Understanding Male Hair Thinning: Causes, Stages, and Prevention
Explore the comprehensive overview of male hair loss, including its causes, stages based on the Norwood Scale, diagnostic methods, and preventive strategies. Understanding these aspects can aid in early detection and effective management of hair thinning. Various treatments like lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and advanced procedures are discussed to help men maintain healthy hair and slow down hair loss progression.
Sponsored
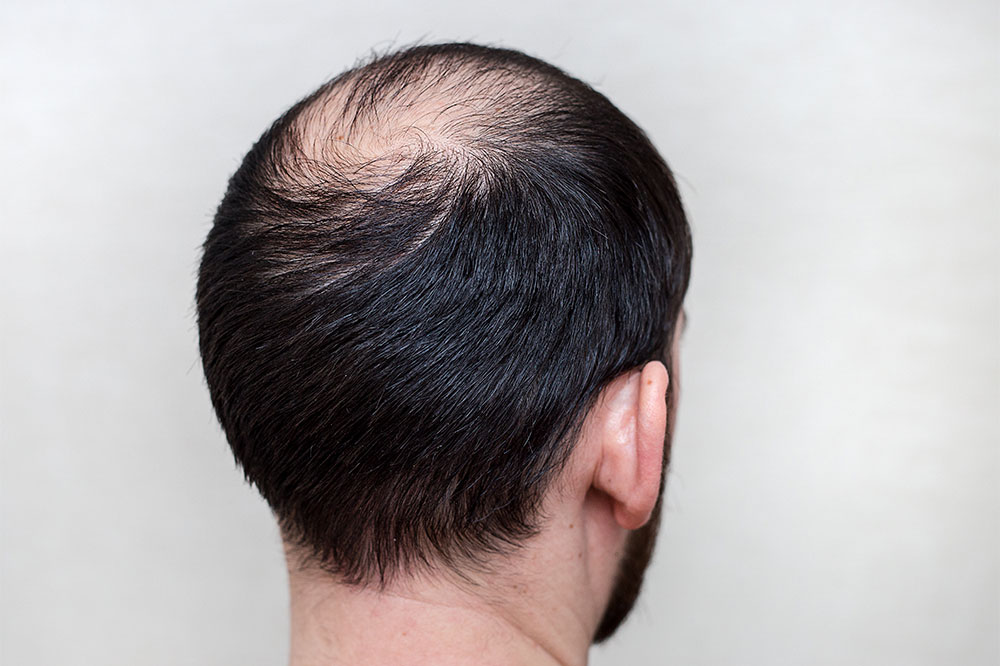
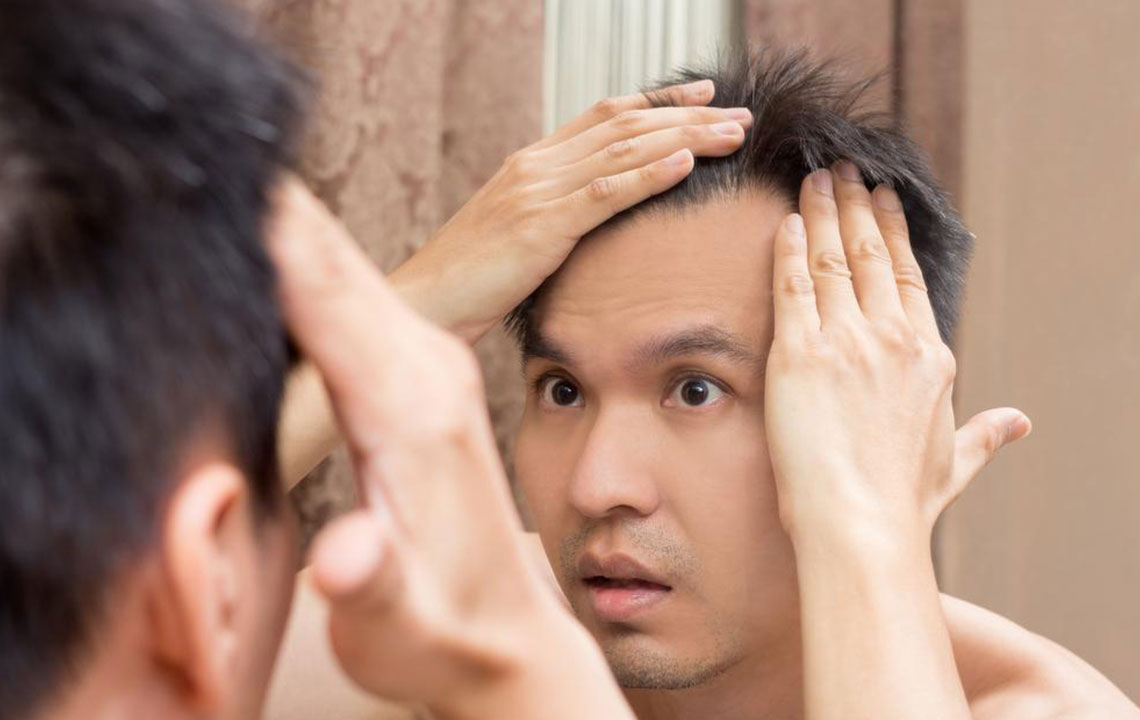
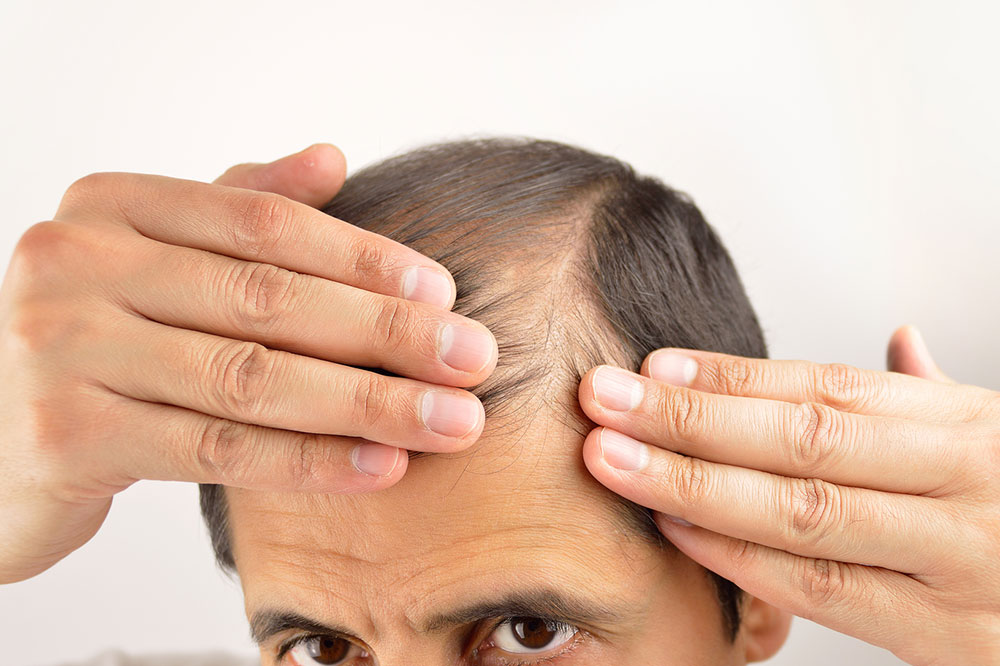
Hair covers most areas of the human body, except for the palms and soles. Composed mainly of keratin, a protein produced in hair follicles, hair constantly renews itself. The scalp typically hosts 100,000 to 150,000 hairs, with about 100 hairs shed daily, which is normal. However, excessive shedding could indicate underlying issues. Male pattern baldness, or alopecia, is categorized into several stages based on factors like age of onset, pattern, and severity. Recognizing these stages helps in timely intervention and management.
Progression of Hair Loss
Hair loss, scientifically known as alopecia, varies in onset and severity. It is classified into seven stages according to the Norwood Scale, which maps the progression in men. The stages range from minimal hairline recession to extensive baldness. Factors influencing these stages include genetics, health conditions, and lifestyle choices.
Stage 1
No noticeable hair loss; hairline appears normal.
Stage 2
The hairline begins to mature with slight recession around the temples.
Stage 3
More prominent recession forms an M, U, or V shape; bald areas appear at the crown.
Stage 4
Significant hair loss at the crown with receding temples. Hair connecting the sides reduces or disappears.
Stage 5
The bald areas on the crown and sides expand, with a narrowing band of hair remaining.
Stage 6
The connecting band is gone, joining balding areas of the crown and temples.
Stage 7
Only a thin band of hair remains; extensive baldness prevails.
Diagnosing Hair Loss
Blood Tests
Detect underlying medical conditions affecting hair health.
Pull Test
Gentle pulling to assess shedding levels.
Scalp Biopsy
Removing hair samples to examine root health.
Microscopic Examination
Analyzing hair samples under a microscope for detailed insights.
Tips to Prevent Hair Loss
To delay or prevent male hair thinning, lifestyle modifications and early treatments are recommended. Avoid hot showers, switch to gentle hair care products, and seek professional scalp massages. For more advanced prevention, options include hair transplants and laser therapy devices, which can help stimulate hair growth and reduce further loss.