Understanding Leukemia: Types and Therapeutic Strategies
Learn about leukemia, its key types such as ALL, CLL, and CML, and various treatment options including chemotherapy, radiation, and bone marrow transplants. Early diagnosis and tailored therapies are essential for effective management of this blood cancer. Understand symptoms, diagnosis procedures, and advancements in treatment strategies to stay informed about this complex disease.
Sponsored
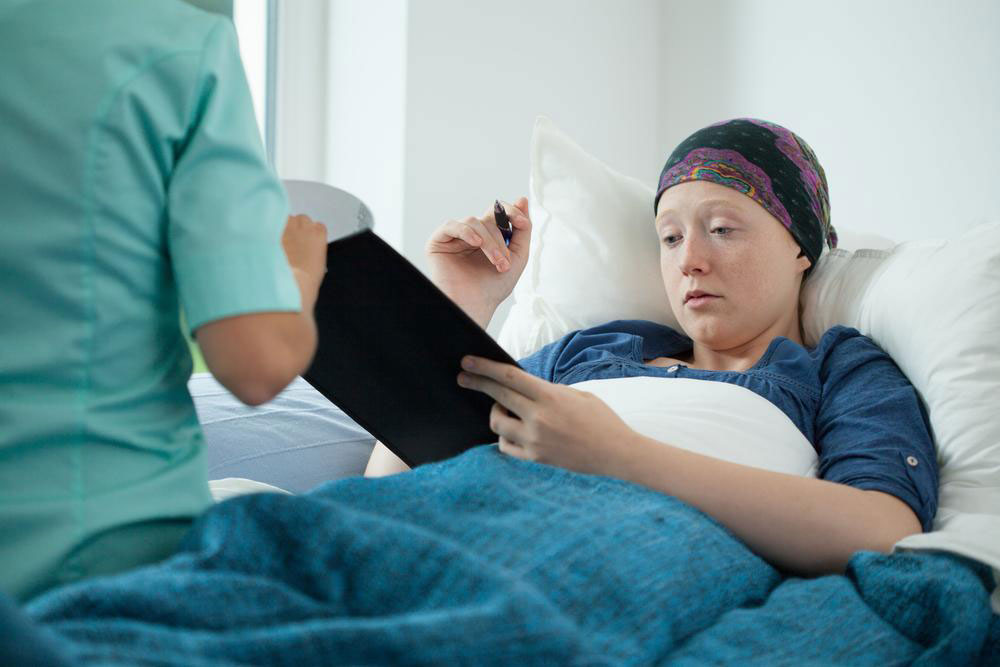
Leukemia is a primary form of blood cancer, alongside lymphoma and multiple myeloma. It affects various blood components, primarily targeting white blood cells (WBCs). The condition is diagnosed ten times more frequently in adults than in children, indicating increased risk with age.
Symptoms vary based on leukemia subtype. Key types include:
Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
This type impacts blood and the bone marrow, which produces blood cells. Common symptoms are bleeding gums, recurrent infections, and bone discomfort.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
Progressing slowly, CLL may show no early signs but later causes fatigue, weight loss, and swollen lymph nodes.
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
This type features elevated WBC levels due to genetic anomalies in the bone marrow, predominantly affecting adults.
Diagnosing leukemia
Early stages often lack noticeable symptoms, making diagnosis challenging. Blood tests and bone marrow examinations are vital resources for confirmation, guiding treatment options.
Leukemia treatments
Depending on factors like age and disease stage, treatments include:
Radiation therapy
Targets leukemia cells with high-energy rays to inhibit their proliferation, preventing organ damage.
Bone marrow transplantation
Replaces diseased marrow with healthy stem cells to restore normal blood cell production.
Chemotherapy
Uses drugs to destroy leukemia cells, though it may cause side effects like fatigue and hair loss.