Essential Facts About Toenail Fungal Infections
Learn vital facts about toenail fungus, including its symptoms, risk factors, and prevention tips. Recognize how age and injury contribute to infection and find effective ways to prevent its spread in shared environments. Early treatment and proper care can manage this common condition effectively.
Sponsored
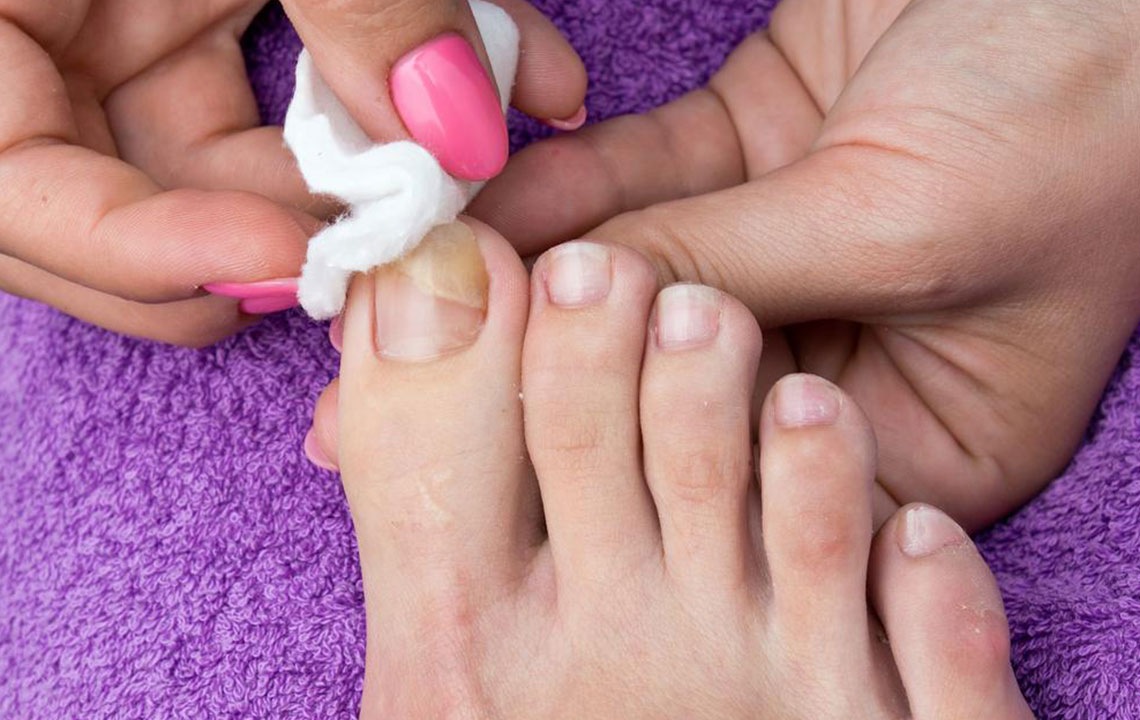
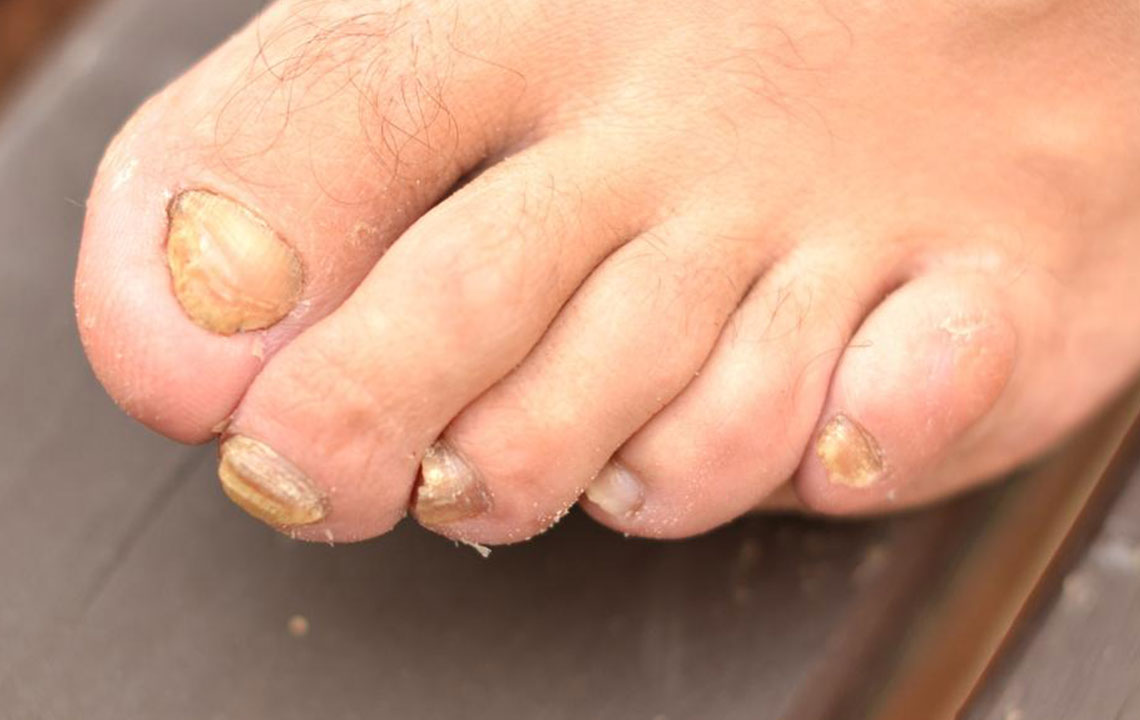
Toenail fungus is a widespread condition that causes nails to become brittle, thickened, and crumbly. While it's common and easily treatable by healthcare professionals, understanding key aspects of this infection is important. Chronic cases may persist for extended periods.
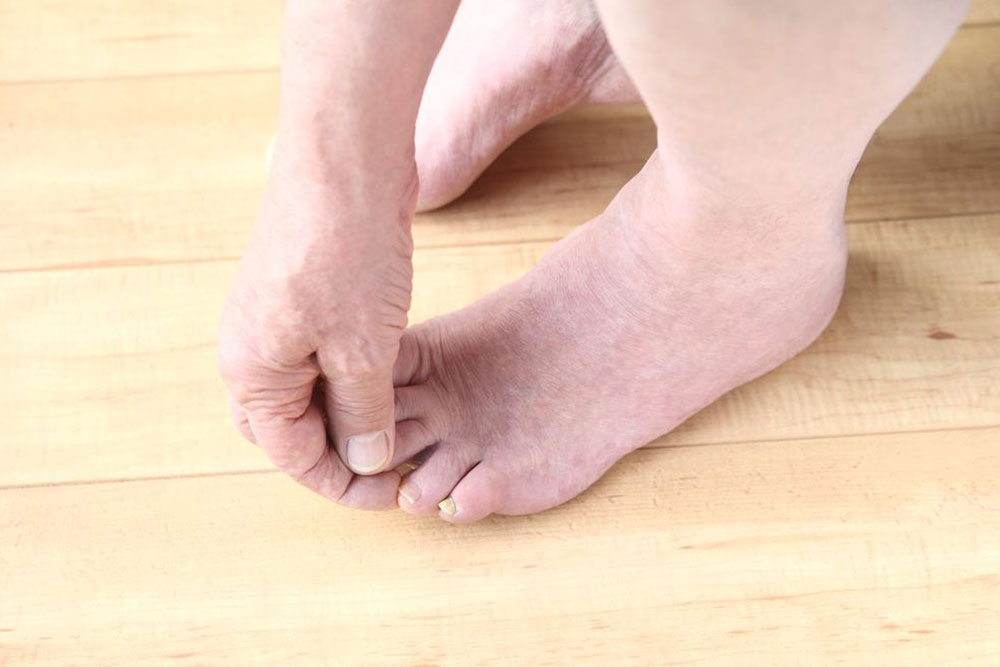
The infection remains localized: Contrary to some beliefs, toenail fungus tends to stay confined to the affected nail without spreading extensively. Even if the infection persists, it generally remains in the initial area.
However, if one toenail develops the infection, nearby nails may also be at risk. To prevent spread, wear clean socks after applying medication and proper treatment to the affected area.
Age influences susceptibility: While anyone can contract toenail fungus, older adults are at a higher risk. Research indicates that individuals over 60 are more prone to this condition. As age increases, special precautions should be taken to reduce the risk.
It is a contagious condition: Toenail fungus can transfer to others in close contact. Be cautious with shared spaces like locker rooms, swimming pools, or bathrooms, where the infection can spread through contact. Preventive measures are essential to avoid transmission.
Take safety measures: Protect your toes from injuries, as wounds can facilitate infection entry. Properly treat and clean any injuries to prevent fungal development.
Typical symptoms include nail discoloration, thickening, and brittleness. The infection usually causes minimal discomfort and doesn't produce unpleasant odors.