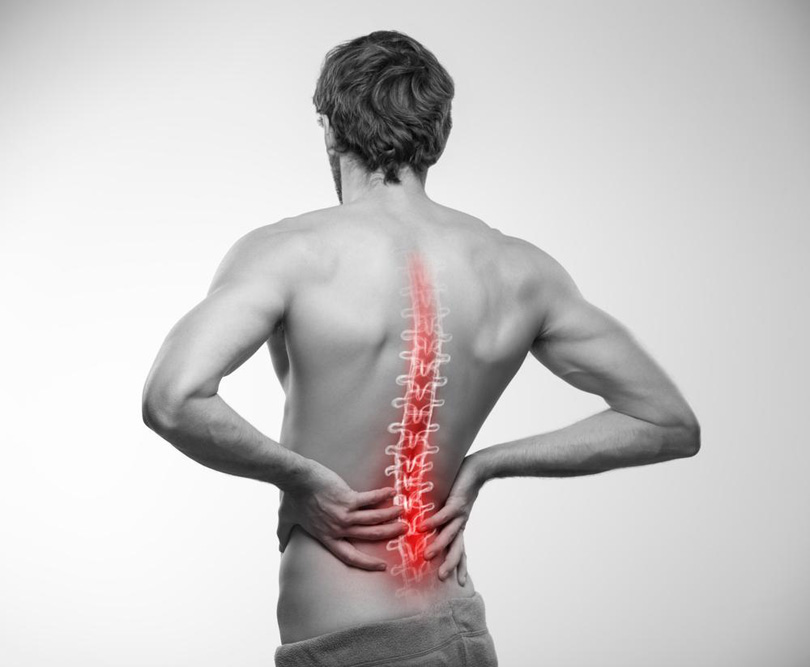
Distinguishing Between Back Discomfort and Kidney Pain
Learn how to distinguish between back pain and kidney discomfort by analyzing pain location, type, radiation, severity, and associated symptoms. This guide helps you identify the root cause to seek proper treatment effectively.
Sponsored

How to Differentiate Between Back Pain and Kidney Discomfort
The kidneys are situated beneath the rib cage near the back. When you experience pain in this region, it can be challenging to determine whether it stems from the back muscles or the kidneys. By examining the location, intensity, and nature of the pain, you can better identify the source. This guide offers insights into differentiating back pain from kidney discomfort effectively.
Location of Discomfort
Back pain typically occurs in the lower back or buttocks, but it can appear anywhere along the back.
Kidney pain is felt in the flank area, on either side of the spine between the lower ribs and hips. Often, it's unilateral but can be bilateral.
Nature of Discomfort
Understanding whether the pain is dull or sharp helps differentiate.
Muscle-related pain tends to be dull and persistent. Nerve irritation typically causes a sharp, burning sensation that may radiate down to the buttocks, legs, or feet.
Sharp, fluctuating pain may indicate kidney stones.
Infection-related discomfort usually manifests as a continuous dull ache that doesn't improve with movement or rest.
Pain Spread and Radiation
Muscle pain remains localized in the back; nerve pain may extend down to the legs.
Kidney pain may radiate toward the lower abdomen or inner thigh.
Intensity of Discomfort
Acute pain can last days to weeks, subacute from 6 weeks to 3 months, while chronic back pain persists beyond three months.
Kidney stones cause intense pain, whereas pain from infections is generally milder.
Additional Symptoms
Back issues may involve numbness, muscle spasms, or swelling in the affected area.
Kidney problems often present with nausea, vomiting, chills, fever, dark urine, painful urination, recent urinary tract infections, or blood in urine.
Seeking medical advice ensures accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment for your condition.