Understanding Plaque Psoriasis: Symptoms, Types, and Effective Management
This article offers a comprehensive overview of plaque psoriasis, including its symptoms, types, and management options. It highlights key signs like dry, scaly patches, and discusses various forms from small to unstable plaques, with treatment tips such as topical creams and light therapy. Understanding these aspects can aid in early diagnosis and effective management, improving quality of life for those affected.
Sponsored

Plaque psoriasis, often called psoriasis vulgaris, is the most prevalent form of psoriasis, accounting for about 80% of cases. While its root causes remain unknown, certain risk factors increase susceptibility. Various types of plaque psoriasis exist, with no cure but manageable symptoms through specific treatments.
Signs and Symptoms
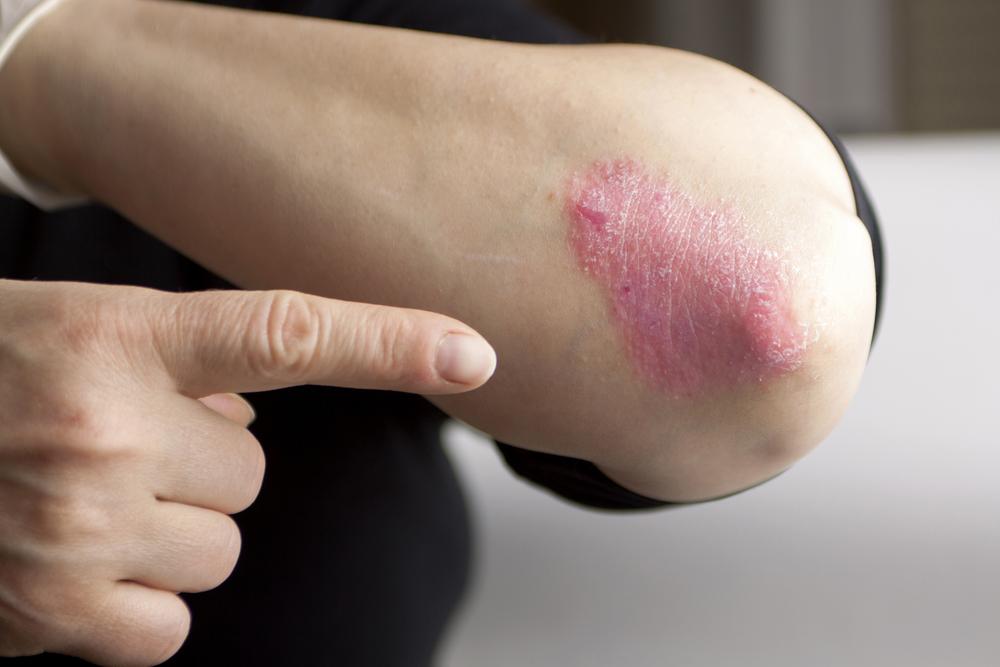
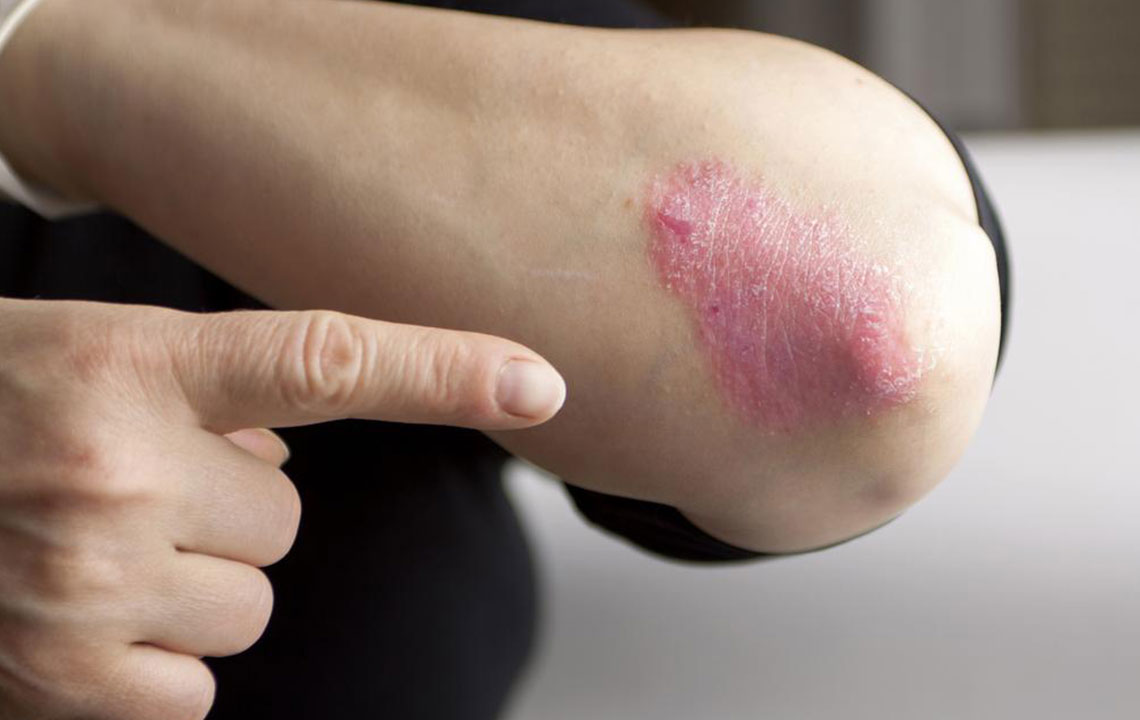
Dry, thick, raised patches with silvery-white scales characterize this condition, often causing intense itchiness. The appearance varies depending on the type, size, and severity of the lesions.
This coating, or scale, is usually flaky and crusty, following the symptoms' variation across individuals. Knowing the different types helps in tailored management strategies.
Types of Plaque Psoriasis
Small plaque psoriasis
Lesions are tiny, just a few centimeters, which can either stay separate or merge into larger patches. These areas are pink with fine, flaky crusts, and tend to respond well to light therapy. It commonly appears after 40 but can happen at any age.
Large plaque psoriasis
Characterized by bigger, more defined patches with a reddish top layer and a whitish-silver scale, often affecting those under 40. It may be linked to genetics and metabolic issues like high cholesterol or blood sugar, making treatment more challenging.
Unstable plaque psoriasis
This form causes lesions to enlarge, lose shape, and sometimes fuse, leading to bigger patches. New plaques can emerge, requiring careful medical evaluation for effective treatment.
Stable plaque psoriasis
Known as chronic plaque psoriasis, it results in persistent patches that tend to recur in common areas such as elbows, knees, scalp, and torso, appearing symmetrically on both sides of the body.
Psoriasis on the scalp
Symptoms include reddish, itchy, inflamed patches with silvery scales, often accompanied by dandruff-like flaking. The scalp may become dry, cracked, and prone to bleeding, sometimes leading to temporary hair loss. Facial psoriasis may present as dry, scaly, reddish patches around the forehead, cheeks, or around the eyes, requiring prompt dermatologist attention.
Management Strategies
Though there's no cure, symptoms can be controlled by reducing triggers and flare-ups. Common approaches include:
Topical treatments: Creams to lessen inflammation and slow skin cell growth, applied post-shower for better absorption.
Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light in clinical settings helps treat widespread lesions while minimizing risks associated with sun exposure.