Effective Strategies to Regulate Blood Glucose Levels
Learn essential tips for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels with proper monitoring, diet, hydration, and exercise. This comprehensive guide emphasizes lifestyle choices to prevent complications and improve overall health for diabetics.
Sponsored

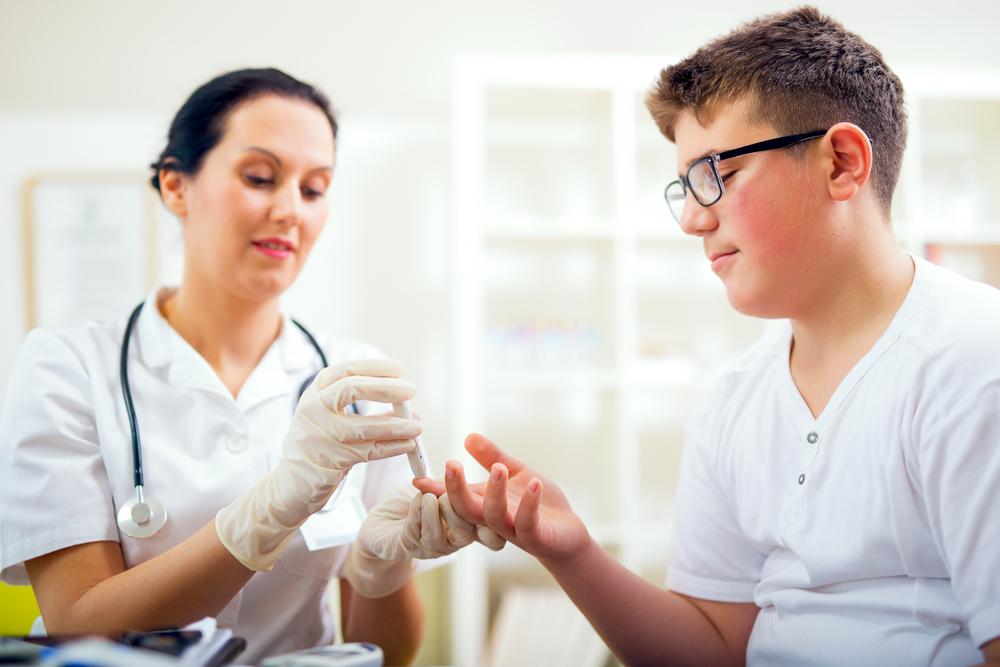
Managing blood sugar is essential for individuals with diabetes, as their levels tend to fluctuate unpredictably. Blood glucose varies throughout the day based on meal choices, physical activity, and overall health. Accurate monitoring helps maintain optimal levels. In the U.S., blood sugar is measured in mg/dl, with long-term control assessed via hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), expressed as a percentage.
Normal ranges for non-diabetics include:
Fasting blood sugar - below 100 mg/dl
Pre-meal - 70–99 mg/dl
Two hours after eating - under 140 mg/dl
HbA1c - less than 5.7%
Diabetes can be diagnosed if:
Two tests show blood glucose over 126 mg/dl
Random test exceeds 200 mg/dl
Oral test over 200 mg/dl
HbA1c at or above 6.5%
Consistent tracking of blood sugar levels, especially post-meal and activity, helps maintain balance. Keeping levels in check is vital to reduce risks like strokes and heart disease.
Factors affecting blood sugar include missed medication, infection, stress, high carbohydrate intake, and inactivity. Symptoms of imbalance include headaches, thirst, blurred vision, fatigue, weight changes, and anxiety.
To stabilize blood sugar, regularly test levels, consult healthcare providers, wear medical ID, and monitor diet. Hydration, exercise, and proper diet are key. Avoid dehydration by drinking water, choose suitable physical activity, and follow dietary advice from professionals. Managing type 1 or type 2 diabetes involves careful monitoring of ketones and hydration. Lifestyle adjustments and medical guidance are essential in controlling blood sugar and preventing complications. Consistent care and patience are crucial for effective diabetes management.