Strategies to Prevent Pediatric Kidney Infections
Discover effective strategies to prevent kidney infections in children, including hygiene practices, recognizing symptoms, and when to seek medical care. Learn how early intervention and proper habits can safeguard your child's urinary health.
Sponsored
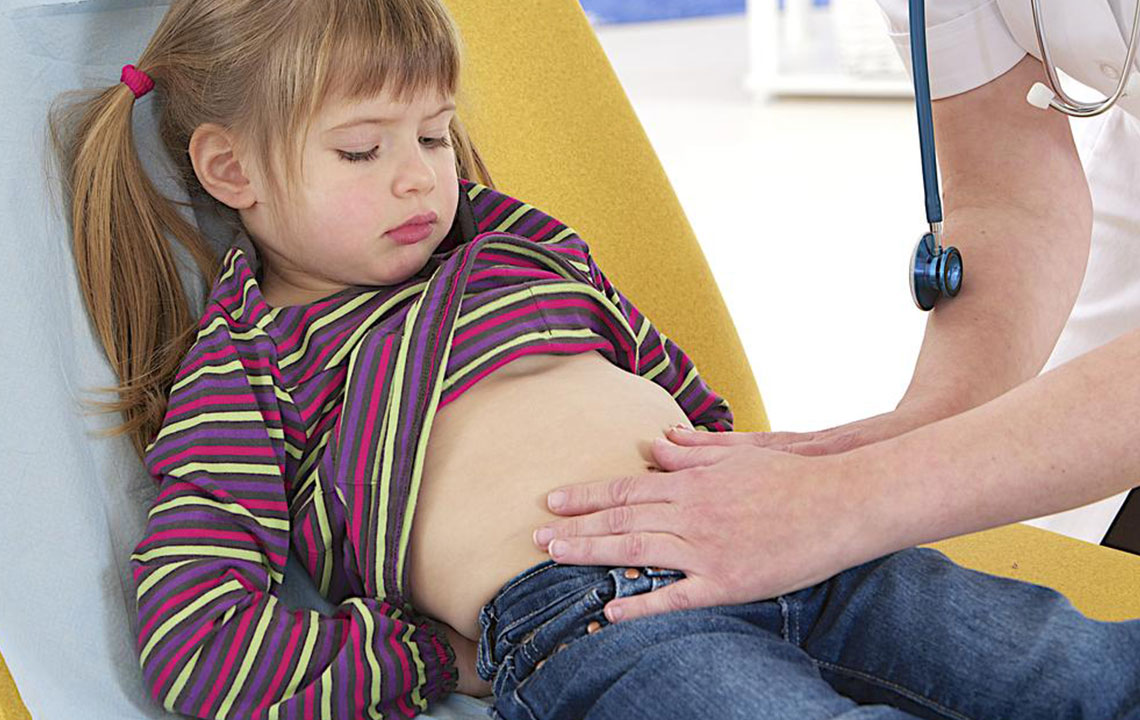
Kidney infections in children are a frequent health concern, classified as a type of urinary tract infection (UTI). The infection begins in the lower urinary tract, typically the bladder, then ascends to involve one or both kidneys, forming a serious upper urinary tract infection.
Causes
In children, kidney stones are often diagnosed during toilet training around ages 2 to 3. Several factors contribute to kidney infections. These include congenital abnormalities hindering urine flow, which can cause bacteria to ascend into the kidneys. Circumcised boys face higher risks. Inadequate cleaning of the perianal area in girls, tight clothing, bubble baths, neurological conditions affecting bladder control, and infrequent urination are also common causes.
Symptoms
Infants and young children may show nonspecific signs. Key indicators of kidney infection include foul-smelling, cloudy urine, pain in the back or lower abdomen, burning sensation during urination, difficulty urinating, or reduced urine output.
Preventive Measures
Parents can help reduce risk factors by practicing daily diaper changes, using gentle wipes, cleaning the genital area front to back, encouraging increased water consumption, and dressing children in loose, comfortable clothing. Early detection and proper medical treatment with antibiotics are essential if infection symptoms appear. With attentive care, kidney infections in children can be effectively prevented.