Effective Non-Invasive Strategies for Managing Persistent Back Pain
Explore effective non-invasive methods for managing chronic back pain, including physical therapy, dietary changes, lifestyle modifications, injections, and alternative therapies. Discover how these options can provide relief without surgery and improve your quality of life safely.
Sponsored
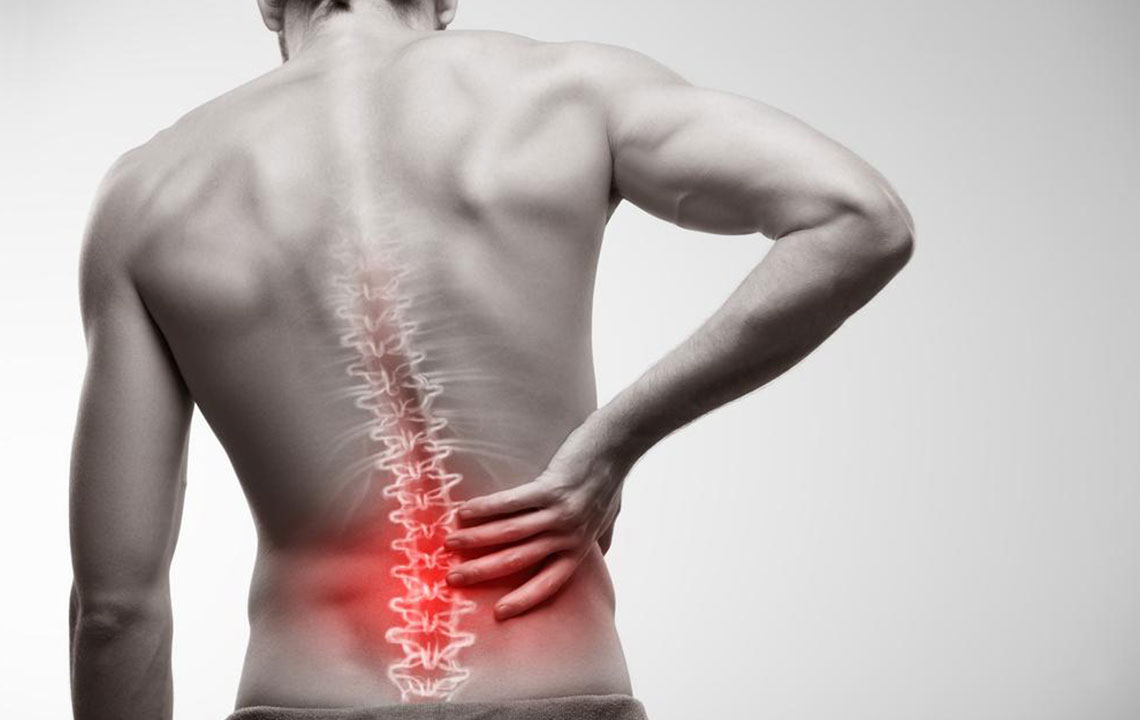
If back pain persists for more than three months, it is classified as chronic. You might experience episodes of pain interspersed with moments of relief, leading to frustration when discomfort returns. Chronic back pain can be especially challenging if its origin is unclear. Identifying causes such as spinal stenosis, myofascial syndromes, or disc issues like herniation can guide treatment options. Before considering surgery, exploring non-invasive therapies is essential to determine their effectiveness in alleviating your pain.
Non-Invasive Treatment Options for Chronic Back Pain
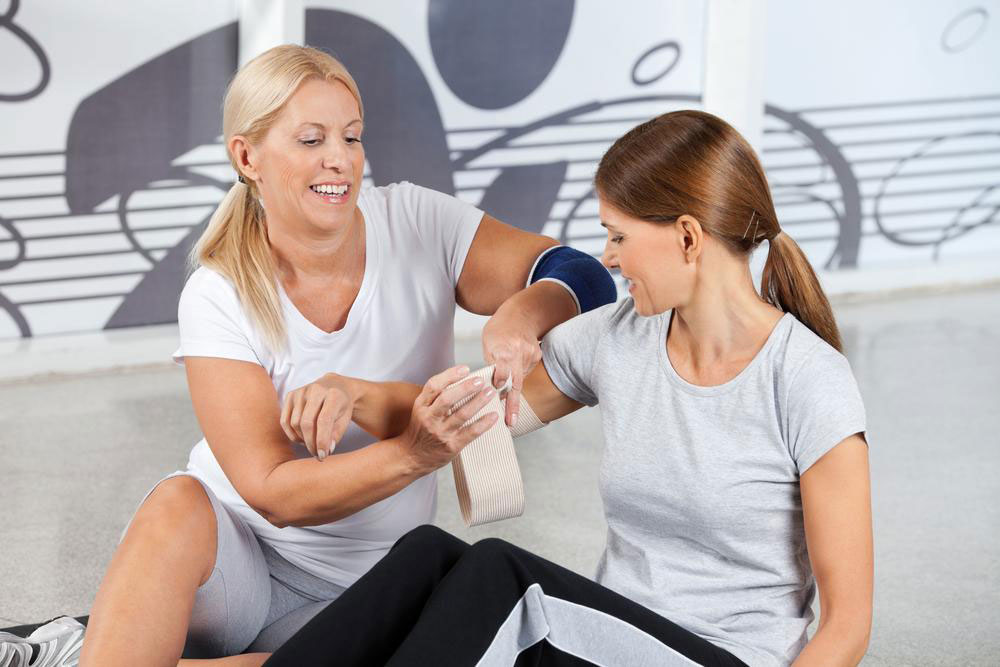
Physical therapy
Engaging in targeted exercises under professional supervision can significantly reduce back discomfort. Customized workout plans designed by healthcare providers focus on your specific condition. Consistent practice at home enhances recovery. Types of therapy include posture retraining, aerobic routines, flexibility exercises, and core strengthening to support spine health.
Mental health approaches
Managing emotional stress through meditation and mindfulness can combat feelings of depression and frustration linked to chronic pain. Therapies like yoga or tai chi also help distract the mind from pain sensations. Psychologists specializing in rehabilitation can offer additional support to encourage psychological resilience.
Dietary and Lifestyle Changes
Certain foods, such as processed foods rich in trans fats, refined sugars, and additives, might exacerbate inflammation and pain. Consulting a healthcare provider helps identify dietary triggers. Maintaining optimal weight reduces pressure on the spine and can lessen pain. Adapting daily routines, like avoiding activities that trigger discomfort, taking frequent breaks during physical tasks, and quitting smoking—since nicotine hampers healing—are vital lifestyle modifications that support pain management.
Injection Therapies
When a clear cause of pain is identified, procedures like epidural steroid injections, nerve blocks, or ablations can provide temporary relief. These interventions are useful for diagnostic purposes or short-term pain reduction but are not long-term solutions alone. Their success depends on proper patient selection and should be combined with other therapies.
Alternative Treatments
Techniques such as laser therapy, acupuncture, biofeedback, massage, or electrical nerve stimulation offer additional non-surgical options. Collaborate with your healthcare provider to select the most suitable approach based on your specific condition.
Medicinal Approaches
Over-the-counter painkillers, muscle relaxants, and anti-inflammatory drugs may ease symptoms temporarily. However, long-term use can lead to side effects; opioids should be avoided unless prescribed under close supervision. Medications do not address underlying issues and should be part of a comprehensive treatment plan, ideally after consulting a specialist.