Essential Insights into Botox: Uses, Risks, and Benefits
Discover essential information about Botox, including its medical and cosmetic applications, how it works, potential side effects, and safety considerations. Learn how Botox treatments can reduce wrinkles and treat medical conditions effectively when administered properly.
Sponsored
What You Should Know About Botox
Botulinum toxin, commonly known as Botox, is a powerful protein produced by the bacteria Clostridium botulinum. While it can be toxic in high doses, when used properly, Botox offers medical and cosmetic advantages. It works by blocking nerve signals to muscles, leading to temporary paralysis, which helps reduce wrinkles or treat various medical conditions. Found naturally in certain bacteria, Botox has been embraced worldwide for both aesthetic and therapeutic purposes.
Below are essential facts about Botox to consider:
Each year, over 5 million non-surgical Botox treatments are performed across the country.
Medical uses include alleviating excessive sweating, migraines, muscle spasms, and bladder issues.
An overdose, known as Botulism, can be life-threatening, causing respiratory failure.
The typical cost for a Botox session ranges from $350 to $500, depending on procedure complexity and provider.
How Botox Works
Injected in very small amounts, Botox blocks the release of acetylcholine, a chemical responsible for muscle contraction. By preventing nerve signals from reaching muscles, it induces temporary paralysis, reducing stiffness and unwanted movements.
Injections are made at nerve-muscle junctions. When Botox inhibits acetylcholine release, muscles relax, smoothing out wrinkles or alleviating spasticity.
Common Medical Applications of Botox
The FDA approves Botox for various treatments, including:
Relief from eyelid spasms (blepharospasm).
Beyond that, it treats severe neck and shoulder muscle contractions (cervical dystonia).
Chronic migraine headache prevention.
Managing urinary overactivity and incontinence caused by an overactive bladder.
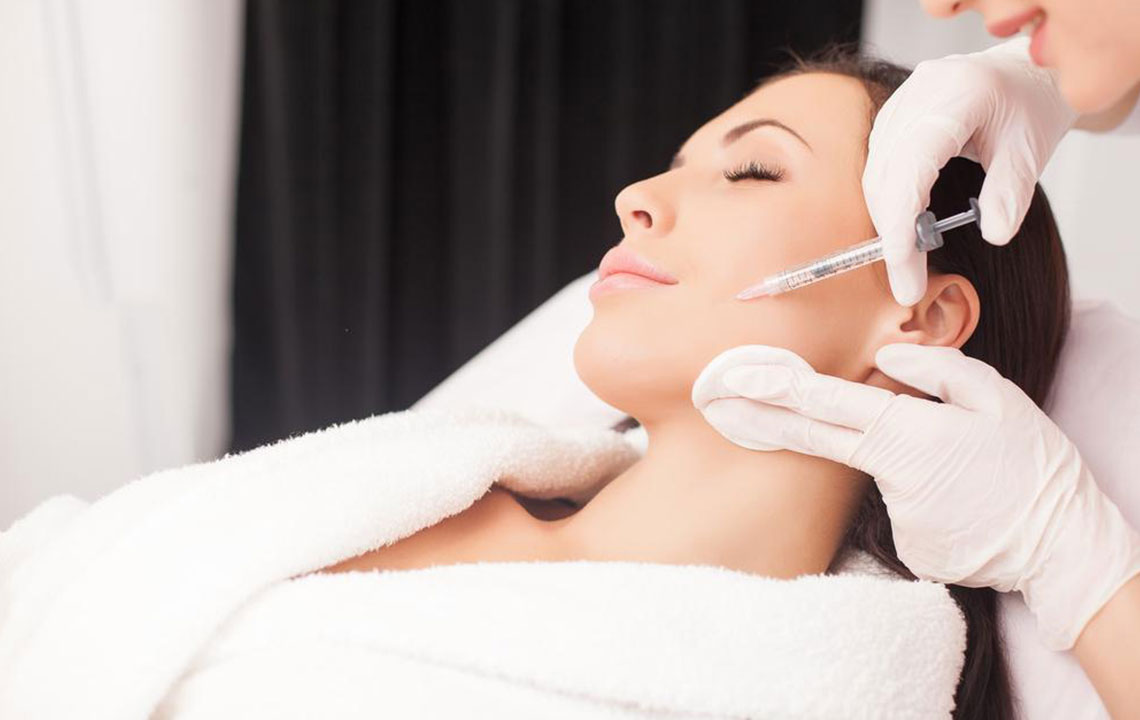
Procedure and Precautions
Botox is diluted with saline and injected directly into targeted neuromuscular areas. Effects typically appear within 24-72 hours, with some cases taking up to five days for full results.
Potential Side Effects
Women who are pregnant or breastfeeding should avoid Botox due to potential risks. Other side effects include:
Dry mouth, fatigue, neck weakness, and blurred vision.
Mild pain or swelling at injection sites.
Skin redness (erythema), which may lead to skin issues.
Temporary nausea and muscle weakness near treated areas.
Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
Nerve-related issues like brachial plexopathy affecting shoulder and neck nerves.