Effective Strategies for Managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome
This article explores effective management strategies for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), highlighting dietary changes, medications, and probiotics. While IBS remains incurable, these approaches can significantly reduce symptoms such as pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation, helping patients lead normal lives. Understanding treatment options empowers individuals to better manage their condition with medical guidance and lifestyle adjustments.
Sponsored
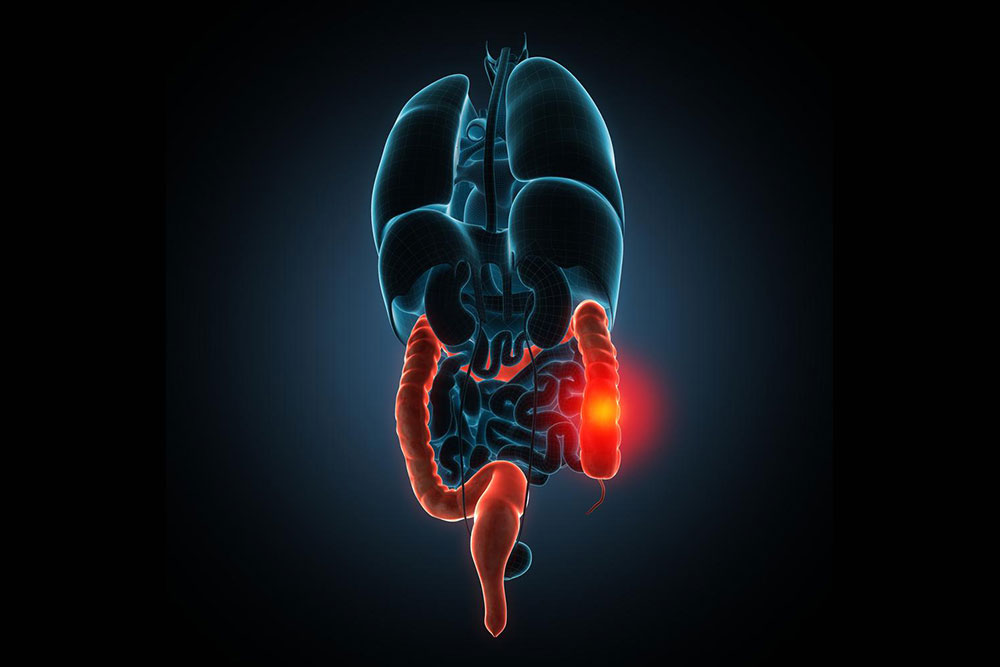
Advancements in science and medicine have significantly improved health care in the 21st century, allowing us to combat many serious illnesses. Nevertheless, some conditions, such as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), remain complex with unknown origins, requiring patience to manage effectively.
While the exact cause of IBS is still unclear, symptoms like diarrhea, constipation, abdominal discomfort, and bloating can be addressed through targeted treatments. Although IBS isn't entirely curable, various approaches help alleviate its symptoms, enabling patients to maintain a normal lifestyle.
Diagnostic indicators include symptoms such as irregular bowel movements, abdominal pain, and bloating. Medical professionals focus on symptom relief rather than complete eradication. Here are some common treatment options:
Dietary Modifications - Adjustments to your diet, including reducing gas-inducing foods and eliminating gluten, can lessen symptom severity, especially diarrhea.
Dietary Fiber Supplements - Incorporating fiber like psyllium or methylcellulose with fluids aids in managing constipation associated with IBS.
Anti-Diarrheal Medications - Drugs such as loperamide help control diarrhea, while bile acid binders can reduce symptoms but may cause bloating.
Antispasmodics - To relieve severe abdominal cramps, physicians may prescribe antispasmodic medications.
Probiotics and Antibiotics - Introducing healthy bacteria through probiotics can help balance gut flora, whereas antibiotics may be used if harmful bacteria exacerbate symptoms.
Though IBS can't be completely eradicated, these treatments effectively control its symptoms, allowing patients to live more comfortably.