Understanding Hernias: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments
This article explores hernias, highlighting their causes, symptoms, and available treatments. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis and discusses lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical options to effectively manage hernias and prevent severe complications.
Sponsored
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak point or opening in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue, most commonly in the abdomen or groin. This condition often results in a noticeable bulge and discomfort. Types include inguinal, hiatal, umbilical, and incisional hernias. While many hernias remain harmless, they do not resolve independently and may require medical intervention to prevent complications. Various treatment options, including lifestyle adjustments, medications, and surgery, are available to manage the condition effectively.
Primary Causes of Hernia
Weakness in the abdominal wall combined with muscular strain leads to hernia formation. Factors such as congenital defects, persistent coughing or sneezing, aging, previous abdominal surgeries, weight gain, pregnancy, fluid buildup, severe constipation, and heavy lifting increase the risk.
Key Symptoms
The earliest sign is a lump or swelling in the affected area. For inguinal hernias, lumps are typically felt near the groin. These may become more noticeable when standing, coughing, or bending over. In infants, crying can reveal the hernia. Other symptoms include abdominal heaviness, pressure, burning sensations at the bulge, acid reflux, chest pain, and swallowing difficulties. Some hernias are asymptomatic and diagnosed during routine exams.
Diagnosis involves physical exams and imaging tests such as ultrasound, endoscopy, or X-rays with contrast agents like barium. Treatment depends on the hernia's size and severity. Lifestyle modifications, medications, or surgery are common options.
Lifestyle Strategies
While hernias cannot be cured completely, symptom alleviation is possible through diet and activity adjustments. Avoid large meals, heavy lifting, and unnecessary strain after eating. Maintaining healthy weight, performing gentle strengthening exercises under medical guidance, and avoiding trigger foods like spicy items and tomatoes can reduce discomfort. Proper exercise techniques prevent aggravating the hernia.
Medications to Alleviate Symptoms
Medications such as proton pump inhibitors, H-2 blockers, and antacids help control stomach acid, reducing symptoms like reflux and pain.
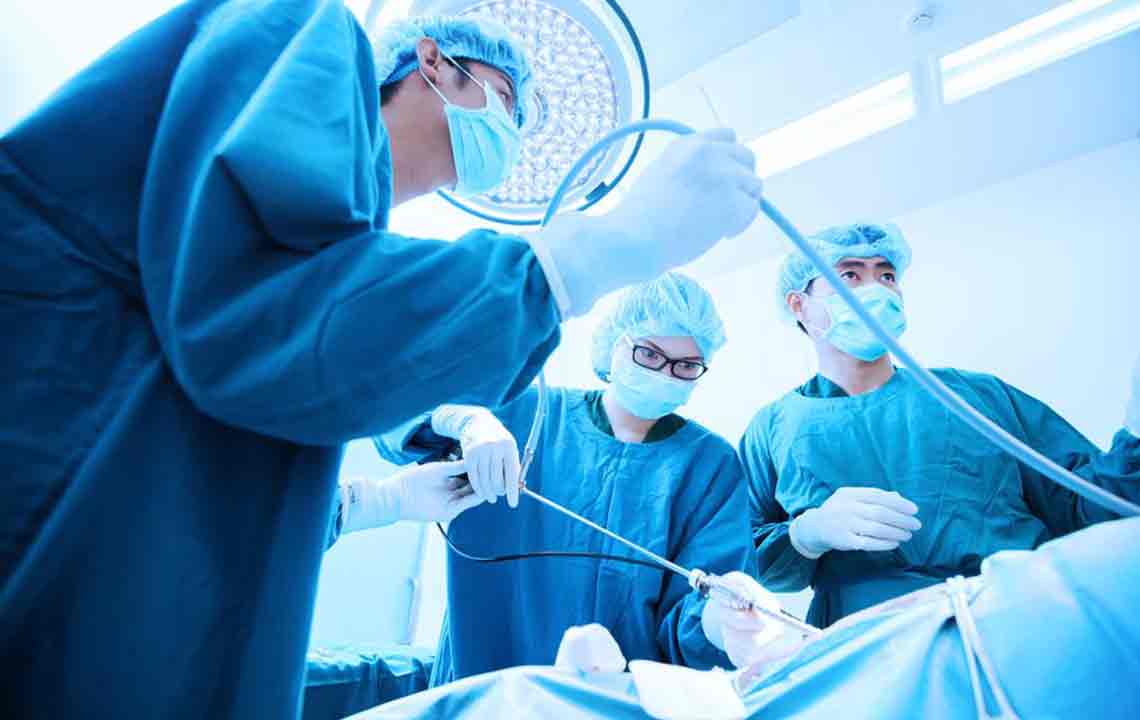
Surgical Intervention
Surgery is typically recommended for painful or enlarging hernias. Repair involves closing the defect, often reinforced with surgical mesh, through open or laparoscopic procedures. Laparoscopy requires small incisions and offers quicker recovery, while open surgery may involve a longer healing period. Early detection and treatment are essential to prevent serious complications like strangulation.





