Effective Strategies for Managing Diarrhea
Discover effective strategies to manage and treat diarrhea, including understanding causes, medication options, hydration importance, and dietary tips. Early intervention and proper care can prevent complications and promote quick recovery.
Sponsored

Key methods for alleviating diarrhea
Experiencing diarrhea is common across all age groups, from infants to seniors. Typically, symptoms include stomach bloating, cramps, and watery stool. Most recover with home remedies; however, some cases become severe. Recognizing the right treatment early is crucial. Before starting remedies, understanding the causes of diarrhea and preventive measures is essential.
Common Causes of Diarrhea
Diarrhea often results from food poisoning, bacterial or viral infections, or contaminated water intake. Sometimes, side effects from antibiotics can trigger it. The condition reflects gastrointestinal imbalance due to these causes. Symptoms typically improve once the underlying issue resolves. Mild cases tend to clear within a week, while severe ones may take longer to recover.
Treatment Options for Diarrhea
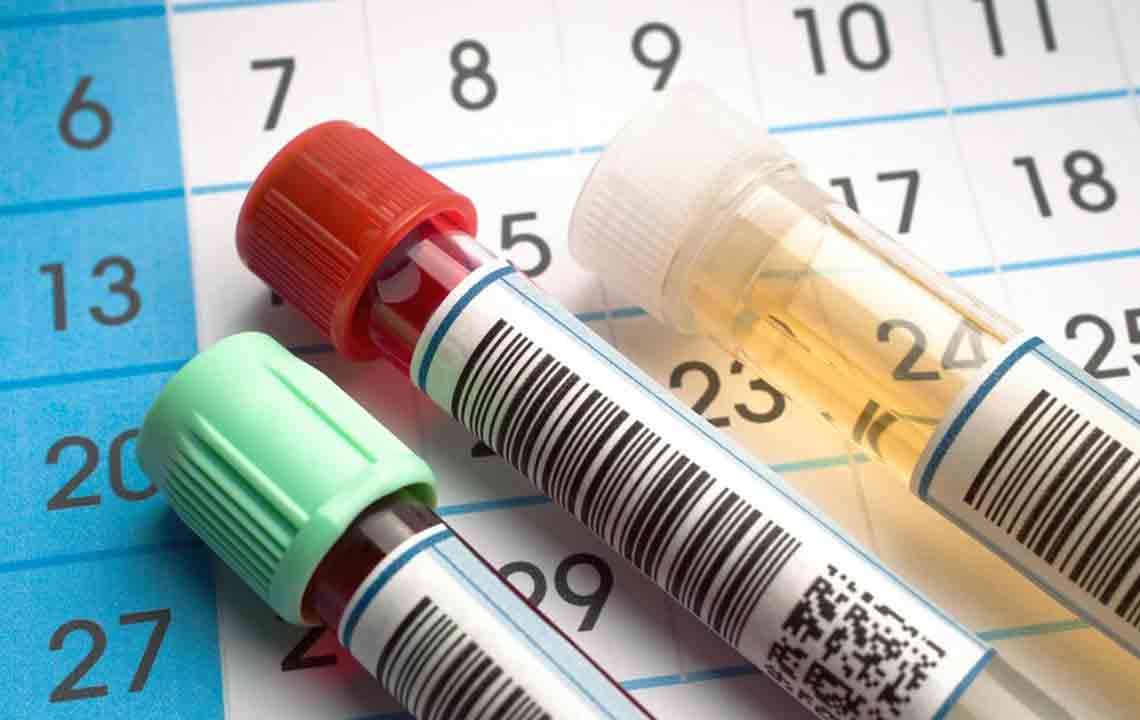
Many cases resolve without medication within a few days. If symptoms persist beyond two days, consulting a healthcare professional for blood or stool tests is recommended. Severe or chronic cases might require procedures like colonoscopy for diagnosis.
Medications for Diarrhea
Prescribed based on the cause identified in tests, antibiotics target bacterial or parasitic infections. Viral diarrhea generally doesn’t respond to antibiotics. Doctors may recommend drugs such as Quinaglute, Cytotec, or Reglum. In some instances, corticosteroids are used.
In addition to medication, hydration and home care are vital for recovery.
Importance of Hydration
Frequent bowel movements can cause dehydration; hence, drinking oral rehydration solutions (ORS) and fluids like Pedialyte is essential. Infants should be breastfed regularly. Avoid caffeinated, carbonated drinks, alcohol, and milk, which may worsen symptoms.
Role of Probiotics
Consuming probiotics, or healthy bacteria, can significantly help. Foods like yogurt, fermented vegetables, cottage cheese, and miso contain probiotics. They can also be taken as supplements in powder or pill form, aiding gastrointestinal health.
Diet and Nutrition Tips
During recovery, stick to a fluid or low-fiber diet—e.g., bananas, toast, baked potatoes, chicken soup, and oatmeal. Eating gentle, easily digestible foods helps healing.
Foods to Avoid
Skip greasy, fried, spicy foods, and foods that cause bloating. Artificial sweeteners and alcohol should also be avoided, as they can aggravate symptoms.
Ignoring early signs of diarrhea can worsen the condition. Follow proper dietary guidelines and seek medical advice if home remedies don’t work. Consulting gastrointestinal specialists can also expedite recovery.
Timely medical consultation ensures effective treatment, symptom relief, and a healthy life.