Common Causes of Persistent Leg Discomfort
Persistent leg pain can be caused by various medical conditions such as muscle strains, tendinitis, circulatory problems, and arthritis. Recognizing these causes is vital for appropriate treatment. If leg discomfort persists, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for diagnosis and management.
Sponsored

Leg discomfort is often experienced by many individuals. It can result from injuries, excess weight, or overuse of leg muscles. Usually, the pain subsides over time or with home treatments. However, ongoing leg pain should prompt a medical consultation, as it may signal underlying health issues. Several factors can contribute to chronic leg discomfort, including muscle injuries, inflammation, or circulatory problems. Let’s explore the primary causes behind long-lasting leg pain.
Muscle Overuse and Strains
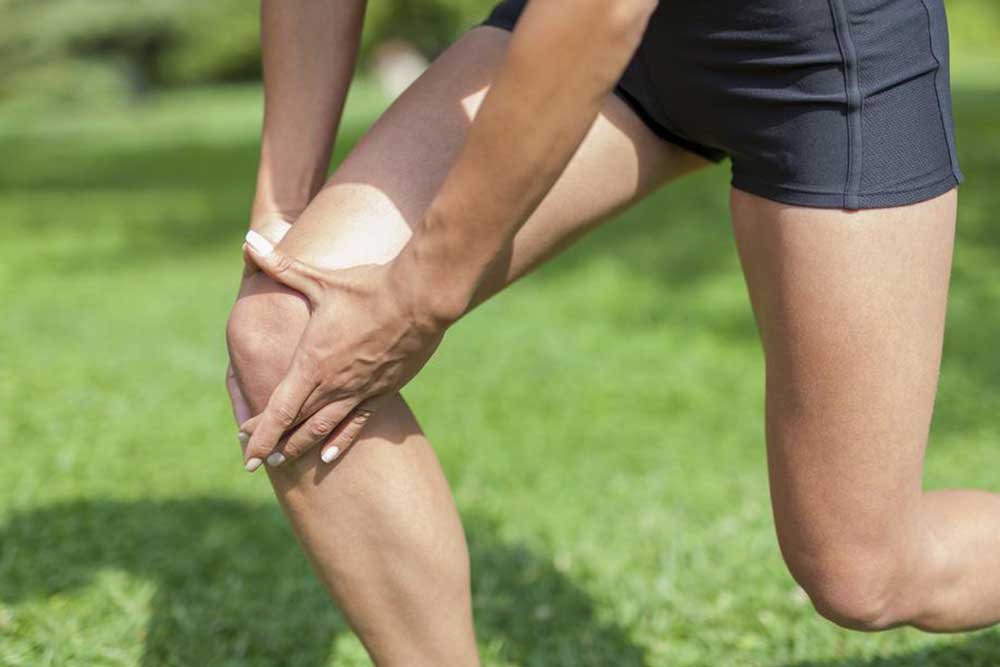
Overstretched muscles can tear fibers, leading to persistent discomfort. Larger muscles like calves, quadriceps, and hamstrings are particularly susceptible. Muscle strains often cause ongoing pain, especially if not properly treated.
Tendon Inflammation (Tendinitis)
Tendons connect muscles to bones. When tendons become inflamed, movement becomes painful and restricted. Tendinitis near the heel or hamstring area frequently causes persistent leg discomfort.
Blood Vessel Blockages (Atherosclerosis)
This condition involves the buildup of fats and cholesterol in arteries, leading to narrowing and hardening. Reduced blood flow can deprive leg tissues of oxygen, causing pain and discomfort.
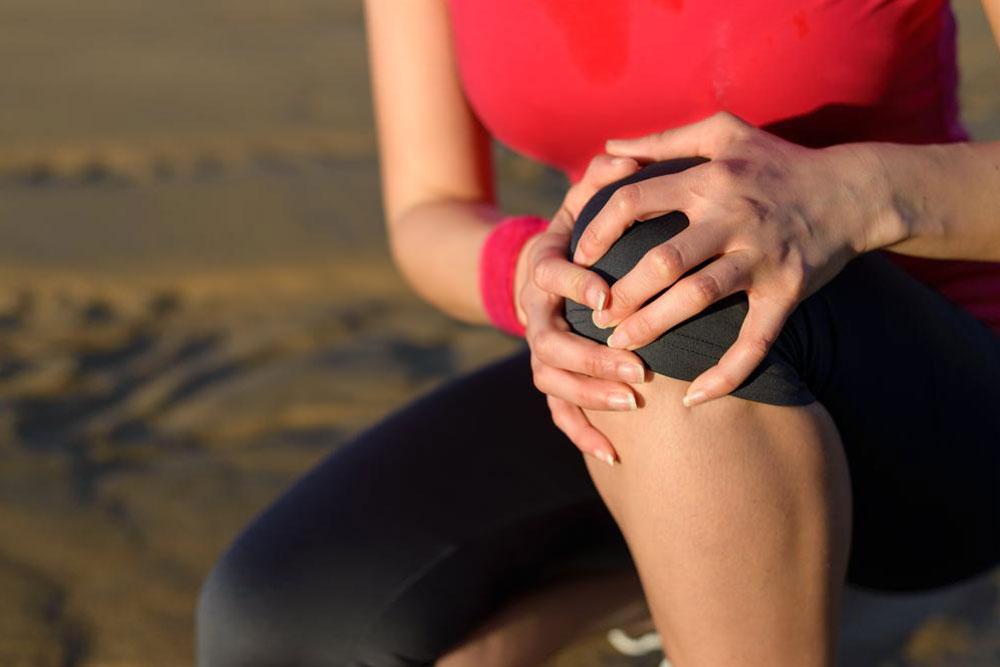
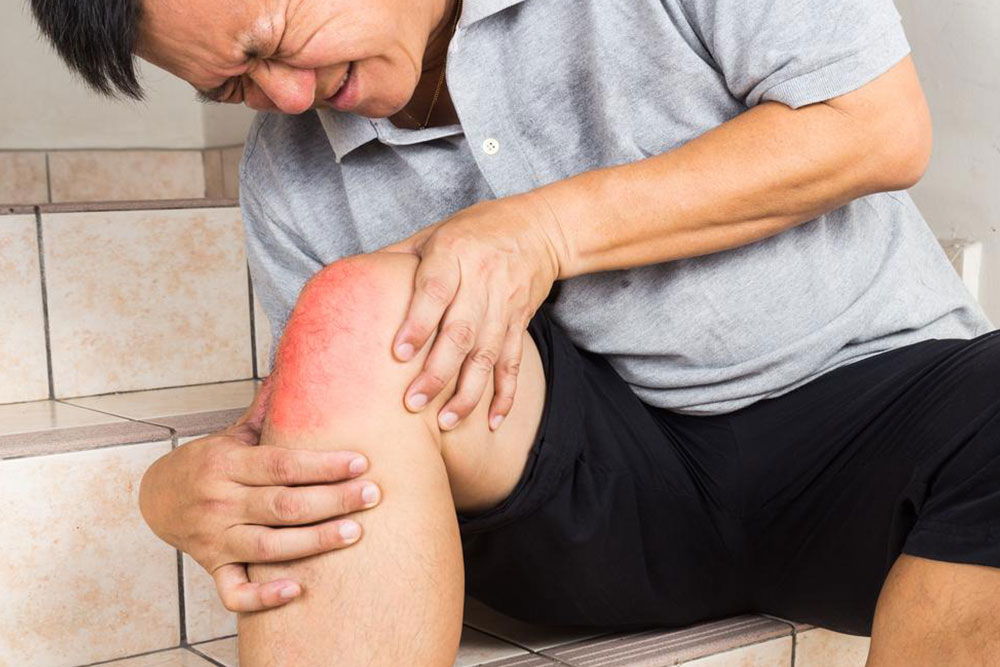
Joint Inflammation (Arthritis)
Arthritis impacts the hips and knees, resulting in swelling, redness, and constant pain, which can contribute to chronic leg ache.
Gout
Gout, a form of arthritis caused by excess uric acid, often affects the lower leg, producing sharp pain and swelling.
These health issues and injuries can be underlying causes of persistent leg pain. It’s advisable to see a healthcare professional to accurately diagnose and address the root cause.