Understanding Liver Cirrhosis: Stages, Causes, and Prevention Strategies
Liver cirrhosis is a severe condition marked by liver scarring, often caused by hepatitis infections and fatty liver disease. Recognizing early warning signs and understanding its stages are crucial for effective management. While irreversible in advanced stages, early intervention and lifestyle changes can slow progression and improve quality of life. Preventative measures, including vaccination and avoiding hepatitis risk factors, play a vital role in reducing the risk of cirrhosis. Regular medical check-ups and healthy habits are essential for liver health.
Sponsored
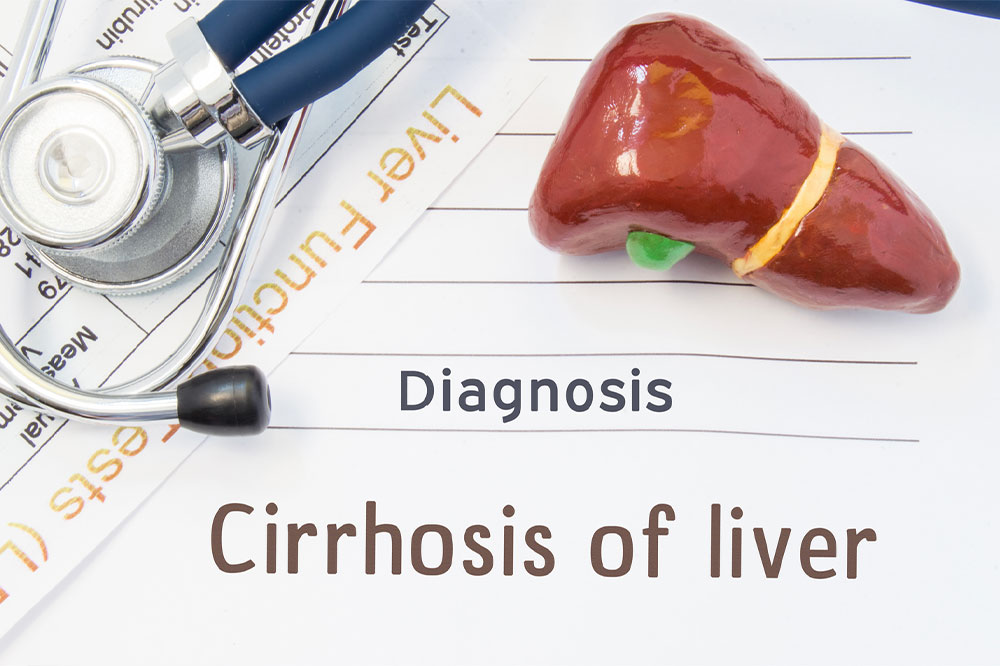
Liver cirrhosis involves scarring of the liver tissue, which can lead to severe liver dysfunction. Early stages often show no symptoms, making diagnosis challenging. Common causes include hepatitis infections and fatty liver disease. Treatment varies based on the root cause, with options like lifestyle adjustments, medications, or liver transplantation in advanced cases. Recognizing early signs is crucial for better outcomes. Cirrhosis damages healthy liver tissue, impairing its ability to process toxins, produce proteins, and regulate hormones. In late stages, the damage becomes irreversible, but early detection and intervention can slow progression.
Is liver cirrhosis reversible?
Usually, cirrhosis is considered irreversible once advanced damage occurs. However, identifying and treating underlying conditions early can halt or slow its progression. The disease's stage influences treatment options and prognosis.
Stages of liver cirrhosis
Doctors classify cirrhosis as either "compensated" or "decompensated." In the compensated phase, the liver still works well and symptoms are often absent, allowing many individuals to live normal lives for years. In the decompensated stage, significant scarring impairs liver function, leading to symptoms and serious health issues.
What are the typical symptoms?
Once damage is extensive, cirrhosis is difficult to reverse. Nonetheless, a substantial portion of liver function remains, and managing health conditions like hepatitis, weight, and blood sugar can help slow disease progression. Early diagnosis enables better management, allowing many patients to maintain a good quality of life. Consulting healthcare providers for personalized treatment plans is essential.
Preventing liver cirrhosis
Preventative measures revolve around avoiding hepatitis infections, the primary cause. Vaccinations against hepatitis B are recommended for high-risk individuals, though no vaccine exists for hepatitis C. Proper safety protocols and early treatment of hepatitis infections significantly reduce the risk of developing cirrhosis. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding alcohol, and monitoring liver health are vital steps to protect this essential organ.