Effective Strategies to Alleviate Heel Discomfort
Learn effective methods to treat heel pain, including medication, physical therapy, orthotics, and surgical options. Early treatment helps reduce discomfort and prevent long-term issues. Recognize symptoms and seek medical advice if pain persists beyond a week or worsens. Preventive measures and appropriate care are key to restoring foot health and preventing chronic problems.
Sponsored
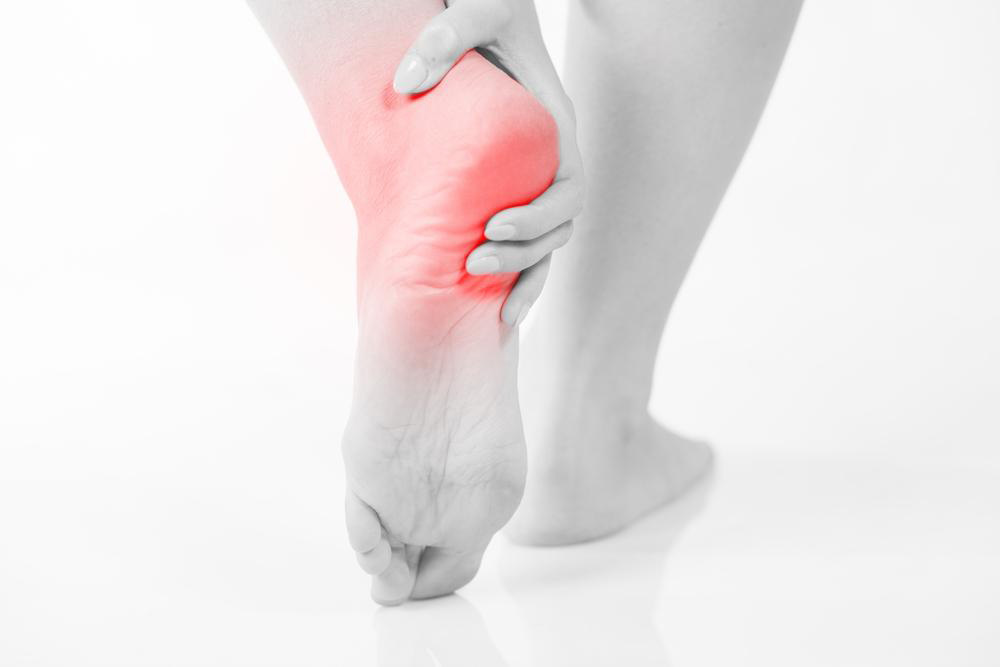
Strategies to Relieve Heel Discomfort
Heel discomfort is among the most common foot issues encountered. The pain typically occurs underneath the heel and is known as plantar fasciitis. Alternatively, pain behind the heel may indicate Achilles tendinitis, where the Achilles tendon connects to the heel bone. While the pain can sometimes be intense and impair mobility, it generally is not life-threatening. Mild cases often resolve spontaneously. Persistent or severe heel pain warrants prompt medical attention to prevent complications.
Heel pain often develops gradually without injury, possibly triggered by flat footwear or extended periods of inactivity. It frequently worsens after rest, especially upon waking or after prolonged sitting, a condition known as post-static dyskinesia. Severe symptoms accompanied by swelling, fever, or numbness should prompt medical consultation. Durations exceeding one week require professional evaluation to determine appropriate treatment.
To manage heel discomfort, several interventions can be effective:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - These medications help reduce pain, fever, and inflammation.
Corticosteroid injections - Used when NSAIDs are ineffective; administered directly to the irritated area, often with ultrasound guidance.
Physical therapy - Targeted exercises to stretch the plantar fascia and Achilles tendon, alongside strengthening lower leg muscles, to enhance foot stability.
Night splints - Worn during sleep to maintain the heel and tendon in a stretched position, promoting healing.
Orthotic devices - Custom insoles or supports used to correct foot alignment and provide cushioning during recovery.
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy - Focused sound waves stimulate tissue repair, suitable for chronic cases.
Surgical options - Considered only after all other treatments fail; involves detaching the plantar fascia, with potential risks to foot structure.