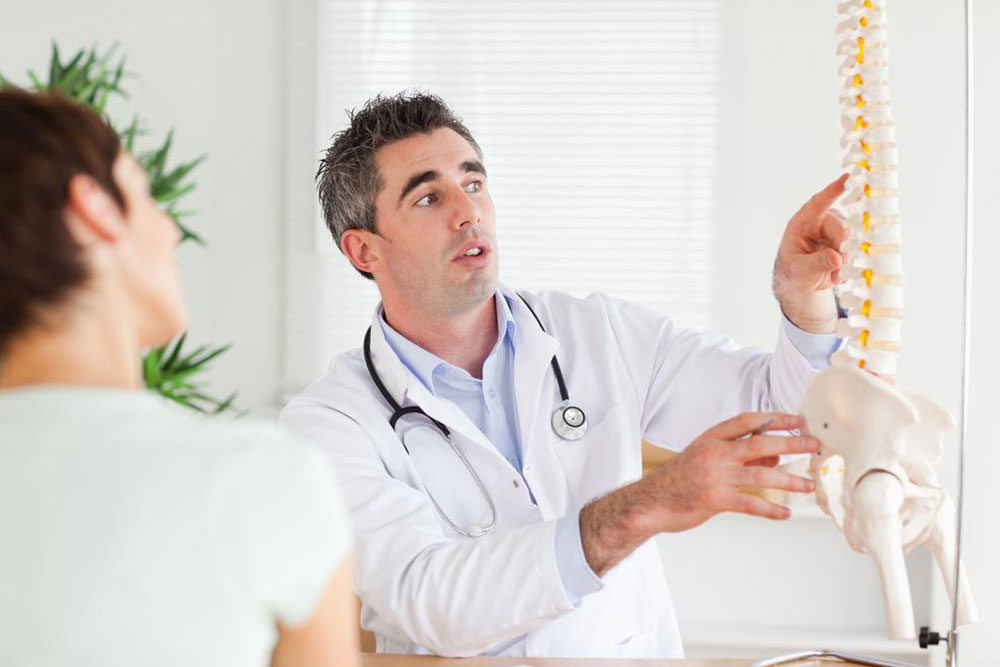
Extended smartphone use can lead to pain in the back, neck, or hands, often due to strain on tendons and muscles. This may result in conditions like visual display terminal syndrome.
Research indicates a direct link between usage duration and discomfort in the affected tissues.
To mitigate this, reducing screen time is advisable. Incorporating stretching exercises can also help prevent soreness.
Headaches, fatigue, and visual discomfort
Overusing smartphones may cause headaches, tiredness, and eye strain, including dryness and discomfort. These symptoms are linked to continuous, extended screen exposure and can be alleviated by limiting usage periods.
Dangers for drivers
Using a smartphone while driving significantly increases the risk of accidents. Data from 2013 indicates around 27% of road crashes involved mobile device use, emphasizing the dangers of distracted driving.
Development of texting-induced muscle issues
Constant texting can cause 'text claw', resulting in cramping and soreness in fingers, wrists, and forearms. Using speech-to-text features available on many smartphones can help reduce this strain.
Digital motion sickness
This condition, also known as cybersickness, occurs from rapid scrolling or viewing action-rich content for long durations, leading to nausea and dizziness.
Phantom vibrations phenomenon
Studies confirm that users may sometimes feel their phone vibrate or ring when it isn't. College students are particularly vulnerable to experiencing this phantom sensation, which can happen even with phones turned off.
Food cravings triggered by digital content
Images and videos of food shared on social media often stimulate cravings, potentially leading to overeating and health issues such as obesity and diabetes.
In summary, moderation is key. Enjoy the benefits of smartphones responsibly to ensure safety and well-being.