Understanding Severe Diarrhea: Symptoms and Effective Treatments
Severe diarrhea requires prompt attention and proper management. Recognizing symptoms such as frequent, watery stools, bloating, and fever helps in timely intervention. Diet modifications, hydration, and suitable medications like probiotics and antidiarrheal drugs are essential for effective recovery. Avoiding aggravating foods during treatment and resting the digestive system speed up healing. If symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring swift recovery.
Sponsored
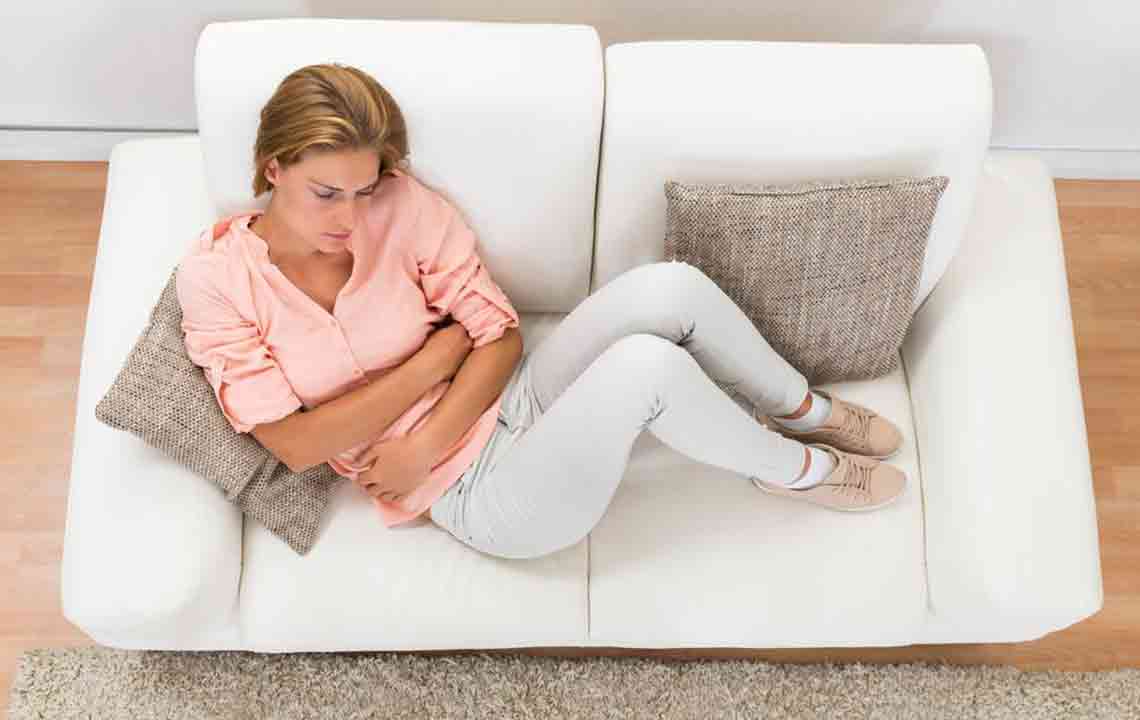

The human digestive system is resilient, capable of processing numerous foods based on individual health and lifestyle. However, diarrhea can disrupt this system periodically, typically once or twice annually. In some cases, it can persist for days, causing significant discomfort. Addressing severe diarrhea promptly is crucial. Recognizing its causes and symptoms helps in managing the condition effectively and seeking appropriate treatment at home or through medical advice.
Primary causes of diarrhea
Diarrhea is often caused by infections like the stomach or intestinal flu, which affect gut health. Lifestyle choices and environmental factors also play significant roles.
Dietary allergies or intolerances to certain foods can trigger diarrhea.
Individuals with high blood sugar or diabetes may be more susceptible due to compromised immunity.
Conditions like ulcerative colitis impact intestinal health and can lead to diarrhea.
Medication side effects may include diarrhea in some cases.
Hyperthyroidism or an overactive thyroid gland can contribute.
Cancer treatments like radiation therapy can cause gastrointestinal issues.
Food poisoning and bacterial infections are common culprits.
Surgical procedures involving the intestines may result in diarrhea as a side effect.
Malabsorption issues prevent proper nutrient absorption, leading to symptoms.
Excessive alcohol intake damages the digestive tract.
Laxative abuse or reaction can also cause loose stools.
Key symptoms indicating severe diarrhea include:
Bloated abdomen or persistent swelling
Intense stomach cramps
Passing thin, loose stools
Frequent urge to defecate
Nausea and vomiting tendencies
Presence of blood or mucus in stool during severe episodes
Unexpected weight loss
High fever, which requires immediate attention
Managing severe diarrhea involves specific care routines. During treatment, avoiding disruptive foods and habits is advisable. Proper diet, hydration, and rest are essential for recovery. Here’s how to manage it effectively at home:
Foods to avoid include artificial sweeteners, berries, alcohol, coffee, cabbage, chickpeas, corn, leafy greens, peas, peppers, prunes, and dairy products.
Beneficial foods for recovery involve bland, easy-to-digest options like mashed boiled bananas, white rice, plain toast, mashed boiled potatoes, light chicken broth or baked chicken, and oatmeal. These help in binding loose stools and restoring gut health.
Medications such as bismuth subsalicylate and loperamide (Imodium), alongside probiotic-rich foods like yogurt and kimchi, can aid treatment. Always consult a healthcare professional before initiating drugs or supplements.
Resting the digestive system, eating small portions of gentle foods, staying hydrated, and seeking medical advice if symptoms persist are key recovery strategies. Proper management ensures quicker healing and comfort.