Enhancing Kidney Disease Management and Dialysis Support in the US
This article explores strategies to improve kidney disease management in the US, emphasizing the importance of dialysis as a life-sustaining treatment. It discusses government support, types of dialysis, costs, and ongoing efforts by organizations to enhance patient outcomes. With rising cases linked to common health issues like diabetes and hypertension, the article highlights the need for comprehensive care and continuous innovation in the field of nephrology.
Sponsored
Advancing Kidney Health and Dialysis Treatment
Kidney failure remains a pressing concern in today’s developed world, with over 666,000 cases reported in the US alone, highlighting the urgent need for effective management. While kidney transplantation is often the preferred treatment, challenges such as limited donors and surgical risks make dialysis the primary alternative. With a steady 8% annual increase in donors, many patients rely on dialysis to maintain survival.
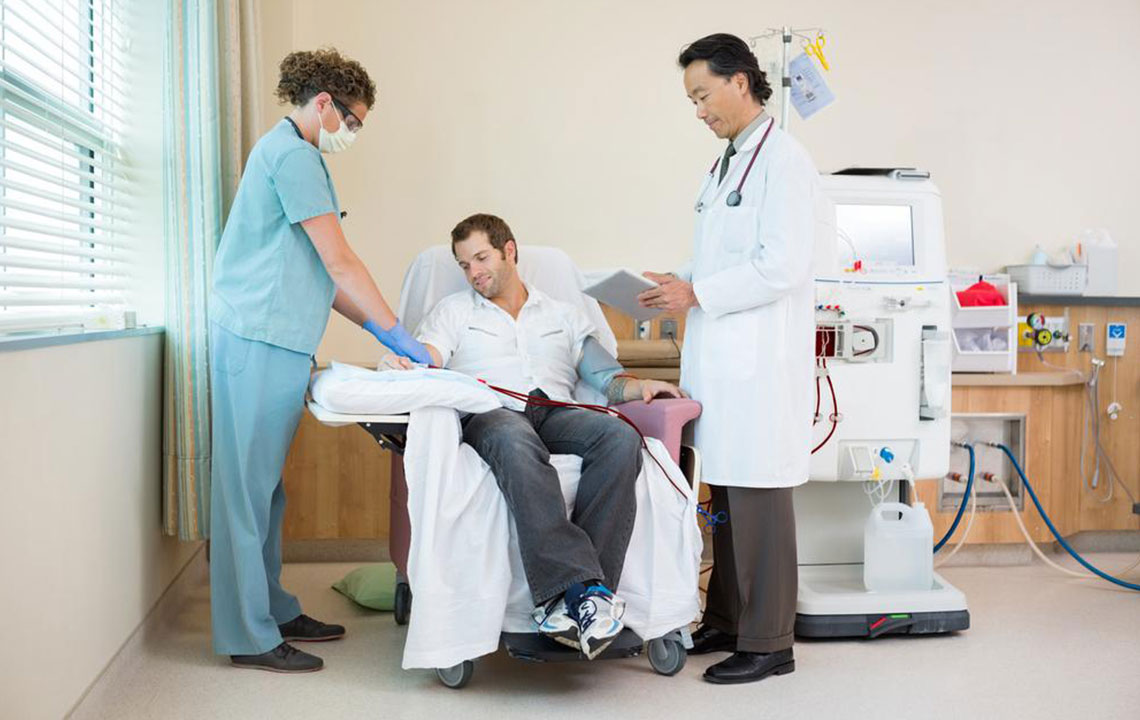
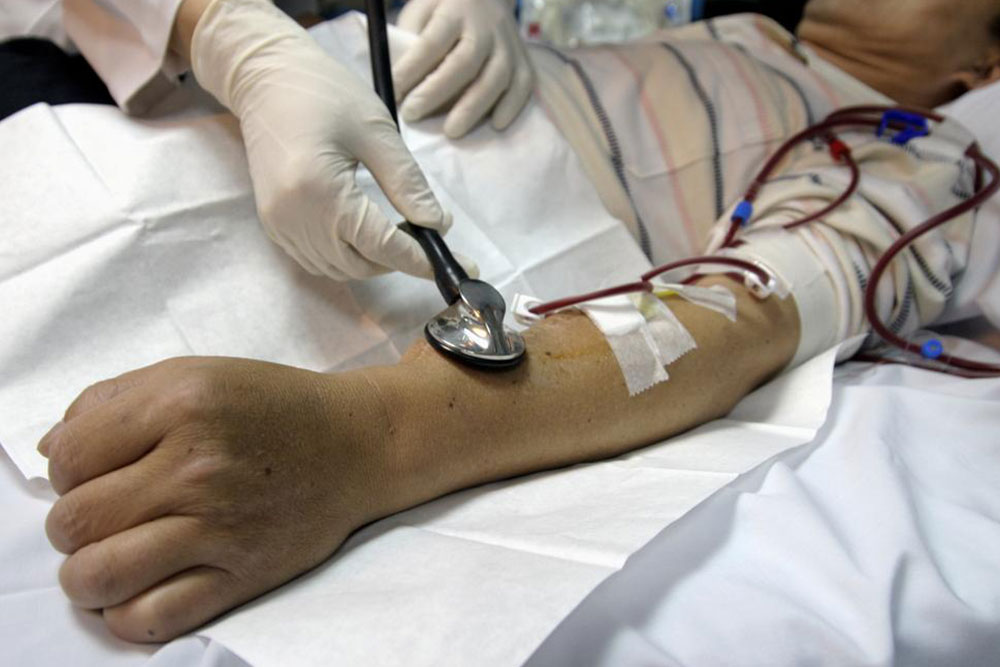
Despite its daunting nature, kidney dialysis has significantly reduced mortality rates by 35%, offering hope for patients. Early detection of kidney issues is difficult, leading to late-stage diagnoses like End-Stage Renal Disease, where dialysis becomes critical. The main types are hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis, with hemodialysis being more common in the US.
Dialysis requires comprehensive physiological and mental resilience but allows patients to lead relatively normal lives, including working and routine activities, either at hospitals or at home. Although demanding and initially uncomfortable, dialysis keeps blood chemistry balanced, supporting organ health. It remains ongoing until a suitable donor is found for transplantation. Many patients report improved quality of life, and access to dialysis centers across the US is straightforward.
The high costs of treatment are offset by federal aid programs such as Medicare, which covers many expenses for eligible patients. Additional assistance comes from Medicaid, state programs, and organizations like the American Kidney Fund, which help with medications and related costs. Private insurance is also a viable option, providing further financial support. Beneficiaries include those with Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) and Supplemental Security Income (SSI), ensuring ongoing medical coverage.
With the US ranking third globally in kidney disease prevalence, the rising cases of diabetes, hypertension, and obesity contribute heavily to this trend. As kidney transplants aren’t always feasible, dialysis remains vital. The National Kidney Foundation strives to improve dialysis quality through guidelines, education, and coordination with healthcare providers. Efforts focus on enhancing patient outcomes, compliance, and overall kidney health.
Addressing kidney disease requires understanding its links with broader health issues like cardiovascular problems and metabolic conditions. The US promotes integrated care models, such as dual-modality approaches, combining treatments for better survival. Proper diet, education, government aid, and support systems are essential to managing dialysis effectively, ensuring patients maintain a good quality of life despite their condition.