Comprehensive Guide to Managing Migraines
This comprehensive guide explores migraine types, trigger foods, and effective treatment options. It emphasizes preventive and abortive therapies, medication use, and lifestyle tips for managing migraines. With medical advances, relief from this neurological disorder is increasingly attainable, helping sufferers regain control of their daily lives.
Sponsored

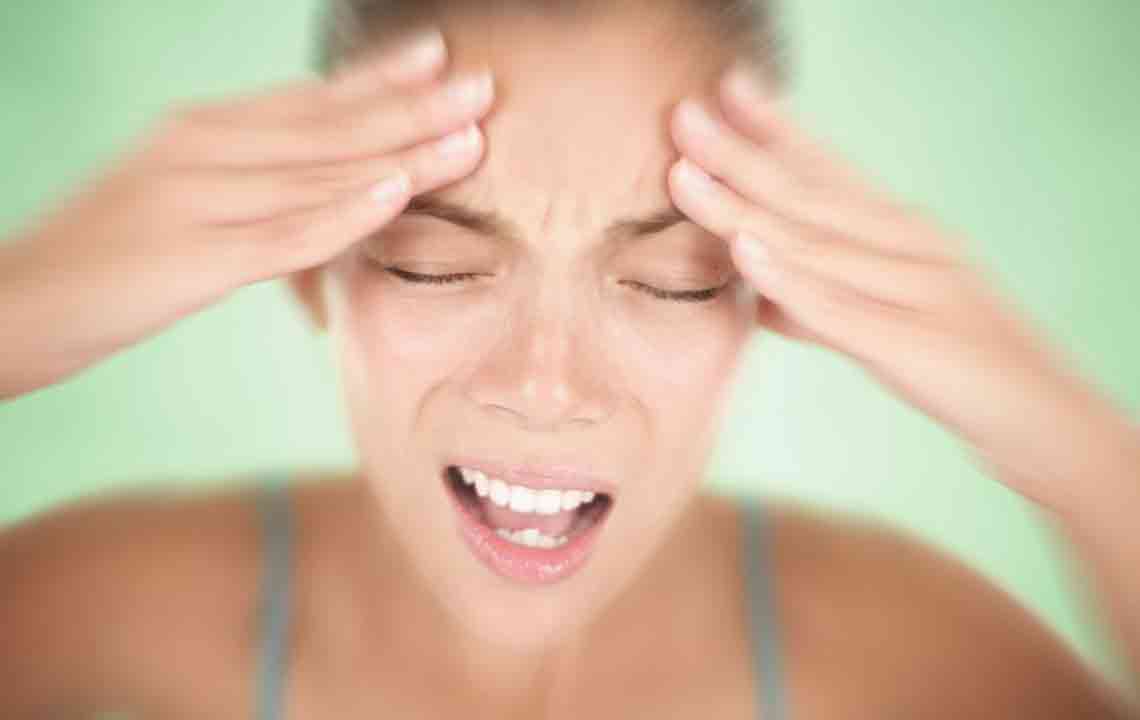
Migraines, whether classic or common, are debilitating neurological episodes that affect many individuals worldwide. Classic migraines may come with aura symptoms like visual disturbances lasting 15-30 minutes, while common migraines typically lack aura and disrupt daily routines more significantly.
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can trigger or worsen migraine attacks. Key culprits include:
Avocado
Processed meats
Red plums
Soy sauce
Raisins
Pea pods
Pickles and olives
Treatment Options
Migraine treatments fall into preventive and abortive categories.
The preventive approach involves daily medication to minimize frequency, whereas abortive treatments aim to alleviate symptoms during attacks.
Abortive Treatments – Common medications like ergots and triptans (e.g., sumatriptan, almotriptan) are used to stop migraine symptoms. These can be administered orally, via injection, or as nasal sprays. Some drugs, including zolmitriptan and rizatriptan, should be avoided during this therapy.
Preventive Therapy – For severe or frequent migraines, medications such as beta-blockers (timolol, propranolol), anticonvulsants (topiramate, divalproex), and antidepressants (nortriptyline, amitriptyline) are prescribed to reduce attack occurrence.
Medications tailored to migraine severity include pain relievers like Tylenol, Motrin, Excedrin, and Aleve. Resting in a quiet, dark room, applying gentle pressure to the temples, or massaging the forehead can provide temporary relief during episodes. Advancements in medical science are continuously improving migraine management, offering hope for those affected by this neurological condition.