Understanding the Different Forms of Radiation Therapy
This comprehensive guide covers the main types of radiation therapy used in cancer treatment, including external beam and internal brachytherapy. It explains how each method works, their applications, and factors influencing treatment decisions. Radiation therapy is crucial in shrinking tumors and targeting cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissue, making it an essential part of modern oncology. Understand how these therapies are chosen and their potential side effects for better treatment planning.
Sponsored
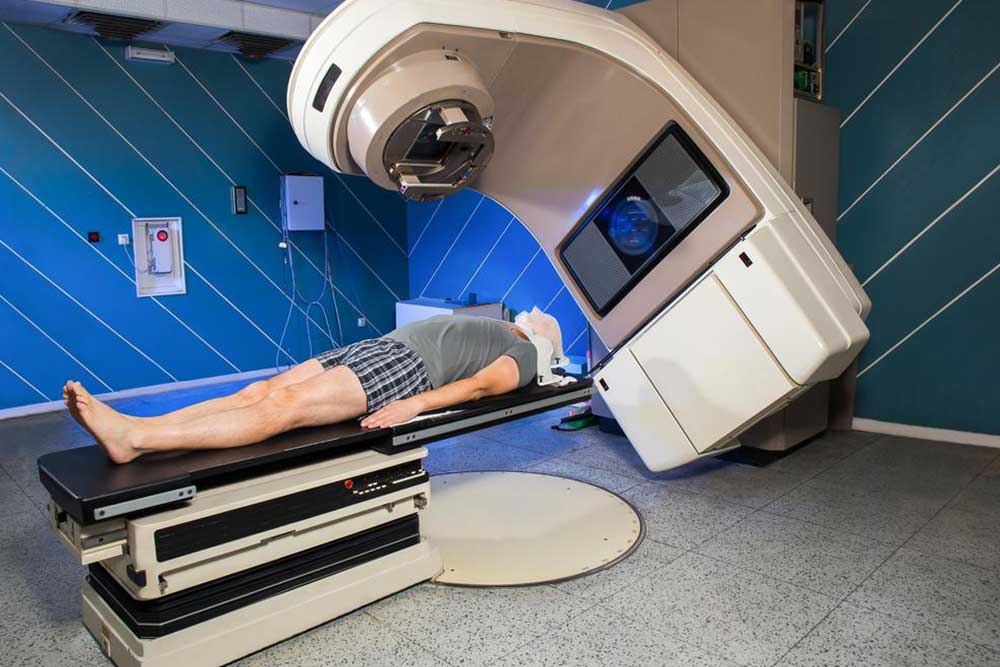
Radiation therapy, or radiotherapy, plays a vital role in cancer treatment by targeting and destroying malignant cells or reducing tumor size. It utilizes high-energy radiation, which can be visualized through imaging techniques like X-rays. Apart from cancer, radiation is also employed to treat bone fractures, dental issues, blood disorders, benign growths, and thyroid problems. This article explores the primary types of radiation therapy and their applications.
Types of Radiation Therapy
External Beam Radiation
This localized treatment directs radiation beams precisely at cancerous regions, minimizing impact on surrounding healthy tissue. The beams, consisting of protons, electrons, or photons, originate from large machines outside the body. For instance, lung cancer treatments target only the chest area, leaving the rest of the body unaffected. Variants include 3-D conformal therapy, IGRT, stereotactic radiosurgery, tomotherapy, IMRT, and stereotactic body radiation therapy.
Internal Radiation (Brachytherapy)
In this approach, radioactive sources are placed directly inside or near the tumor. Liquid sources are used for systemic therapy, often in thyroid cancers or advanced prostate cancers. Solid sources, called brachytherapy implants, are employed to treat cancers in the breast, cervix, prostate, head, neck, and eye.
Choosing the Right Therapy
Selection depends on factors such as tumor size, type, location, nearby healthy tissue sensitivity, patient health, medical history, and age. As radiation therapy can cause side effects, it must be undertaken under strict medical supervision for safe and effective results.