Effective Strategies for Managing Neuropathy Symptoms
Discover effective methods for managing neuropathy symptoms, including medications, therapies, and alternative treatments. Early diagnosis and prompt intervention are vital for better symptom control and improved quality of life. Consult healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans tailored to your condition.
Sponsored
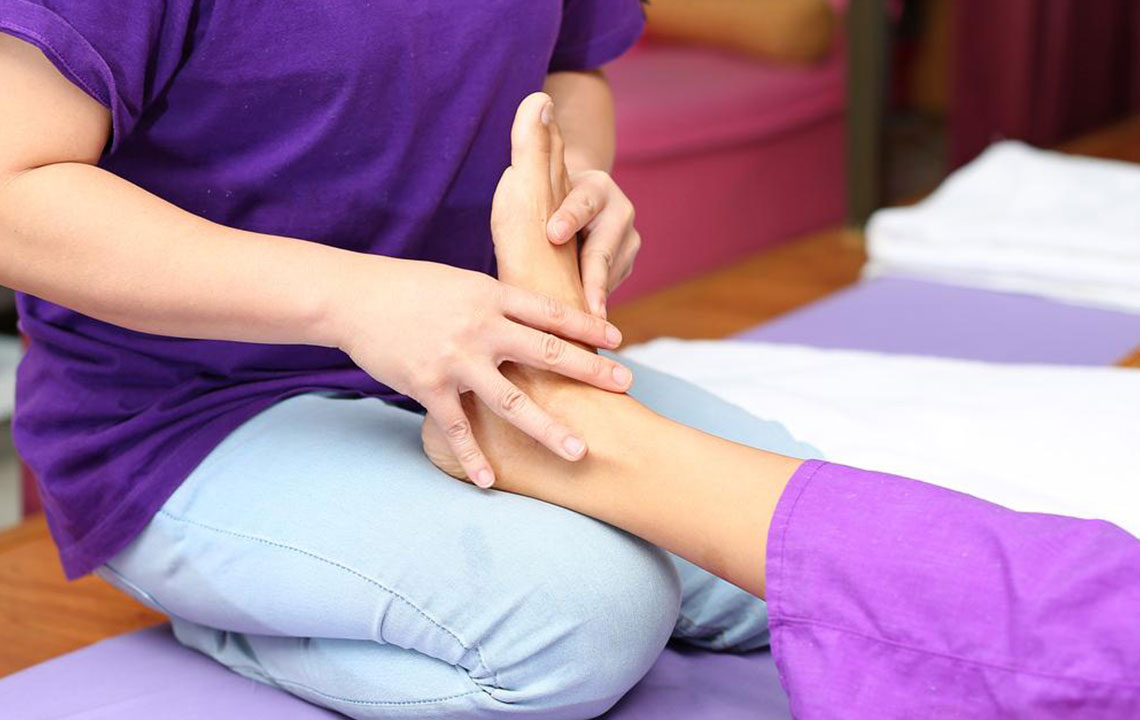

Understanding Reliable Methods to Alleviate Neuropathy
The main focus of neuropathy management is to identify and treat the root cause. Using targeted medications, individuals can experience significant relief from the uncomfortable symptoms linked to nerve damage. Diagnostic tests help pinpoint underlying conditions, and if results are inconclusive, doctors advise close monitoring of symptoms to observe any changes. Based on your diagnosis, healthcare providers may recommend specific treatments, including various medications tailored to your needs.
Popular Medications for Neuropathy Relief
When treating neuropathy, several medications are used to alleviate associated symptoms. Pain-relieving drugs are most common, including over-the-counter options like NSAIDs, effective for mild discomfort. For more intense pain, prescribed medications such as opioids, anticonvulsants, topical agents, and antidepressants are often employed, always under medical supervision to manage potential side effects and dependence risks.Pain relievers, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), are commonly used for mild symptoms. For severe pain, opioids like Tramadol, Oxycodone, and others may be prescribed, though they carry dependency risks and are usually reserved for resistant cases.
Anti-seizure medication options such as Pregabalin and Gabapentin help reduce nerve pain linked to neuropathy. Common side effects include dizziness and drowsiness, necessitating professional oversight during use.
Topical treatments like capsaicin creams, derived from hot peppers, can offer relief for peripheral nerve pain. Lidocaine patches are another option, with possible side effects including numbness, dizziness, and drowsiness.
Antidepressants such as nortriptyline, doxepin, amitriptyline, duloxetine, and venlafaxine, work by altering pain signaling pathways in the brain and spinal cord. These medications may cause side effects like constipation, nausea, and dry mouth.
Therapeutic approaches include immune-modulating therapies, physical therapy, and TENS (transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation). These methods help manage inflammation, improve mobility, and reduce nerve discomfort, respectively.
Surgical interventions are primarily for cases where nerve compression from tumors or other structural issues is the cause, aiming to relieve pressure and prevent further nerve damage.
Alternative remedies such as acupuncture, alpha-lipoic acid supplements, and herbal options like evening primrose oil can provide additional relief. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any alternative treatments, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are on medications.
Early intervention is crucial for effective neuropathy management. Delaying treatment can worsen symptoms and complicate pain control. Seek medical advice promptly if you experience persistent or severe nerve pain, and communicate openly with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.