Guide to Identifying Symptoms of Bronchitis and Pneumonia Effectively
This comprehensive guide explains how to recognize bronchitis and pneumonia symptoms, emphasizing differences between acute and chronic forms. It covers causes, common signs, preventive measures, and treatments, helping individuals identify symptoms early and seek proper medical care to ensure effective recovery.
Sponsored
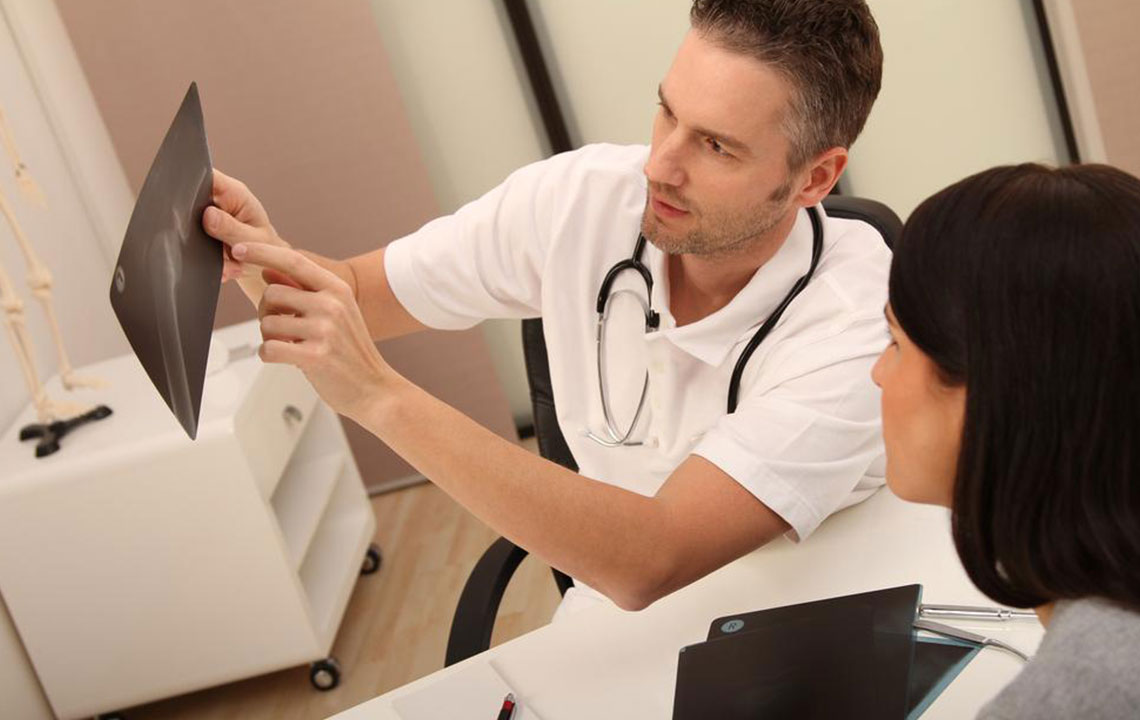

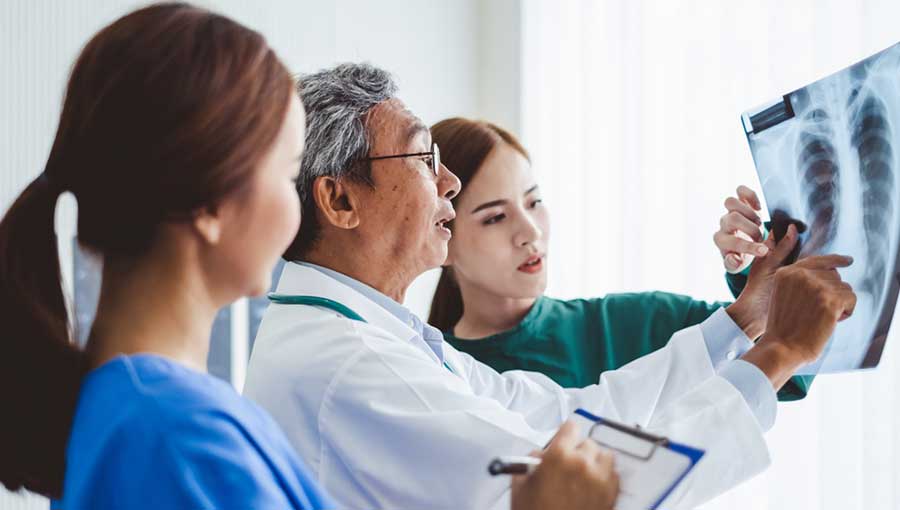
Bronchitis involves an infection of the bronchi—the airways leading to the lungs. Pneumonia affects lung tissue itself. While both can cause coughing and often follow colds or flu, their differences are significant. Only healthcare professionals can provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Common symptoms include persistent cough with mucus, shortness of breath, mild fever, wheezing, chest discomfort, and fatigue. There are two main types: acute, which is short-term, and chronic, which persists over time.
Pneumonia becomes more serious when the infection penetrates deeper into the lungs, filling the air sacs with fluid, especially affecting smokers, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals. It mainly results from bacterial infections and exposure to lung irritants like tobacco smoke, dust, and pollutants.
Signs of Acute Bronchitis or Pneumonia
It is a short-term illness often following a viral or cold infection, prevalent among many. Symptoms include a lasting cough of about three weeks, mild fever, chest tightness, wheezing, body aches, fatigue, and nasal congestion. Transmission occurs via airborne droplets or contact. Prevention involves avoiding pollutants and smoking. Rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medicines like acetaminophen or NSAIDs alleviate symptoms.Chronic bronchitis or pneumonia symptoms
A persistent cough lasting three months or more annually for at least two years signifies chronic bronchitis. Common causes include smoking, with air pollution and genetics contributing to lesser extents. Management involves quitting smoking, vaccinations, inhalers, steroids, and sometimes oxygen therapy or surgery.Common Symptoms
Breathing difficulties are typical, including chest tightness, productive cough (mucus: clear to green), shortness of breath, wheezing, fatigue, low-grade fever, sore throat, headaches, and exhaustion. Persistent symptoms warrant medical consultation.Treatment Strategies
Rest, hydration, warm moist air inhalation, and cough suppressants help relieve symptoms. For ongoing issues, doctors may prescribe inhalers, anti-inflammatory medications, steroids, oxygen therapy, or antibiotics (for bacterial infections). Lifestyle changes like quitting smoking and breathing exercises strengthen recovery. Seek medical advice if symptoms last beyond a few weeks, as prolonged cough suggests complications.