Effective Strategies to Alleviate Back Muscle Discomfort
Discover effective methods to relieve back muscle pain, including medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Learn how to prevent discomfort through proper ergonomics, weight management, and regular exercise. Consult healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans and avoid self-medication. Maintaining an active lifestyle is essential for long-term back health and pain prevention. Protect your back by understanding causes, treatment options, and preventive strategies to stay comfortable and mobile every day.
Sponsored

Many individuals experience sudden and severe pain in their back muscles, a common issue affecting various age groups. This discomfort often results from prolonged sitting due to modern work habits, heavy lifting, accidents, or other factors. Back muscle pain can significantly impact daily life and needs appropriate management. Understanding the causes and treatment options is essential for relief and prevention.
Numerous medical approaches are available to address back pain. The right treatment depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Here are some common methods used to relieve back muscle discomfort:
Over-the-counter medications: NSAIDs like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) are effective for reducing inflammation and relieving acute or chronic back pain. Always consult a healthcare professional before use to ensure safe and appropriate application.
Muscle relaxants: These may be prescribed for severe muscle spasms, often in conjunction with other medications. They can cause drowsiness, so caution is advised when driving or operating machinery.
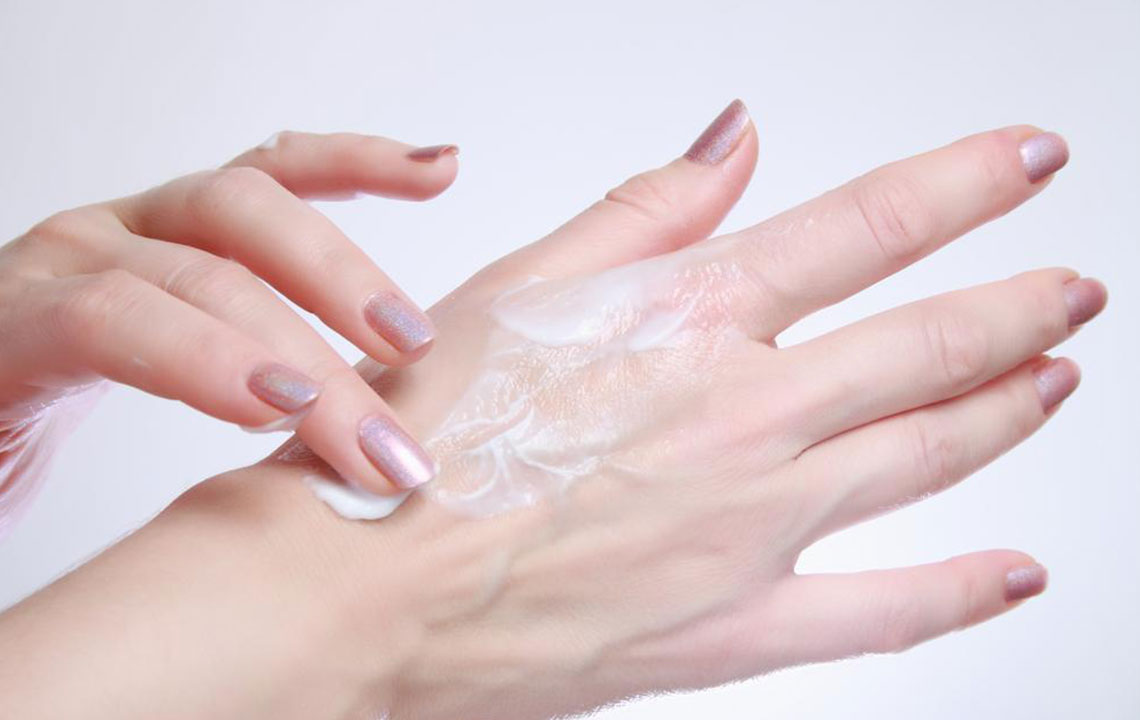
Topical treatments: Creams, balms, and ointments applied directly to the skin can provide quick, temporary relief by numbing affected muscles. Note that these address symptoms rather than root causes.
Prescription opioids: Drugs like Hydrocodone or Codeine might be used under strict medical supervision for severe pain. However, due to addiction risks, their long-term use is generally discouraged.
Antidepressants: Low-dose medications such as amitriptyline have been found effective for certain chronic back pain cases.
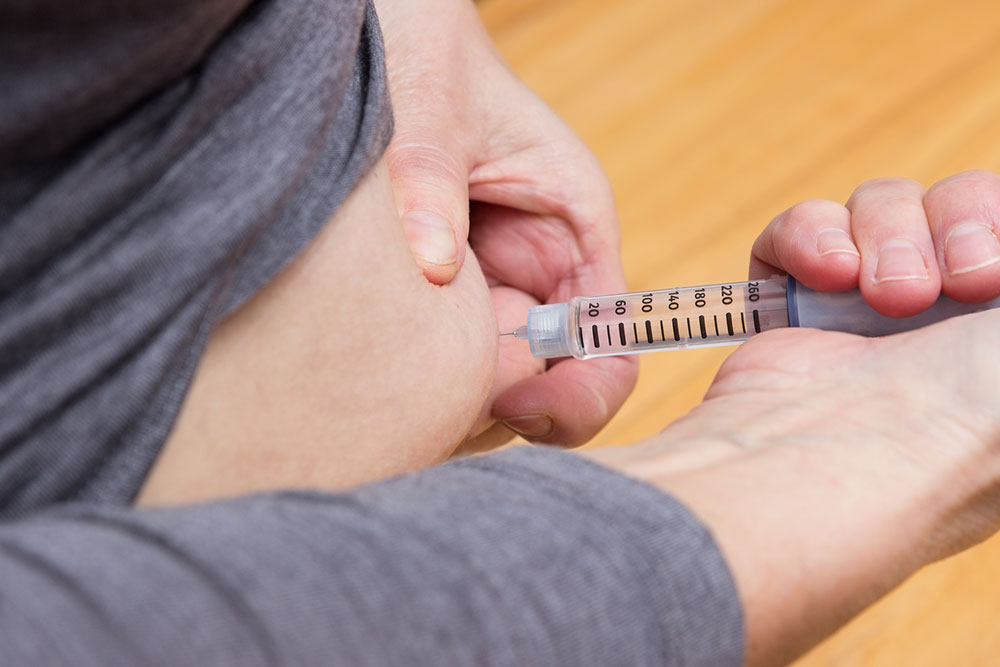
Injections: Cortisone injections can reduce inflammation and numb pain, especially if pain radiates down the legs. These are temporary solutions and typically part of a broader treatment plan.
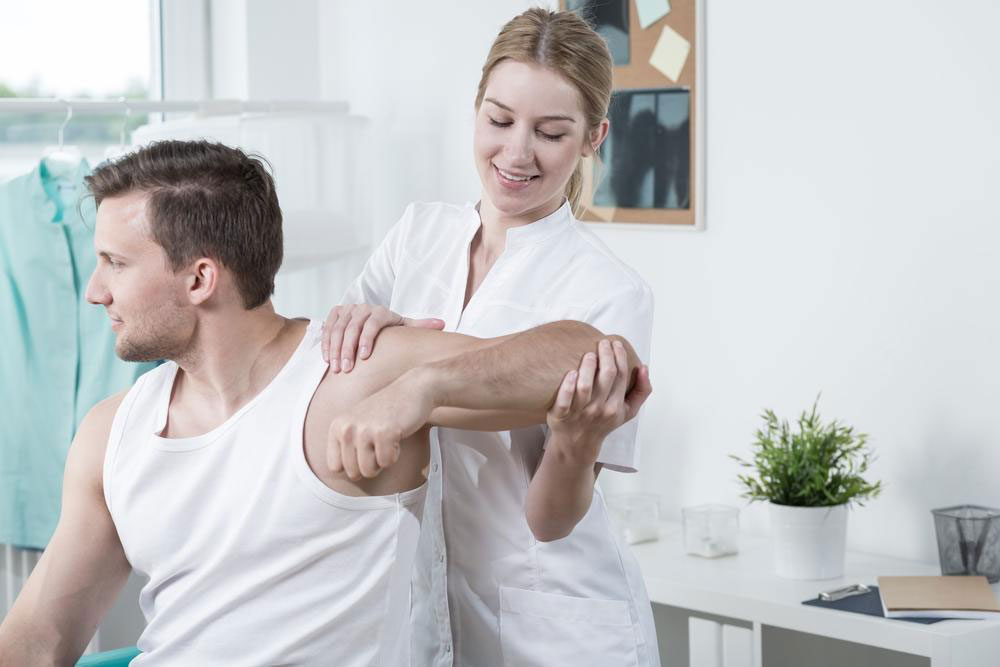
Physical therapy: Professionals may use ultrasound, heat therapy, electrical stimulation, and muscle-release techniques. They may also teach exercises to strengthen the back and prevent future issues.
Surgical intervention: Rarely, surgery becomes necessary for severe or persistent cases that do not respond to conservative treatments.
If persistent back pain occurs, seek medical advice promptly. Avoid self-medicating without guidance. Prevention primarily involves maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and practicing proper ergonomics. Regular exercise, such as brisk walking for 30 minutes daily, helps keep back muscles strong and reduces the risk of pain.
Overall awareness and proactive care play vital roles in avoiding back discomfort. An active lifestyle and weight management are key to maintaining back health. Stay vigilant, stay healthy, and enjoy pain-free living!