Essential Treatment Strategies for Testicular Cancer Patients
This comprehensive overview explores vital treatment options for testicular cancer, including surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and advanced therapies. Early diagnosis and personalized treatment plans improve survival chances and manage side effects effectively. Consult specialists promptly for the best outcomes.
Sponsored

Critical Treatment Approaches for Managing Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer involves abnormal cell growth within the testicles, often presenting as a lump. This serious disease requires prompt and effective treatment options to improve survival rates. Below are key therapies to consider in fight against this cancer.
*body*
The disease originates from germ cells in the testicles, which produce sperm and testosterone. These glands are located in the scrotum, with the spermatic cord supporting them. Cancertypically begins when these germ cells produce abnormal, premature sperm cells that accumulate and become malignant.
Symptoms of testicular cancer include painless or painful lumps, swelling, or heaviness in the scrotum, as well as discomfort in the lower abdomen, back, or groin areas. Recognizing these signs early can be life-saving.
Various treatment options exist, such as surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Each has potential side effects like infertility and sexual health issues, depending on the disease stage and individual health.
Radiation Therapy
This involves directing high-energy beams at affected regions. Damaged cancer cells are unable to recover, while healthy cells recover over time. Radiation is typically administered in multiple sessions, but can cause fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, and weakness.
Orchiectomy
This surgical procedure removes the affected testicle to prevent cancer spread. Conducted through an incision in the groin, it requires careful postoperative care to avoid infection and complications.
Lymph Node Removal (RPLND)
For advanced cases, removal of lymph nodes in the abdomen may be advised. Particularly for stage 2 cancer where the disease has spread, this procedure targets nodes around the aorta. Your doctor can help determine if this approach fits your condition.
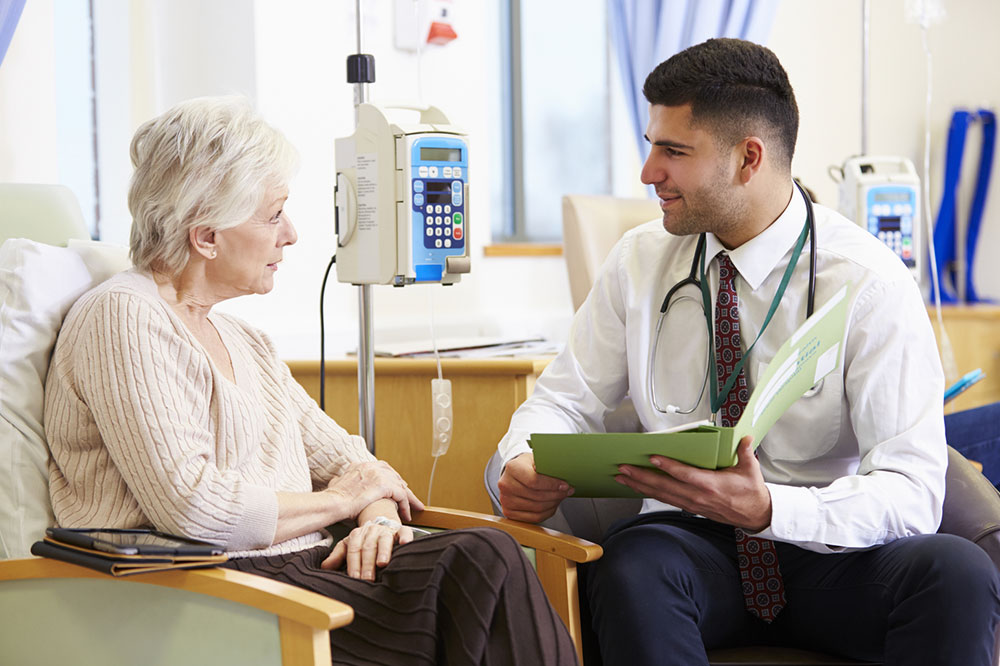
Chemotherapy
Administered via pills or intravenous infusion, chemotherapy fights cancer cells spreading beyond the testicles. While effective, it may result in side effects such as infertility, fatigue, hair loss, nausea, and organ impact, especially in advanced stages.
High-Dose Chemotherapy with Stem Cell Support
This intensive treatment is used in progressive cases, involving higher chemotherapy doses combined with stem cell transplants to restore blood cell production. Stem cells are collected beforehand from the patient's bone marrow.
Consult your healthcare provider to identify the most appropriate treatment plan based on your diagnosis and overall health.