Health Risks Associated with Lupus: Common Complications
Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease impacting multiple organs, leading to joint pain, digestive issues, thyroid problems, and increased risk of blood clots and heart complications. Recognizing these symptoms early can help manage the risks associated with the condition and prevent serious health outcomes.
Sponsored

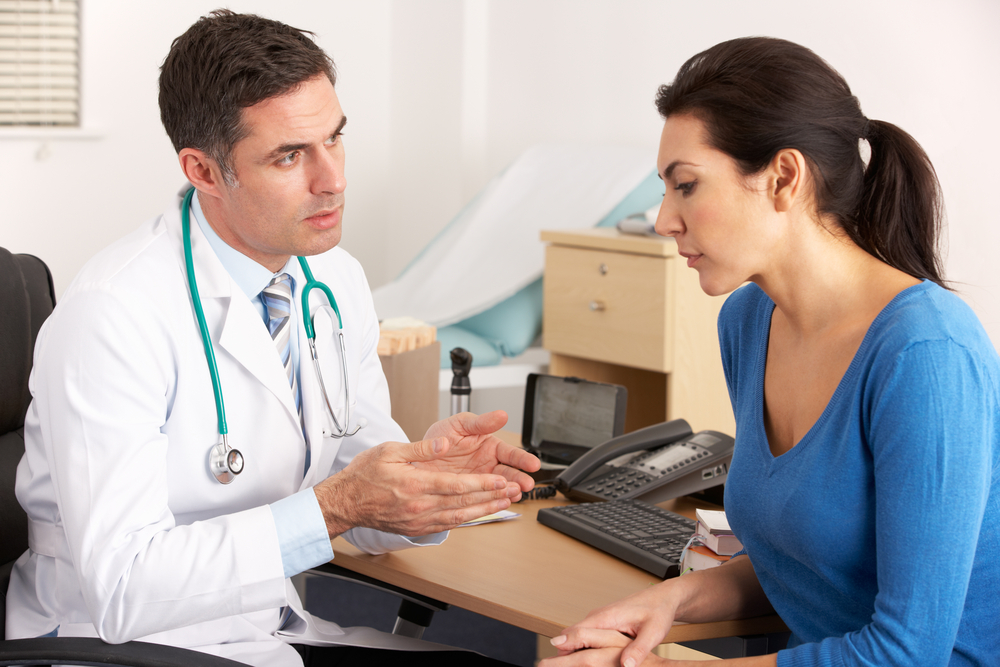
Health Risks Linked to Lupus
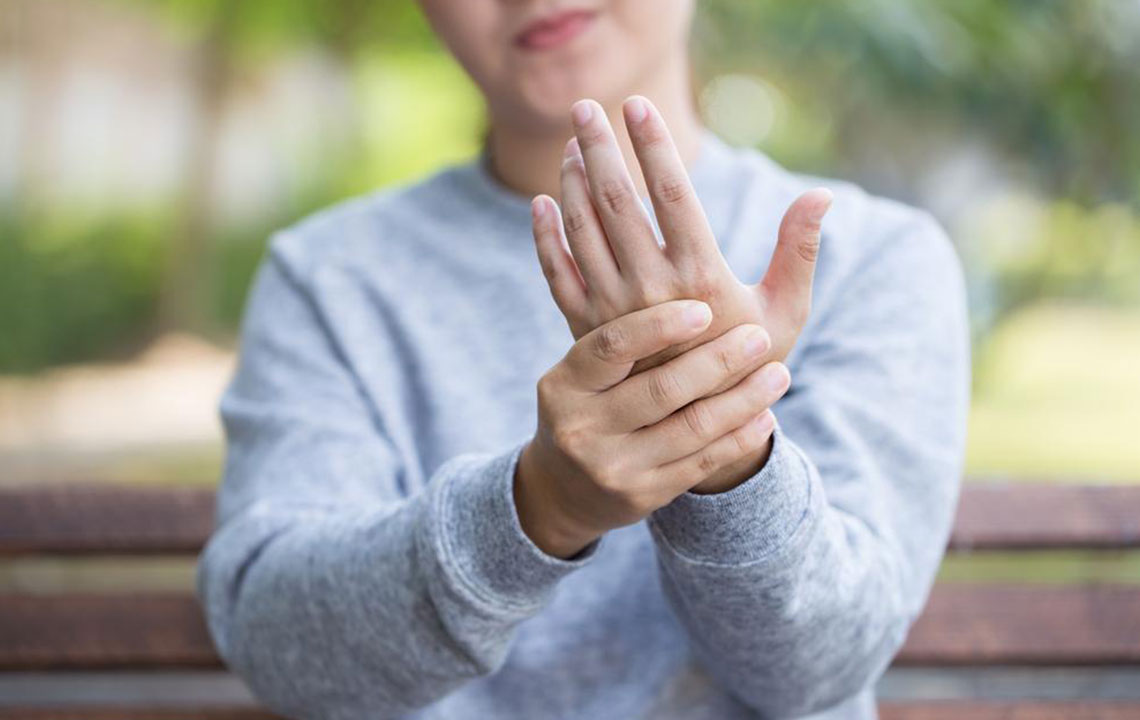
Lupus symptoms vary based on the organs affected. The small joints in the hands are frequently impacted, leading to pain, swelling, and morning stiffness that can be mistaken for minor issues. If OTC medications don't alleviate symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial to rule out other conditions such as arthritis. The digestive system is also prone to lupus-related symptoms like acid reflux and heartburn. Managing these involves antacids, smaller meals, and avoiding immediate rest after eating. Persistent gastric issues warrant medical evaluation to exclude other diseases.
Lupus can target vital organs such as the liver and pancreas, causing complications like protein leakage from the intestines, resulting in nutrient deficiencies and diarrhea, known as protein-losing atrophy. Patients may experience dry mouth, dry eyes, or vaginal dryness, often due to Sjogren’s syndrome, an autoimmune disorder affecting gland function.
The condition also increases the risk of autoimmune thyroid diseases, which affect metabolism and vital organ function. Hypothyroidism causes sluggishness and weight gain, while hyperthyroidism results in rapid heartbeat, weight loss, and excessive sweating. Before long, lupus can lead to serious cardiovascular problems such as pericarditis, which causes chest pain. Many patients develop antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), raising the risk of blood clots, miscarriages, and strokes. Clots can travel, leading to severe outcomes like heart attacks, strokes, or limb gangrene, potentially resulting in amputations.