Understanding Nail Fungus: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
This article explores nail fungus causes, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options. It emphasizes preventive measures and proper nail hygiene to avoid infections. Treatments include topical and oral antifungals, with professional medical advice recommended. Good hygiene, avoiding injury, and maintaining dry, clean nails are key to prevention. Recognizing early signs can lead to prompt treatment, minimizing complications like nail loss or spread of infection.
Sponsored
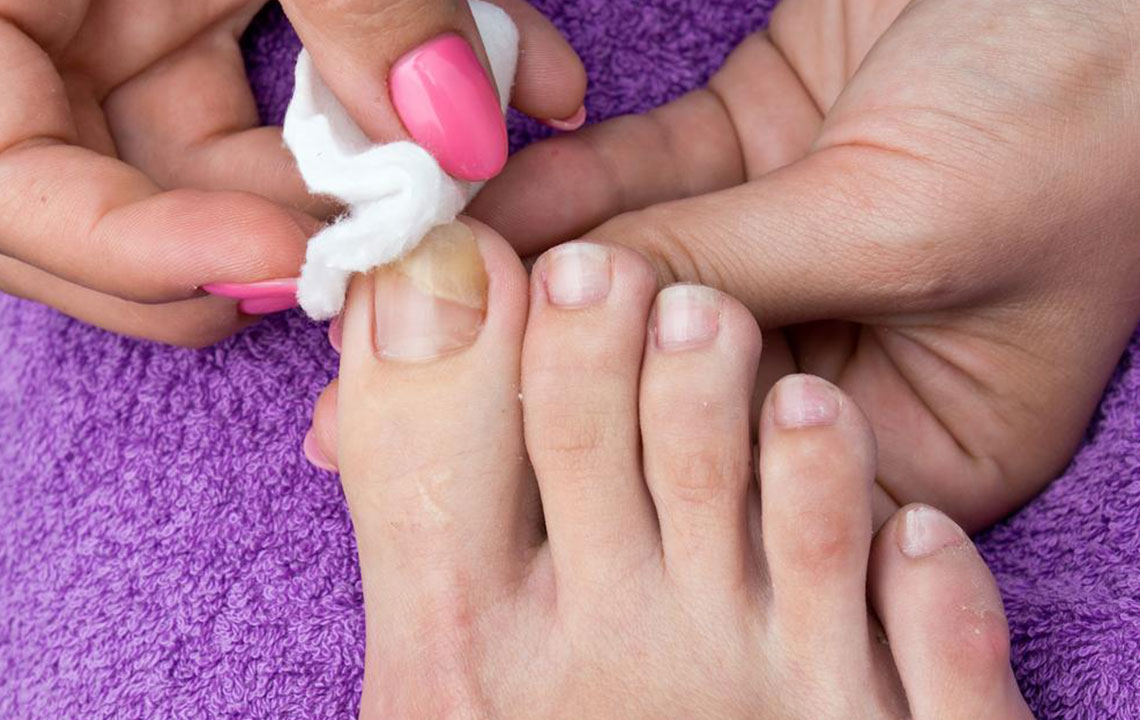

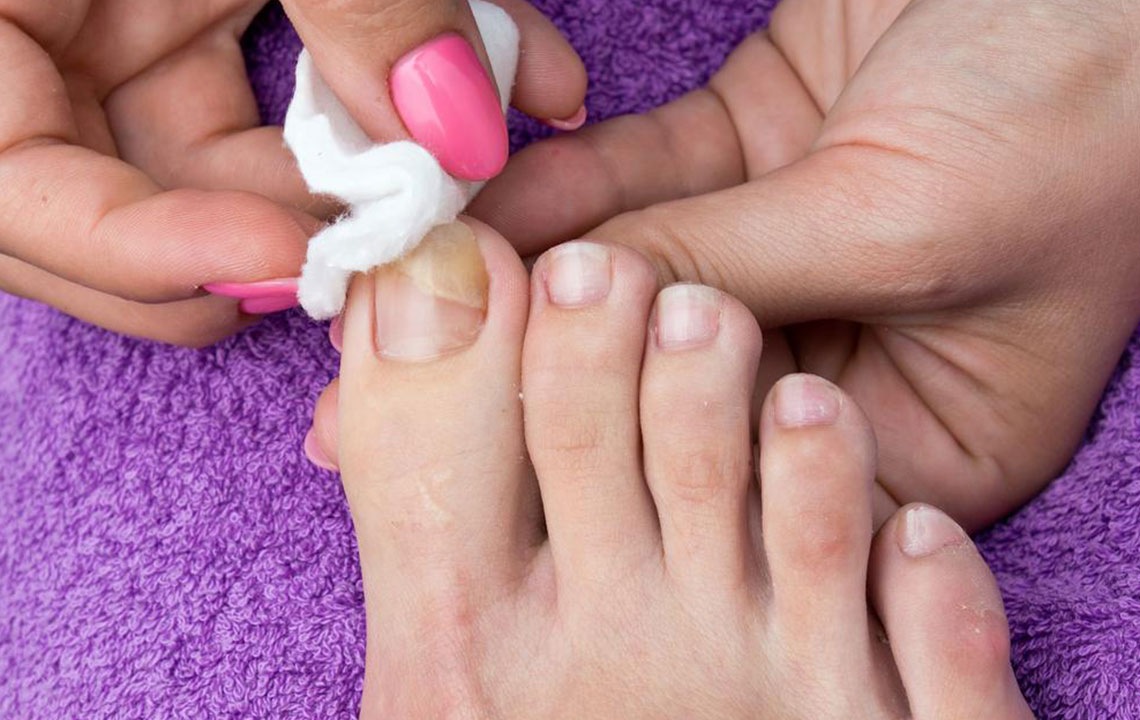
Nail infections caused by fungi happen when microorganisms invade the nail bed. The primary reason for fingernail fungal infections is damaged or cracked nails or cuticles. It can also originate from bacteria within the body. The infection often presents as thickened, yellowed nails with cracks. Several treatment options are available, though results may take time. Before exploring cures, it's essential to understand the causes and visible signs of fungal infections.
Causes of Nail Fungus
Fungal growth beneath or within the nail is the main cause of infection. Warm, moist environments promote fungal proliferation, making such settings ideal for growth. These fungi are often the same ones responsible for athlete’s foot, ringworm, or jock itch.
Fungal infections can also spread from other areas of the body and are contagious. Men are more susceptible than women, especially if infections run in the family. Toenails are more prone to fungus than fingernails because they are enclosed in shoes, providing a warm, damp environment conducive to fungal growth.
Risk Factors for Fungal Nail Infections
Various factors increase the likelihood of developing a fungal nail infection. Although preventable, awareness of these risk factors is vital:
Diabetes
Poor circulation
Age over 65
Use of artificial nails or nail injuries
Swimming in public pools
Skin injuries near nails
Not thoroughly drying hands or feet
Weak immune system
Older adults are at higher risk due to slower nail growth and thicker nails. Proper hygiene and precautions can help reduce infection chances.
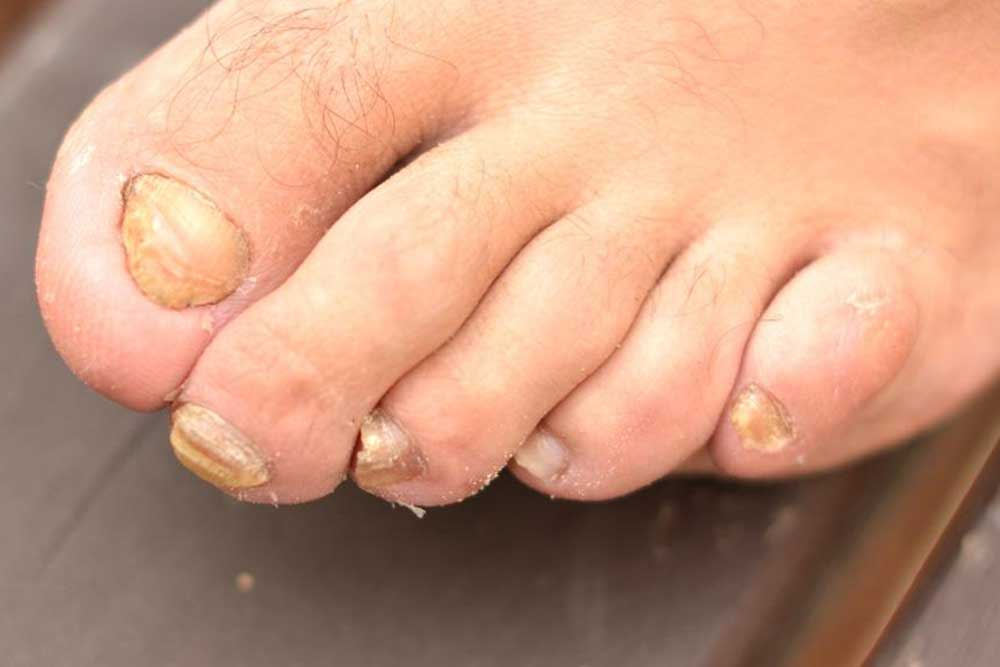
Signs and Symptoms of Nail Fungal Infection
Infections may affect single or multiple nails, with common signs including:
Scaling under the nail (subungual hyperkeratosis)
White or yellow streaks on nails (lateral onychomycosis)
Decaying edges or tips (distal onychomycosis)
Yellow spots at the nail base (proximal onychomycosis)
Pitted or flaky spots on the nail surface
Nail loss
Additional indicators are brittle, thickened nails, foul odor, and nails that lift off easily.
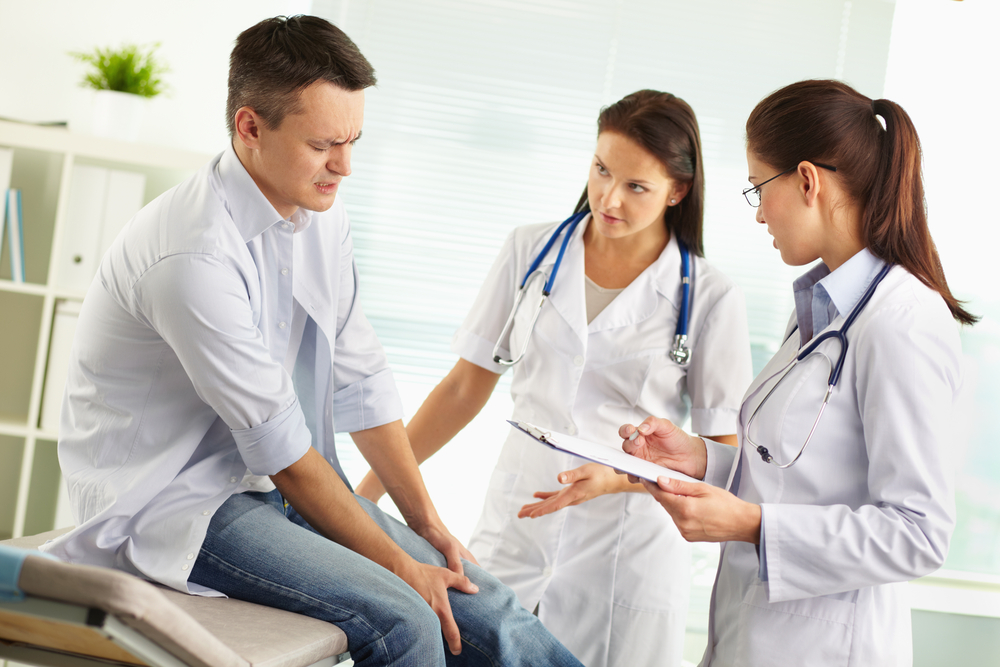
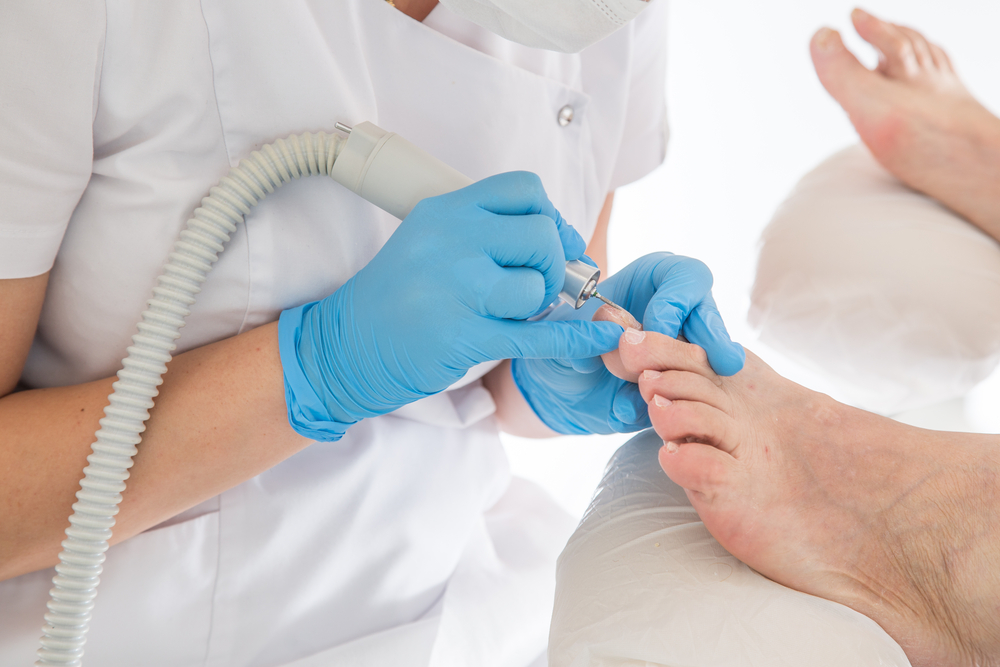
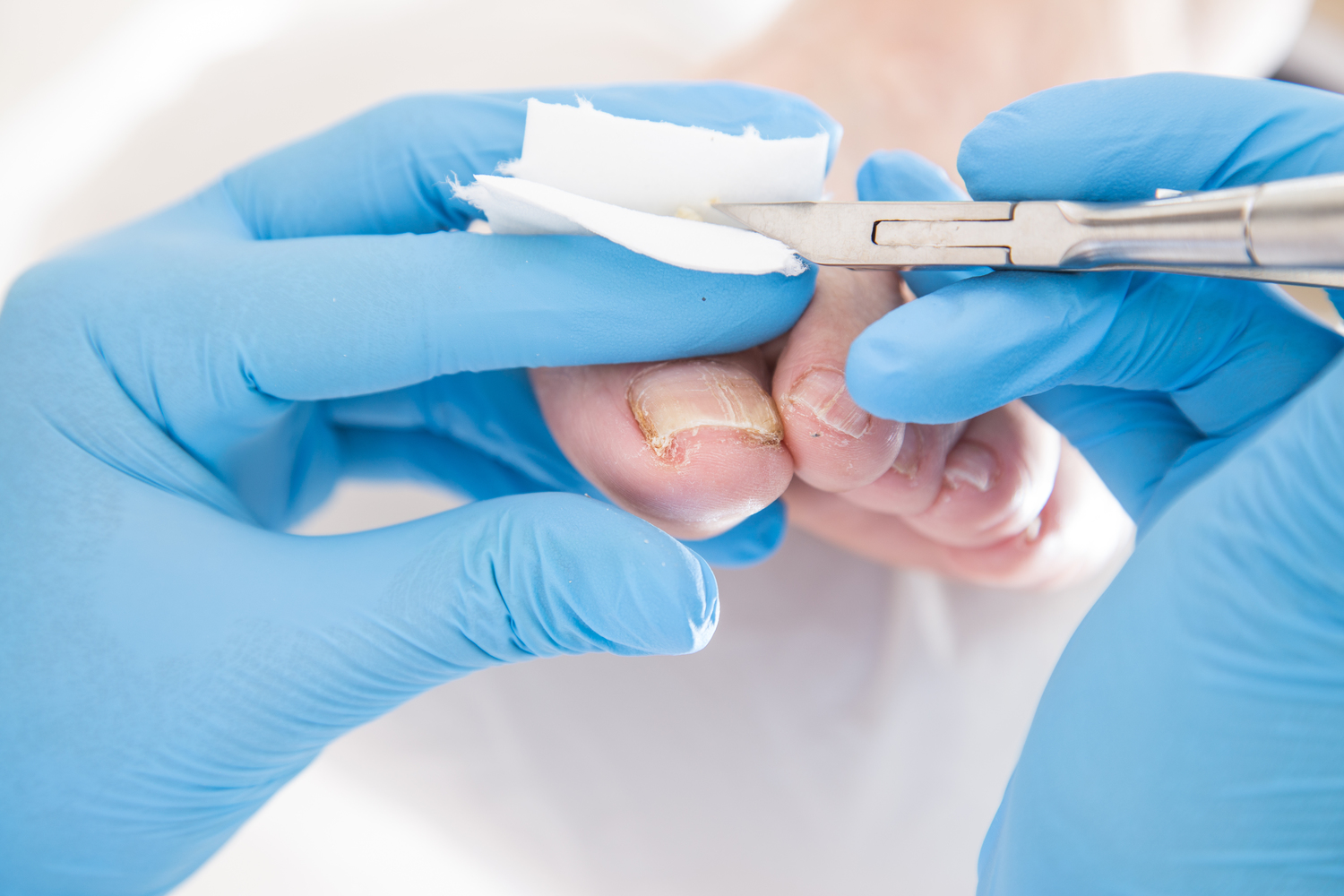
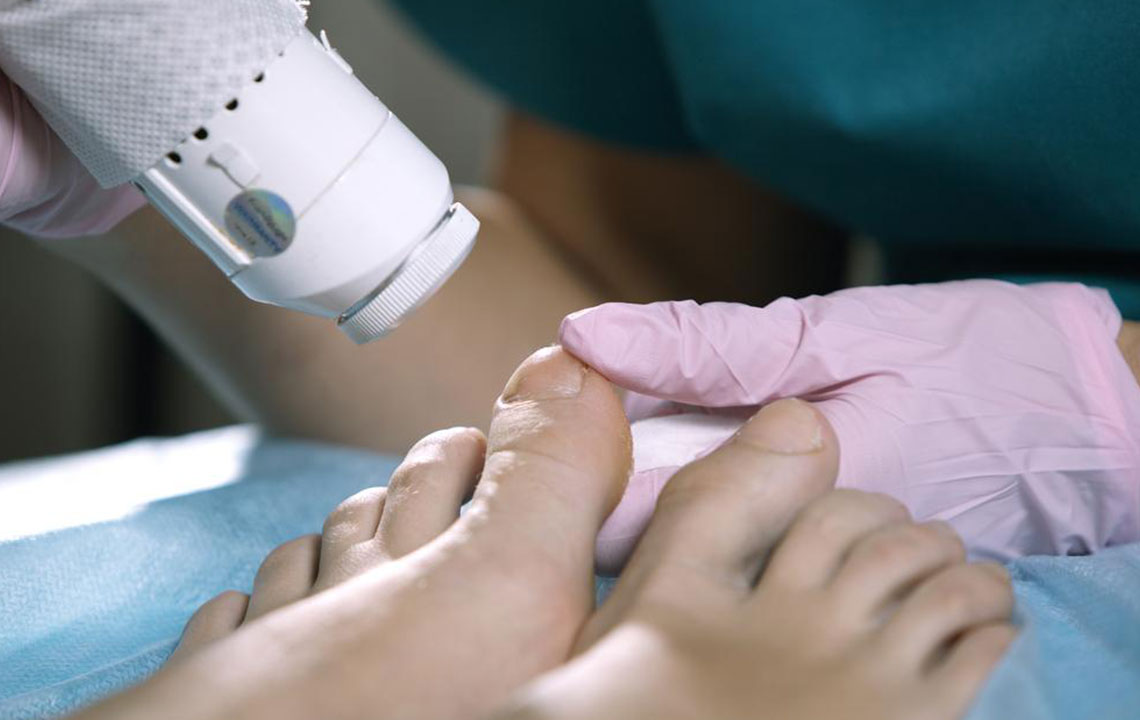
Treatment Options for Nail Fungus
Most treatments are prescribed by a healthcare professional. Topical antifungal agents like lacquers or solutions are common, and oral antifungals can be effective for severe cases. Over-the-counter remedies are generally not recommended without medical advice. Consistency with treatment helps ensure better outcomes.
Potential Complications
Recurrence of the infection
Permanent nail damage or loss
Nail discoloration and spread to other areas
Infection entering the bloodstream
Development of bacterial skin infections such as cellulitis
Adopting proper self-care habits minimizes infection risks. Maintaining clean, trimmed nails, keeping hands and feet dry, and avoiding injury are important preventive measures.
Additional tips include regularly using antifungal powders or sprays, practicing good hygiene, avoiding walking barefoot in public spaces, and limiting artificial nail use and polish. Proper nail and foot care greatly reduce the chance of fungal infections.