Understanding Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: Causes, Signs, and Treatment Options
Non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) is the most common lung cancer type, with causes linked to smoking and environmental exposures. Symptoms often mimic other respiratory illnesses, making early detection challenging. Diagnosis involves imaging and biopsy, and treatment includes surgery, radiation, and targeted therapies aimed at slowing disease progression. Recognizing early symptoms is vital for better prognosis.
Sponsored
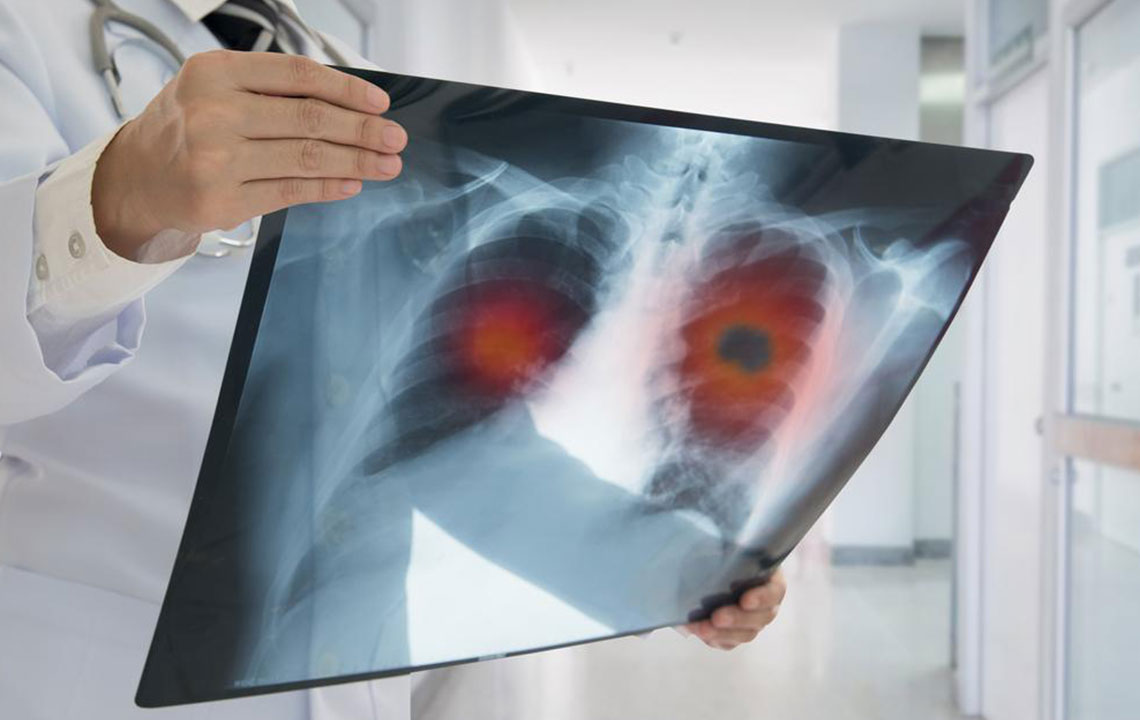
Non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) is the most common form of lung cancer worldwide. It accounts for roughly 80-85% of all lung cancer cases, while small cell lung cancer makes up the remaining 10-15%. This disease involves abnormal growth of lung cells that quickly proliferate and may spread to other body parts. NSCLC encompasses various subtypes, including adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, large cell carcinoma, and sarcomatoid carcinoma.
The development of NSCLC is often linked to smoking and exposure to harmful substances such as radon, asbestos, air pollutants, and radiation. Despite its severity, early detection is challenging as symptoms are subtle or resemble other respiratory illnesses.
Common symptoms include a persistent or worsening cough, chest pain that worsens with breathing or coughing, voice changes such as hoarseness, difficulty breathing, noisy or wheezy breathing, sudden weight loss, fatigue, loss of appetite, and prolonged lung infections like pneumonia or bronchitis that don't respond to treatment. As cancer advances, symptoms like headaches, bone pain, dizziness, jaundice, or limb numbness may occur due to metastasis.
Diagnosis involves physical assessments, medical history review, and imaging tests like X-Rays, CT scans, MRI, and PET scans to determine the cancer's spread. Sputum cytology and biopsy procedures help confirm the presence of cancer cells and stage the disease. Treatment plans vary based on the stage and spread of cancer, typically combining surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and laser treatments to eliminate cancer cells and manage symptoms. Awareness of early signs is crucial for timely intervention, as early detection improves treatment outcomes.