Understanding Meningitis B: Risks and Prevention Strategies
This article discusses the key risk factors for Meningitis B and outlines effective prevention strategies. It highlights the importance of vaccination, good hygiene, healthy lifestyle habits, and safe food practices, especially for vulnerable groups like children, pregnant women, and immunocompromised individuals. Understanding these risks and adopting appropriate measures can significantly reduce the chances of infection. The comprehensive guide helps readers stay informed and protect themselves and others from this serious bacterial disease.
Sponsored

Meningitis B is a bacterial infection that inflames the protective membranes around the brain and spinal cord. It often presents with symptoms such as high fever, seizures, and severe headaches. Certain factors can raise the likelihood of developing this disease. Recognizing these risks and adopting preventive measures are crucial for protection. This article explores the key risk factors associated with Meningitis B and provides practical prevention tips.
Major Risk Factors for Meningitis B
Age: Children under 20 are significantly more vulnerable to Meningitis B.
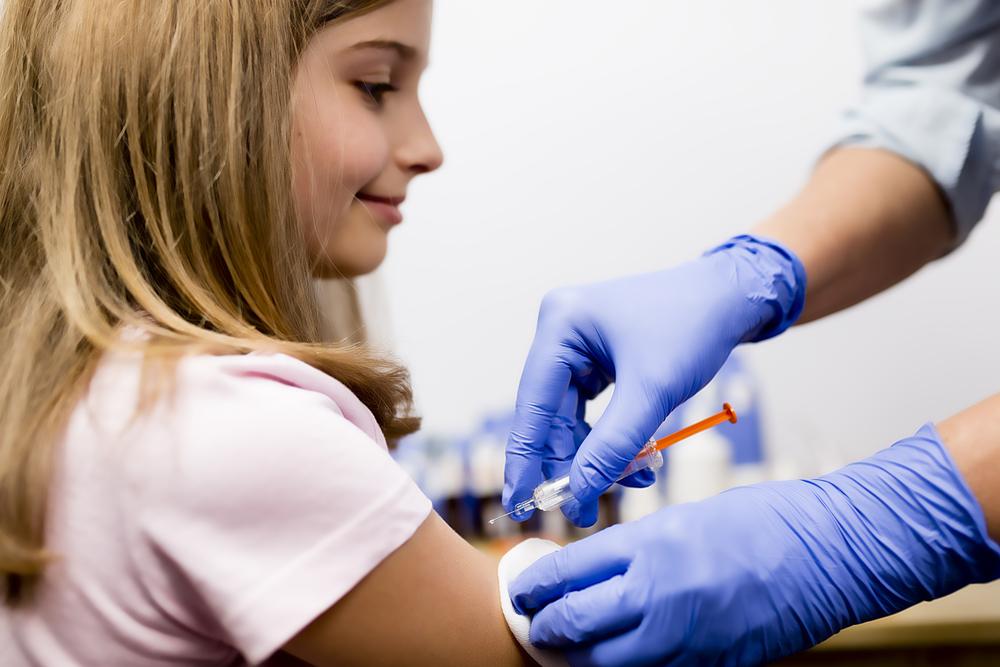
Lack of vaccination in childhood: Not receiving vaccines early can increase susceptibility.
Pregnancy: Pregnant women are at higher risk of infections like listeriosis, which can lead to Meningitis B, and also pose risks such as miscarriage and stillbirth.
Weakened immune defenses: Individuals with compromised immune systems, including those with chronic illnesses like AIDS, diabetes, or without a spleen, face greater risk.
Living in close quarters: Shared living spaces such as dorms, military barracks, or childcare centers facilitate bacterial transmission due to close contact.
Preventive Measures Against Meningitis B
Good Hygiene Practices: Wearing masks if unwell, maintaining daily hygiene, and cleaning living areas help curb bacteria spread. Always wash hands thoroughly before meals.
Health Maintenance: Consuming a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, staying hydrated, and exercising fortifies immunity.
Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Sharing utensils, drinks, or personal care articles can transfer bacteria, so personal belongings should not be shared.
Vaccinations: Available vaccines are vital for children and at-risk adults, especially those with weakened immune defenses.
Food Safety for Pregnant Women: Fully cook meats, including processed varieties like hot dogs, and consume only pasteurized dairy products to prevent infection transmission.