The Significance of Managing Stable Blood Glucose Levels
Maintaining stable blood glucose levels is essential for health and disease prevention. Regular monitoring using glucose charts helps individuals, especially diabetics, manage their blood sugar effectively. Lifestyle choices like diet, exercise, and stress reduction play a significant role in keeping glucose within healthy ranges, thereby supporting overall well-being and reducing complication risks.
Sponsored
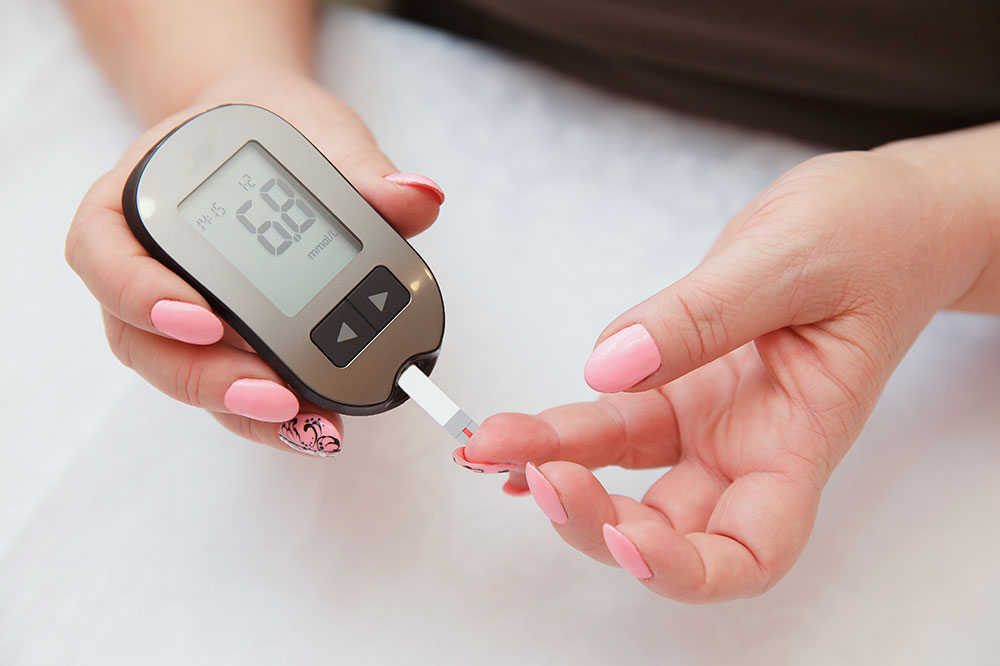

Monitoring blood glucose levels reflects the sugar concentration in a person's bloodstream at any given moment. This sugar fuels the body's cells with energy, sourced from our daily diet. The body meticulously regulates blood sugar to prevent levels from becoming dangerously high or low. Notably, blood sugar refers to glucose, distinct from the common table sugar we consume.
Throughout the day, blood glucose fluctuates—lowest in the early morning and rising after meals before stabilizing. Healthy fasting blood sugar should stay below 99 mg/dl, whereas diabetics often experience broader swings. Ideal pre-meal levels are under 130 mg/dl, and post-meal should stay below 180 mg/dl.
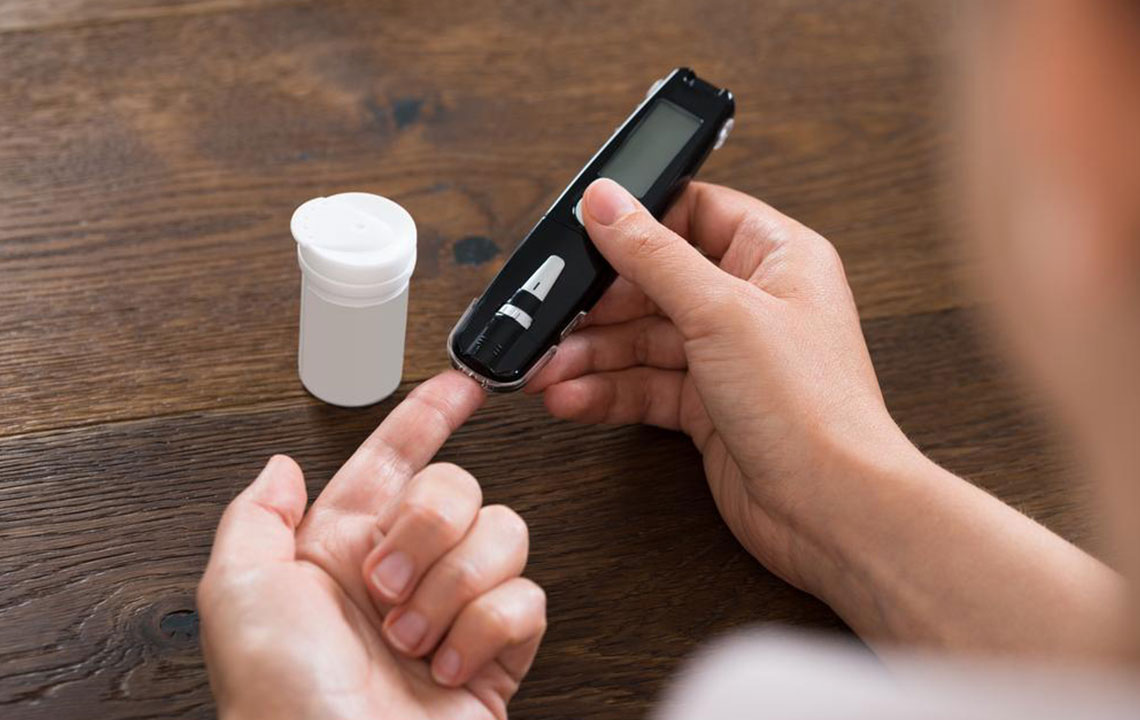
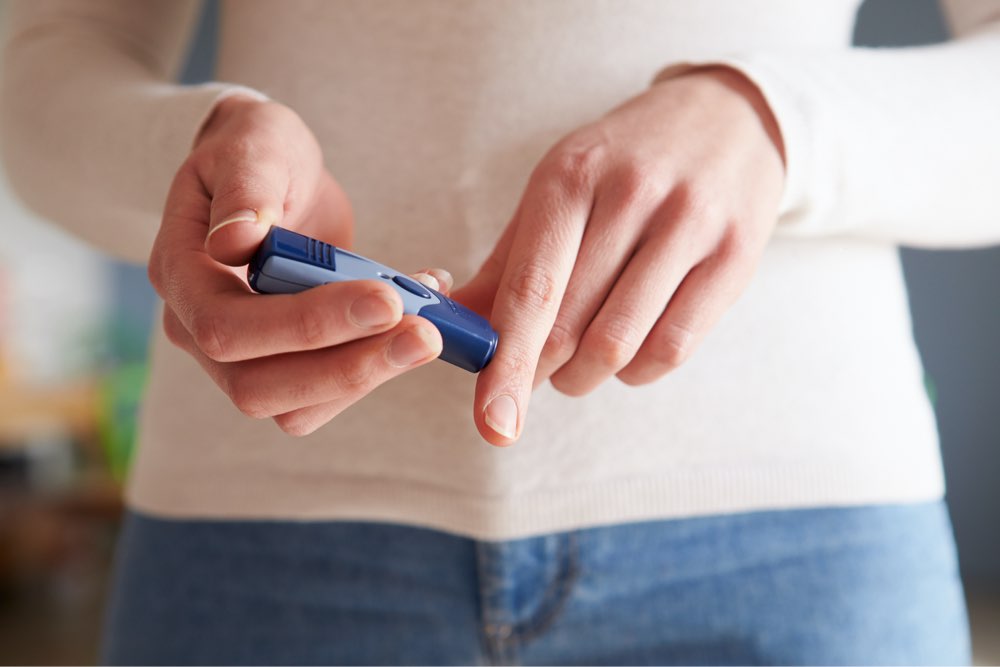
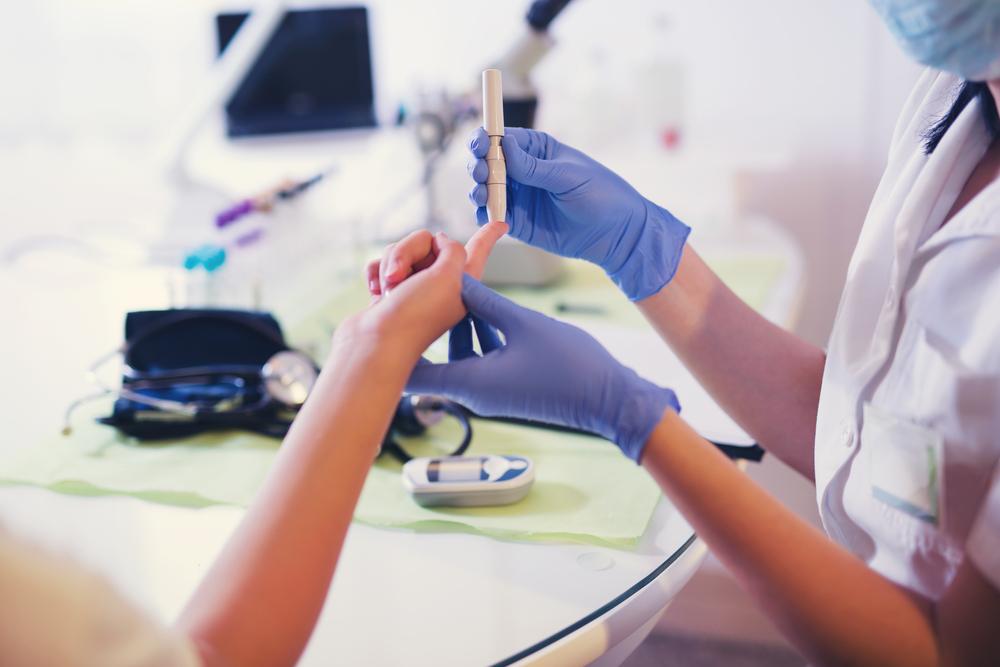
A blood sugar or glucose monitoring chart tracks these fluctuations, offering insights crucial for managing diabetes. Blood sugar is inherently dynamic, peaking after eating and dipping before meals. Regularly recording these numbers helps in maintaining health, particularly for those with or at risk of blood sugar issues.
Maintaining proper glucose levels is vital for overall health, impacting organs like kidneys, eyes, and the heart. Regular documentation helps detect harmful spikes or drops early. For diabetics, continuous monitoring prevents complications and promotes well-being.
Various devices can assist in recording blood sugar levels—consult your healthcare provider for proper use. Key measurements include fasting sugar levels and post-meal readings. Deviations from normal ranges indicate potential health concerns, emphasizing the importance of lifestyle factors such as balanced diet, sufficient sleep, and regular exercise like walking or jogging. Eliminating smoking and excessive alcohol, along with managing stress, further supports blood sugar control.