Recognizing Common Signs and Symptoms of Insect Bites
Learn to identify common insect bite signs and symptoms, including reactions to spider and tick bites, to ensure prompt treatment and prevent complications. Early recognition of symptoms like pain, rashes, and systemic reactions is essential for effective care.
Sponsored
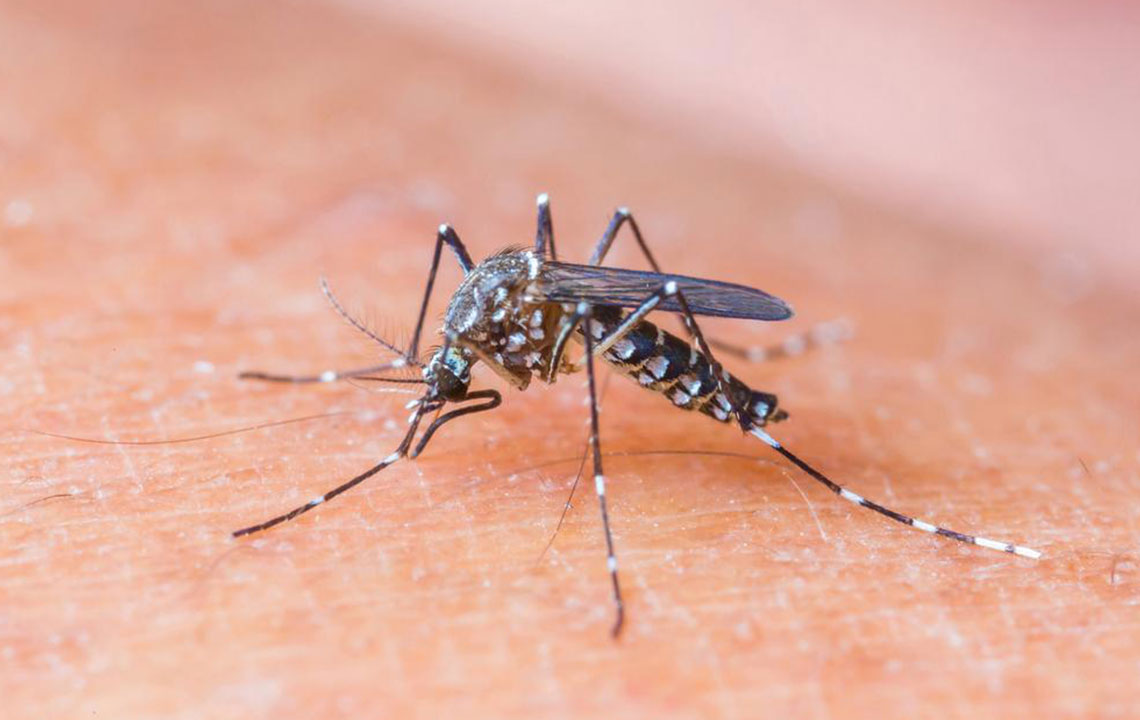

Detecting insect bites early is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. Understanding the typical signs and symptoms associated with different insect bites can help reduce discomfort and identify serious reactions promptly.
Here are some frequent indicators that may appear following an insect bite and what you should look out for:
Brown Recluse Spider Bites
Spotting brown recluse spider bites can be challenging since they often go unnoticed. These bites typically cause a sharp sting and intense pain, with symptoms emerging within four to eight hours after being bitten.
Visible signs include blisters, with skin potentially turning purple or blue. Additional symptoms may encompass sweating, itching, seizures, nausea, fever, chills, and, in severe cases, kidney issues or coma.
Tick Bites
Ticks can transmit Lyme disease, which often presents with circular skin rashes that may persist for a month. Failing to recognize such bites can lead to symptoms like headaches, muscle and joint pain, irregular heartbeat, and immune system dysfunction. Some tick bites may also carry Rocky Mountain spotted fever, resulting in widespread rashes over time.
Other Common Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing various symptoms helps ensure timely and correct treatment for insect bites.
Poisonous bites often cause intense pain near the bite site. Other symptoms may include muscle spasms, abdominal pain, fever, chills, breathing trouble, difficulty swallowing, headaches, dizziness, convulsions, stomach cramps, sudden blackouts, coma, wheezing, numbness, and rapid inflammation.
If symptoms are severe or appear suddenly, consult your healthcare provider immediately and consider using prescribed medications or auto-injectors under medical guidance.