Effective Strategies for Managing Fever Symptoms
Learn effective methods to manage and treat fever in children and adults. This guide covers when to seek medical help, how to measure temperature, and comfort strategies to alleviate symptoms. Understanding fever as a sign of infection helps in proper care and timely intervention, ensuring safety and relief during illness.
Sponsored
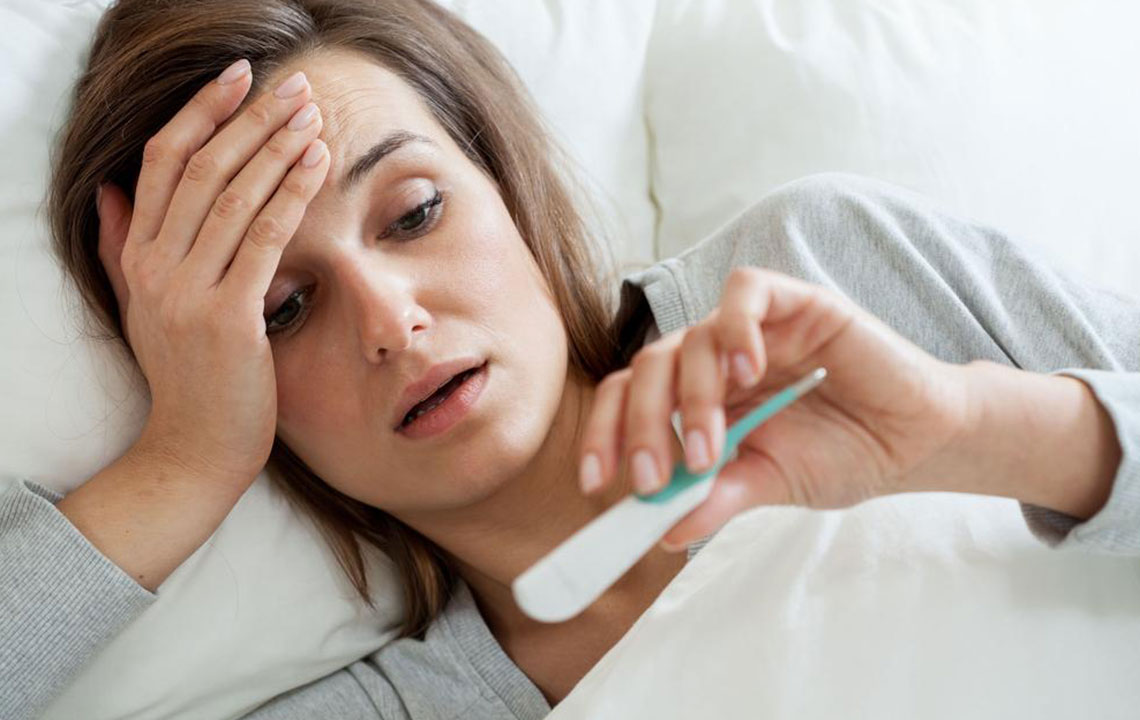

A fever refers to an elevation in body temperature, often indicating an underlying infection. Generally harmless and sometimes beneficial, a common fever usually doesn’t require medical intervention. Normal body temperature is approximately 98.6°F (37°C), but it can vary between 97°F (36.1°C) and 99°F (37.2°C) depending on activity and time of day. Older adults tend to have lower baseline temperatures. Recognizing a fever involves monitoring temperature with a reliable chart—fever is usually indicated when readings reach 100.4°F (38°C) or higher via ear, rectal, or temporal measurements.
Is treatment necessary for a fever?
The main goal of fever management is to relieve discomfort and promote rest. Treating a mild fever doesn't alter the course of illness but helps improve comfort.
Fever Care for Children
Many kids with high temperatures don’t appear very sick. Comfort measures include encouraging hydration, dressing in lightweight clothing, and using a light blanket if chills are experienced. Administering age-appropriate doses of ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help, but always follow label instructions. Infants under six weeks should not be given these medications; medical advice is essential in such cases.
Fever Treatment for Adults
Adult care depends on symptoms and temperature levels. An adult with a temperature above 103°F (39.4°C) may feel fatigued and unwell. Medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen are typically recommended for relief.
When to consult a healthcare professional
For infants under three months, prompt medical evaluation is necessary rather than relying solely on home remedies. Children aged 3-6 months with temperatures over 102°F (38.9°C) and persistent discomfort should see a doctor. If a fever lasts more than a day or exceeds 102°F in children aged 2-17 for more than three days without improvement, professional care is advised.
Emergency care indications
Seek urgent medical attention if fever persists for several days accompanied by severe symptoms like intense headache, neck stiffness, persistent vomiting, seizures, confusion, or high irritability.
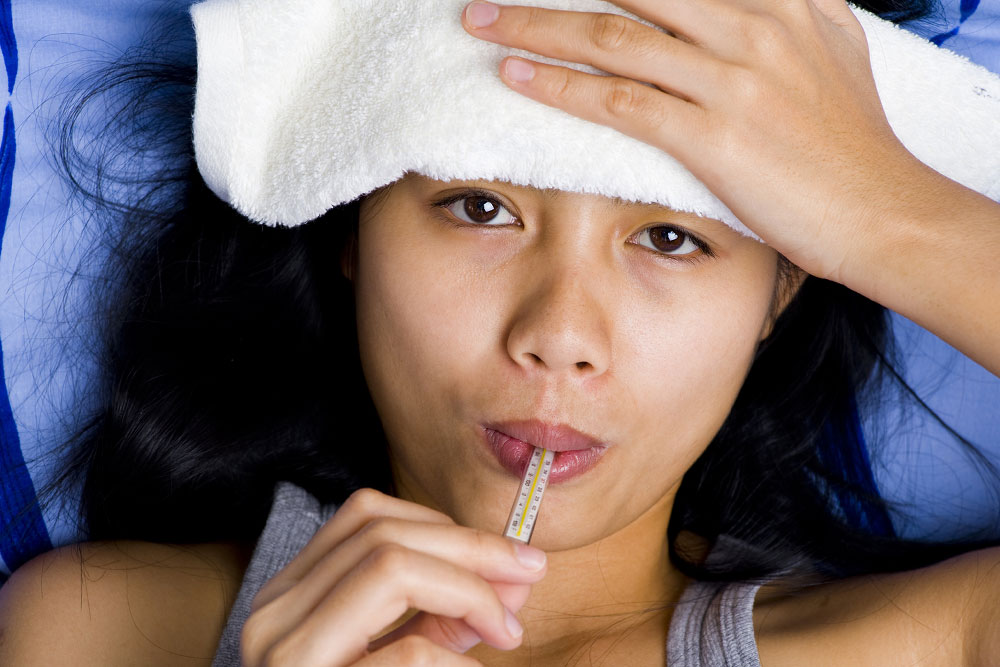
Measuring body temperature accurately
Use a digital thermometer—digital, ear, or temporal artery types—all effective for monitoring. Follow manufacturer instructions carefully, clean after each use, and compare readings against a fever chart to assess severity.
Frequency of temperature checks
Regular monitoring is vital, especially for children. Increase frequency if fever is high or persistent, aiming for hourly checks during acute phases. Advanced thermometers enable gentle readings without disturbing sleep.
Elevated body temperature signals the immune system fighting infection rather than a disease itself. It’s often accompanied by symptoms like headache, fatigue, or nausea and serves as an important warning of illness that typically resolves with proper care.